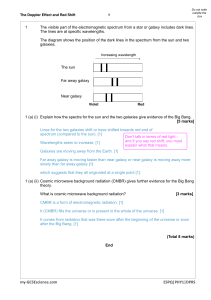
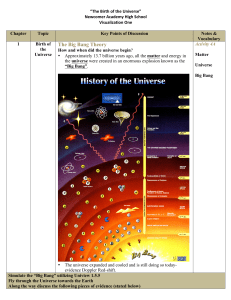
Explaining the early universe
... One pioneer in space exploration was an American astronomer named Edwin Hubble. He was the first astronomer to identify other galaxies besides the Milky Way. Then he made an astonishing discovery. He noticed that all the galaxies he was observing were not staying still. Rather, they were moving awa ...
... One pioneer in space exploration was an American astronomer named Edwin Hubble. He was the first astronomer to identify other galaxies besides the Milky Way. Then he made an astonishing discovery. He noticed that all the galaxies he was observing were not staying still. Rather, they were moving awa ...
Olber`s Paradox
... So if the universe is infinitely big then the sky should be bright But the sky is dark So the universe is not infinitely big So it should have collapsed ...
... So if the universe is infinitely big then the sky should be bright But the sky is dark So the universe is not infinitely big So it should have collapsed ...
Big Bang and Synthesis of Elements
... As the universe expanded further, and thus cooled, common particles began to form. These particles called baryons that include photons, neutrinos, electrons and quarks. These would become the building blocks of life as we know it. During the baryon genesis period there were no recognizable heavy par ...
... As the universe expanded further, and thus cooled, common particles began to form. These particles called baryons that include photons, neutrinos, electrons and quarks. These would become the building blocks of life as we know it. During the baryon genesis period there were no recognizable heavy par ...
Formation of the Universe
... Two elements, hydrogen and helium were created in the primordial fireball, along with small amounts of lithium and beryllium. ...
... Two elements, hydrogen and helium were created in the primordial fireball, along with small amounts of lithium and beryllium. ...
Name
... 11. Explain the big bang theory in as much detail as possible. Make sure you answer the following questions: 1. Is the universe expanding or getting smaller? 2. What evidence did the WMAP provide scientists about the big bang theory? 3. Is the universe cooling or getting hotter? 4. How has the amou ...
... 11. Explain the big bang theory in as much detail as possible. Make sure you answer the following questions: 1. Is the universe expanding or getting smaller? 2. What evidence did the WMAP provide scientists about the big bang theory? 3. Is the universe cooling or getting hotter? 4. How has the amou ...
Appendix 2
... galaxies. Observation shows that overall movement of the galaxies is to move away from each other. The speed of any two galaxies is greater the further they are apart. This is understood to be the result of space expanding. Working backwards in time it is thought that all the matter of which the pre ...
... galaxies. Observation shows that overall movement of the galaxies is to move away from each other. The speed of any two galaxies is greater the further they are apart. This is understood to be the result of space expanding. Working backwards in time it is thought that all the matter of which the pre ...
Lesson 01 - Big Bang Theory
... if all runners start the race at the same point, then the faster runner would always be ahead of the slower runner. If runners started at different points (ie. a slower runner having a head start) then a slower runner could be ahead of a faster one ...
... if all runners start the race at the same point, then the faster runner would always be ahead of the slower runner. If runners started at different points (ie. a slower runner having a head start) then a slower runner could be ahead of a faster one ...
Galaxies and the Big Bang Theory
... A ___________ is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: ...
... A ___________ is a huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity The three different types of galaxies that exist in our universe are: ...
Big Bang Balloon
... An activity you can use in the classroom In the 1920s astronomer Edwin Hubble used the red shift of the spectra of stars to determine that the universe was expanding. By carefully observing the light from galaxies at different distances from Earth, he determined that the farther something was from E ...
... An activity you can use in the classroom In the 1920s astronomer Edwin Hubble used the red shift of the spectra of stars to determine that the universe was expanding. By carefully observing the light from galaxies at different distances from Earth, he determined that the farther something was from E ...
The homogeneous and isotropic universe: Cosmology
... The age of the universe? Hubble’s constant H0 = 100h kms-1Mpc-1 where h =0.72 ± 0.08 The units are a little unusual so on converting kilometres into parsecs and converting seconds to years we find the Hubble time ...
... The age of the universe? Hubble’s constant H0 = 100h kms-1Mpc-1 where h =0.72 ± 0.08 The units are a little unusual so on converting kilometres into parsecs and converting seconds to years we find the Hubble time ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Origin of the Universe
... Solves 3 problems with the Big Bang Model: The Structure problem Models match observed structure better than simple BB models The Relic problem Theories had predicted production of particles and other stuff which should be around today, but which are not observed, e.g. the magnetic monopole. Predict ...
... Solves 3 problems with the Big Bang Model: The Structure problem Models match observed structure better than simple BB models The Relic problem Theories had predicted production of particles and other stuff which should be around today, but which are not observed, e.g. the magnetic monopole. Predict ...
Cosmology2 - NMSU Astronomy
... The results indicate that the universal expansion was slowing down at times further back than 6 billion ...
... The results indicate that the universal expansion was slowing down at times further back than 6 billion ...
2014 Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. 1 Astro 113 Final Exam Review 1. What
... 2. What are the basic stages in the Sun's history? 3. What are the various astronomical distance measures? 4. Suppose the Hubble constant, H = 60 (km/sec)/Mpc. A Certain galaxy is known to ...
... 2. What are the basic stages in the Sun's history? 3. What are the various astronomical distance measures? 4. Suppose the Hubble constant, H = 60 (km/sec)/Mpc. A Certain galaxy is known to ...
Space Test: Practice Questions and Answers 1. Who discovered
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
... The Steady State Theory believed that the universe doesn’t change with time. However, more matter is added as it expands. It also stated that the universe had not beginning or end. In Big Bang the ...
Hypothesis vs. Theory ~The Big Bang
... Our Place in the Universe Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence explorin ...
... Our Place in the Universe Our study of Astronomy requires us to look UP and not DOWN. Humans today are not used to looking UP, we are not used to observing the sky – it appears to be of little use – and city living with its extensive light pollution often prevents us from seeing, and hence explorin ...
Kg m/s2=SI(G) kg2/m2
... appears to be around 46x109 light-years not 13.7x109 light-years (as I had previously thought when I had neglected the acceleration of the universe), because the universe is not only expanding in space and advancing forward in time, but for the last several billion years the rate of expansion has be ...
... appears to be around 46x109 light-years not 13.7x109 light-years (as I had previously thought when I had neglected the acceleration of the universe), because the universe is not only expanding in space and advancing forward in time, but for the last several billion years the rate of expansion has be ...
Slide 1
... “What determines the size of objects that we see around us or indeed even the size of ourselves, and what determines the size of the atoms themselves?” ...
... “What determines the size of objects that we see around us or indeed even the size of ourselves, and what determines the size of the atoms themselves?” ...
solutions
... 8 If the Universe continues to expand forever, what will eventually become of the cosmic background radiation? Recall that the frequency of photons decreases inversely with the expansion factor, R. Therefore as the Universe expands, the temperature of the cosmic background radiation decreases accord ...
... 8 If the Universe continues to expand forever, what will eventually become of the cosmic background radiation? Recall that the frequency of photons decreases inversely with the expansion factor, R. Therefore as the Universe expands, the temperature of the cosmic background radiation decreases accord ...
PowerPoint
... (positively curved). – If k > 0, then the universe is open and unbounded (negatively curved). – If k = 0, then the universe is flat. ...
... (positively curved). – If k > 0, then the universe is open and unbounded (negatively curved). – If k = 0, then the universe is flat. ...
Chapter 14 Origins
... 24. How is the formation of stars (and their possible planetary systems) similar to the formation of galaxies? ...
... 24. How is the formation of stars (and their possible planetary systems) similar to the formation of galaxies? ...
What could it be?: the nature of dark matter
... -studying the surface of spots (thermal fluctuations) in «photons», comparing to distance they travelled when they escaped and their initial surface (conclusion of Boomerang : Balloon observation of millimetric extragalactic radiation and geophysics, 1998)… if ever you want to know more… ...
... -studying the surface of spots (thermal fluctuations) in «photons», comparing to distance they travelled when they escaped and their initial surface (conclusion of Boomerang : Balloon observation of millimetric extragalactic radiation and geophysics, 1998)… if ever you want to know more… ...
The Big Bang Theory
... • 1) Many other galaxies exist (not just the milky way). • 2) All galaxies are getting farther apart from each other (2 evidences support this theory). This means that the universe is expanding and this was most likely caused by the big bang. ...
... • 1) Many other galaxies exist (not just the milky way). • 2) All galaxies are getting farther apart from each other (2 evidences support this theory). This means that the universe is expanding and this was most likely caused by the big bang. ...
God and Cosmology - Evidence for Christianity
... • Edwin Hubble studied the spectra of galaxies and found from their redshifts that nearly all galaxies are receding from us • The speed of recession is roughly proportional to distance ...
... • Edwin Hubble studied the spectra of galaxies and found from their redshifts that nearly all galaxies are receding from us • The speed of recession is roughly proportional to distance ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.