Chapter26
... when the universe became transparent and light could, for the first time, travel great distances before being absorbed or scattered. The cosmic background radiation was produced at the decoupling epoch. deuteron — A nucleus of deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen. A deuteron contains one proton and one ...
... when the universe became transparent and light could, for the first time, travel great distances before being absorbed or scattered. The cosmic background radiation was produced at the decoupling epoch. deuteron — A nucleus of deuterium, an isotope of hydrogen. A deuteron contains one proton and one ...
PARTS OF THE UNIVERSE
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
Lecture24
... The CMB was already visible in the data taken by Dunham and Adams of the properties of CN in the interstellar medium …back in 1937 The saw that CN was excited as if it was immersed in a thermal bath of radiation of temperature ...
... The CMB was already visible in the data taken by Dunham and Adams of the properties of CN in the interstellar medium …back in 1937 The saw that CN was excited as if it was immersed in a thermal bath of radiation of temperature ...
1_Introduction - The Ohio State University Department of
... Why is the universe full of isotropic blackbody radiation (the CMB)? Let’s suppose that the universe was very hot as well as very dense when it started expanding. This hypothesis (hot, dense beginning) is called the Hot Big Bang model. ...
... Why is the universe full of isotropic blackbody radiation (the CMB)? Let’s suppose that the universe was very hot as well as very dense when it started expanding. This hypothesis (hot, dense beginning) is called the Hot Big Bang model. ...
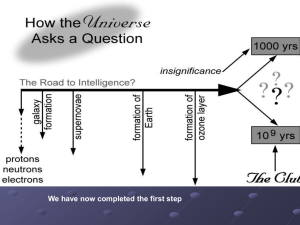
origins of the Universe
... in the early 1900’s astronomers started to find evidence that pointed to a Big Bang. • In 1922, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the universe was expanding. The most distant galaxies he could see through his telescope were moving away at about 40 000 km per second. • This observation led to wha ...
... in the early 1900’s astronomers started to find evidence that pointed to a Big Bang. • In 1922, astronomer Edwin Hubble observed that the universe was expanding. The most distant galaxies he could see through his telescope were moving away at about 40 000 km per second. • This observation led to wha ...
Astronomy - Seton Hall University Pirate Server
... Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and/or Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act. In order to receive such accommodations, students must identify themselves at the Office of Disability Support Services (DSS), provide appropriate documentation and collaborate with the development of an accommodatio ...
... Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and/or Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act. In order to receive such accommodations, students must identify themselves at the Office of Disability Support Services (DSS), provide appropriate documentation and collaborate with the development of an accommodatio ...
Document
... Conclusions from our Observations • The Universe has a finite age, so light from very distant galaxies has not had time to reach us, therefore the night sky is dark. ...
... Conclusions from our Observations • The Universe has a finite age, so light from very distant galaxies has not had time to reach us, therefore the night sky is dark. ...
La constant cosmològica i l*energia fosca: del Big Bang al futur de l
... exists a spatial Cauchy C² hypersurface, Σ, and a trapped surface, and let θ0 be the maximum value of the expansion over it. If θ0 < 0, then there exists at least a lightlike geodesic, which cannot be extended to the future, and which is orthogonal to the trapped surface. Moreover, the value of the ...
... exists a spatial Cauchy C² hypersurface, Σ, and a trapped surface, and let θ0 be the maximum value of the expansion over it. If θ0 < 0, then there exists at least a lightlike geodesic, which cannot be extended to the future, and which is orthogonal to the trapped surface. Moreover, the value of the ...
Chapter 1 - Collins Foundation Press
... making four fundamental forces. Neutrinos separate (decouple) from matter and radiation can stream out into space. ...
... making four fundamental forces. Neutrinos separate (decouple) from matter and radiation can stream out into space. ...
Word - Sam Davyson
... distance. Once again the is determined from the movement of the black lines in the spectrum. The fact that everything measured shows a > 0 indicates that the distances between every pair of objects is increasing (except locally where gravity can cause the reverse effect) and that the universe ...
... distance. Once again the is determined from the movement of the black lines in the spectrum. The fact that everything measured shows a > 0 indicates that the distances between every pair of objects is increasing (except locally where gravity can cause the reverse effect) and that the universe ...
Beverly`s writings on Nassim Haramein
... fictional particles to explain their observations and to make their math work that has kept us from a more accurate description of fundamental forces of creation. With an accurate model of how the universe works, we will open up a whole new level of technology for mankind, as profound as when we di ...
... fictional particles to explain their observations and to make their math work that has kept us from a more accurate description of fundamental forces of creation. With an accurate model of how the universe works, we will open up a whole new level of technology for mankind, as profound as when we di ...
Cosmology Unit – FINAL EXAM PRACTICE TEST
... c. It indicates that the universe was once very hot. d. It can't be explained by the steady state theory. e. It indicates that the universe has a temperature of around 3 K. 23. What does the term nucleosynthesis refer to? a. the creation of atomic nuclei b. the formation of galactic nuclei c. the st ...
... c. It indicates that the universe was once very hot. d. It can't be explained by the steady state theory. e. It indicates that the universe has a temperature of around 3 K. 23. What does the term nucleosynthesis refer to? a. the creation of atomic nuclei b. the formation of galactic nuclei c. the st ...
April 2006 - Otterbein University
... Conclusions from our Observations • The Universe has a finite age, so light from very distant galaxies has not had time to reach us, therefore the night sky is dark. ...
... Conclusions from our Observations • The Universe has a finite age, so light from very distant galaxies has not had time to reach us, therefore the night sky is dark. ...
Formation of Universe
... Formation of the Universe: recent developments The Inflationary Theory: predicts that there was a sudden expansion when the universe was very young, more extreme than predicted by the big bang Considered to be a “revised” Big Band Theory universe expanded until about 10-35 seconds after the big ban ...
... Formation of the Universe: recent developments The Inflationary Theory: predicts that there was a sudden expansion when the universe was very young, more extreme than predicted by the big bang Considered to be a “revised” Big Band Theory universe expanded until about 10-35 seconds after the big ban ...
Origins of the Universe
... The Big Bang Theory • A theory for the creation of the universe • Scientists believe about 14 billion years ago, the universe was unimaginably compact, small, and dense • Universe began its expansion after a giant explosion, coined the Big Bang • It began expanding with unimaginable force from a ho ...
... The Big Bang Theory • A theory for the creation of the universe • Scientists believe about 14 billion years ago, the universe was unimaginably compact, small, and dense • Universe began its expansion after a giant explosion, coined the Big Bang • It began expanding with unimaginable force from a ho ...
Monday, December 8 - Otterbein University
... function of redshift for a given universe Supernovae are further away than expected for any decelerating (“standard”) universe ...
... function of redshift for a given universe Supernovae are further away than expected for any decelerating (“standard”) universe ...
Cosmology
... – Dark matter is ~ 23% of total – Dark energy is ~ 73% of total • Age of 13.7 billion years ...
... – Dark matter is ~ 23% of total – Dark energy is ~ 73% of total • Age of 13.7 billion years ...
review
... that time, the temperature of the universe was about 3000K and the photons had a blackbody spectrum appropriate to that temperature. Since then the expansion has cooled the universe and stretched the original visible light to microwaves. Observations show an excellent blackbody spectrum now with 2.7 ...
... that time, the temperature of the universe was about 3000K and the photons had a blackbody spectrum appropriate to that temperature. Since then the expansion has cooled the universe and stretched the original visible light to microwaves. Observations show an excellent blackbody spectrum now with 2.7 ...
Ch. 26.5: The Expanding Universe
... Exerts gravitational force on visible matter Universe may be 90% + dark matter Why do we think Dark Matter exists? Galaxies are accelerating faster than they should be (based on the observable matter in the Universe). The acceleration due to gravity does not match up with the amount of matter that w ...
... Exerts gravitational force on visible matter Universe may be 90% + dark matter Why do we think Dark Matter exists? Galaxies are accelerating faster than they should be (based on the observable matter in the Universe). The acceleration due to gravity does not match up with the amount of matter that w ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.