Nickel-Titanium Memory Metal
... wire can be heated to the much higher temperature of a candle flame (~500 degrees C), where it can be trained to “remember” a new shape. Subsequently, when the wire is distorted at room temperature and heated by hot air or water, it will return to this new shape. Rods of NiTi can be used to show tha ...
... wire can be heated to the much higher temperature of a candle flame (~500 degrees C), where it can be trained to “remember” a new shape. Subsequently, when the wire is distorted at room temperature and heated by hot air or water, it will return to this new shape. Rods of NiTi can be used to show tha ...
Darmstadt 2004
... In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the study of statistical properties of networks with complex topologies. The Ising model on different complex networks can exhibit nontrivial properties (magnetic ordering in „one” dimension, dependence of the critical temperature for the ferrom ...
... In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the study of statistical properties of networks with complex topologies. The Ising model on different complex networks can exhibit nontrivial properties (magnetic ordering in „one” dimension, dependence of the critical temperature for the ferrom ...
碩士學位論文
... In the phase behavior of binary polymer solutions, a upper critical solution temperature (UCST), a lower critical solution temperature (LCST), both of them, hour-glass shaped and closed miscibility loop phase behavior are encountered. Such phase behavior may be due to highly oriented interactions su ...
... In the phase behavior of binary polymer solutions, a upper critical solution temperature (UCST), a lower critical solution temperature (LCST), both of them, hour-glass shaped and closed miscibility loop phase behavior are encountered. Such phase behavior may be due to highly oriented interactions su ...
CYL110
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
... When a system is at equilibrium, its state is defined entirely by the state variables, and not by the history of the system. The properties of the system can be described by an equation of state which specifies the relationship between these variables. ...
MaterialEASE: Amorphous Materials: A Tutorial on Noncrystalline
... be prepared with an amorphous structure. The higher the critical cooling rate of the materials, the smaller the maximum thickness. So, while there are techniques for achieving rapid cooling – such as melt spinning and splat quenching – the amorphous product is often quite thin. Some metallic glasses ...
... be prepared with an amorphous structure. The higher the critical cooling rate of the materials, the smaller the maximum thickness. So, while there are techniques for achieving rapid cooling – such as melt spinning and splat quenching – the amorphous product is often quite thin. Some metallic glasses ...
Module code SC-2242 Module Title Chemical Thermodynamics and
... standard cell potentials for Galvanic cells -obtain information about the properties of materials from phase diagrams - apply thermodynamic concepts to understand the properties of mixtures and solution phase equilibria Higher order: 10% - present the results of a practical investigation in a ...
... standard cell potentials for Galvanic cells -obtain information about the properties of materials from phase diagrams - apply thermodynamic concepts to understand the properties of mixtures and solution phase equilibria Higher order: 10% - present the results of a practical investigation in a ...
File
... b) What is happening when the line is going up or down? c) Be able to identify the phase change on the graph? d) Which phase changes are endothermic? Why? e) Which phase changes are exothermic? Why? ...
... b) What is happening when the line is going up or down? c) Be able to identify the phase change on the graph? d) Which phase changes are endothermic? Why? e) Which phase changes are exothermic? Why? ...
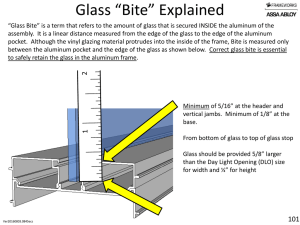
Glass
... • Laboratory equipment are often made of borosilicate glass for its low coefficient of thermal expansion, giving greater resistance to thermal shock and greater accuracy in measurements. For high-temperature applications, quartz glass is used, although it is very difficult to work. • Glass is common ...
... • Laboratory equipment are often made of borosilicate glass for its low coefficient of thermal expansion, giving greater resistance to thermal shock and greater accuracy in measurements. For high-temperature applications, quartz glass is used, although it is very difficult to work. • Glass is common ...
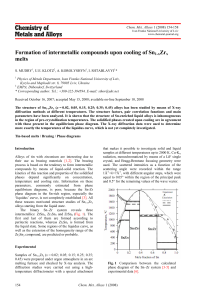
Formation of intermetallic compounds upon cooling of Sn1
... well as s(k1) – height of the principal peak, reveal some discrepancies between them (Table 1). Similar features are also observed for the pair correlation functions. In particular, the most probable interatomic distances are significantly reduced in comparison with liquid tin. Taking into account t ...
... well as s(k1) – height of the principal peak, reveal some discrepancies between them (Table 1). Similar features are also observed for the pair correlation functions. In particular, the most probable interatomic distances are significantly reduced in comparison with liquid tin. Taking into account t ...
Chapter 1 Sect 1.3: Properties of matter Vocabularies: Physical
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
... A large sample of carbon would take up a bigger area than a small sample of carbon, so volume is an extensive property. Some of the most common types of extensive properties are; length, volume, mass and weight. Intensive properties: properties, which do not depend on the size of the sample involved ...
Nuclear Chemistry - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... cp,ice = 2.077 J/g-K cf = 333 J/g cp,water = 4.18 J/g-K cv = 2256 J/g cp,wv = 2.042 J/g-K ...
... cp,ice = 2.077 J/g-K cf = 333 J/g cp,water = 4.18 J/g-K cv = 2256 J/g cp,wv = 2.042 J/g-K ...
Molar Mass by Freezing Point Depression
... When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the temperature rises quickly to the melting point and remains constant. The heat (enthalpy) released ...
... When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the temperature rises quickly to the melting point and remains constant. The heat (enthalpy) released ...
The d-block elements are commonly known as transition
... A metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) transition will be most likely when the metal is in a low oxidation state and the ligand is an easily reduced d-d transition. An electron jumps from one d-orbital to another. In complexes of the transition metals, the d orbitals do not all have the same energ ...
... A metal-to-ligand charge transfer (MLCT) transition will be most likely when the metal is in a low oxidation state and the ligand is an easily reduced d-d transition. An electron jumps from one d-orbital to another. In complexes of the transition metals, the d orbitals do not all have the same energ ...
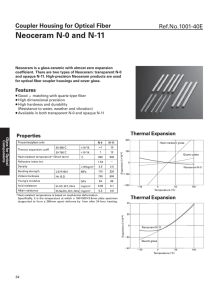
Glass transition
The glass–liquid transition or glass transition for short is the reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline materials) from a hard and relatively brittle state into a molten or rubber-like state. An amorphous solid that exhibits a glass transition is called a glass. Supercooling a viscous liquid into the glass state is called vitrification, from the Latin vitreum, ""glass"" via French vitrifier.Despite the massive change in the physical properties of a material through its glass transition, the transition is not itself a phase transition of any kind; rather it is a laboratory phenomenon extending over a range of temperature and defined by one of several conventions. Such conventions include a constant cooling rate (20 K/min) and a viscosity threshold of 1012 Pa·s, among others. Upon cooling or heating through this glass-transition range, the material also exhibits a smooth step in the thermal-expansion coefficient and in the specific heat, with the location of these effects again being dependent on the history of the material. However, the question of whether some phase transition underlies the glass transition is a matter of continuing research.The glass-transition temperature Tg is always lower than the melting temperature, Tm, of the crystalline state of the material, if one exists.