Thermodynamics: Four Laws That Move the Universe
... because it is of absolutely fundamental importance to this subject. Entropy is the crucial link between temperature and thermal energy. It is a way to quantify how many different ways there are to distribute energy, and as you will learn, it is the foundation for the second law of thermodynamics. By ...
... because it is of absolutely fundamental importance to this subject. Entropy is the crucial link between temperature and thermal energy. It is a way to quantify how many different ways there are to distribute energy, and as you will learn, it is the foundation for the second law of thermodynamics. By ...
PDF of Chapter 6 Foundations of Chemistry
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 The atoms in all objects are the same. 2 You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of a ...
... Before you read, decide if you agree or disagree with each of these statements. As you read this chapter, see if you change your mind about any of the statements. 1 The atoms in all objects are the same. 2 You cannot always tell by an object’s appearance whether it is made of more than one type of a ...
7.1 Equilibrium PPT equilibrium1
... 7.1.1 Outline the characteristics of chemical and physical systems in a state of equilibrium. Physical System at Equilibrium Liquid water evaporates to form water vapor. At a given temperature in a closed system, water will evaporate until the vapor reaches a certain pressure. When that occurs, equ ...
... 7.1.1 Outline the characteristics of chemical and physical systems in a state of equilibrium. Physical System at Equilibrium Liquid water evaporates to form water vapor. At a given temperature in a closed system, water will evaporate until the vapor reaches a certain pressure. When that occurs, equ ...
chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]
... 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
... 2NO2 (g) 2NO (g) + O2 (g) is 158 at 1000K. What is the equilibrium pressure of O2 if the PNO2 = 0.400 atm and PNO = 0.270 atm? ...
Slide 1
... requires the addition of heat, which shifts the equilibrium to the left and reduces the concentration of hydrogen chloride. • Thus, the value of Keq decreases. • Lowering the temperature of the system means that heat is removed, so the equilibrium relieves the stress by shifting to the right, increa ...
... requires the addition of heat, which shifts the equilibrium to the left and reduces the concentration of hydrogen chloride. • Thus, the value of Keq decreases. • Lowering the temperature of the system means that heat is removed, so the equilibrium relieves the stress by shifting to the right, increa ...
Chapter 8 Concepts of Chemical Bonding
... Plan We need to determine the charges and relative sizes of the ions in the compounds. We then use Equation 8.4 qualitatively to determine the relative energies, knowing that (a) the larger the ionic charges, the greater the energy and (b) the farther apart the ions are, the lower the energy. Solve ...
... Plan We need to determine the charges and relative sizes of the ions in the compounds. We then use Equation 8.4 qualitatively to determine the relative energies, knowing that (a) the larger the ionic charges, the greater the energy and (b) the farther apart the ions are, the lower the energy. Solve ...
Theory, Experiment and Computer Simulation of the Electrostatic
... where ∆φx/sol expresses the Galvani potential at the given electrode (x)/electrolyte interface, the last term expresses the difference in chemical potential of charge carriers near the SCrE and reference electrodes, and C is a constant representing all remaining potential jumps in the circuit unrela ...
... where ∆φx/sol expresses the Galvani potential at the given electrode (x)/electrolyte interface, the last term expresses the difference in chemical potential of charge carriers near the SCrE and reference electrodes, and C is a constant representing all remaining potential jumps in the circuit unrela ...
4 Expressing and Measuring Chemical Change
... Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. In section 2.1, you learned how physical and chemical changes differ. Chemical changes always produce new substances with new properties and their own unique chemical formulas. Such changes involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. They are ...
... Chemistry is the study of matter and its changes. In section 2.1, you learned how physical and chemical changes differ. Chemical changes always produce new substances with new properties and their own unique chemical formulas. Such changes involve the breaking and forming of chemical bonds. They are ...
Physics STPM - Chung Hua Middle School STPM Community
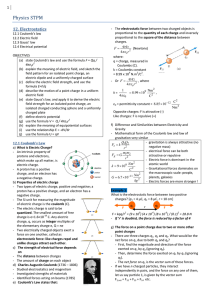
... charge inside the conductor - The charge, Q1, must reside on the outside surface of the sphere (ii) How is the charge distributed on the spherical shell? - The electric field inside the conducting shell is zero. - There can be no net charge inside the conductor - Using Gauss’ Law it can be shown tha ...
... charge inside the conductor - The charge, Q1, must reside on the outside surface of the sphere (ii) How is the charge distributed on the spherical shell? - The electric field inside the conducting shell is zero. - There can be no net charge inside the conductor - Using Gauss’ Law it can be shown tha ...
chemical equilibrium
... • initially, there is no backward reaction but, as products form, it will get faster • provided the temperature remains constant there will come a time when the backward and forward reactions are equal and opposite ; the reaction has reached equilibrium ...
... • initially, there is no backward reaction but, as products form, it will get faster • provided the temperature remains constant there will come a time when the backward and forward reactions are equal and opposite ; the reaction has reached equilibrium ...
Chapter 5 The Electric Potential
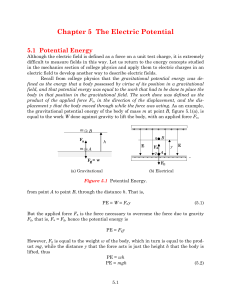
... That is, knowing the potential between the plates, something that is easily measured with a voltmeter, and the distance separating the plates, a new indirect way of determining the electric field intensity is obtained. When equation 5.8 is used to determine the electric field, an equivalent unit of ...
... That is, knowing the potential between the plates, something that is easily measured with a voltmeter, and the distance separating the plates, a new indirect way of determining the electric field intensity is obtained. When equation 5.8 is used to determine the electric field, an equivalent unit of ...









![chap15pptlecture_chapte.ppt [Read-Only]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015369082_1-00cbf06a2d468a4ae1c963f5ca674e31-300x300.png)