Part V The Third Law and Free Energy
... We have noticed that the statement of the third law concerns the entropy of perfect crystals at absolute zero. Now the question is what would be the entropy for other systems under similar circumstances. Consider a solid crystalline solution at the absolute zero that is perfectly ordered with respec ...
... We have noticed that the statement of the third law concerns the entropy of perfect crystals at absolute zero. Now the question is what would be the entropy for other systems under similar circumstances. Consider a solid crystalline solution at the absolute zero that is perfectly ordered with respec ...
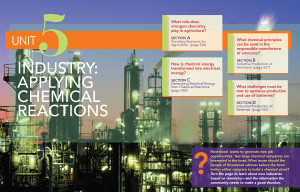
industry: applying chemical reactions
... Several weeks ago, the town council announced that two industrial firms are interested in converting the empty Riverwood Corportion building into a chemical manufacturing plant in Riverwood. Because of a lack of employment opportunities in Riverwood, many of your friends and neighbors have expressed ...
... Several weeks ago, the town council announced that two industrial firms are interested in converting the empty Riverwood Corportion building into a chemical manufacturing plant in Riverwood. Because of a lack of employment opportunities in Riverwood, many of your friends and neighbors have expressed ...
SEKOLAH MENENGAH KEBANGSAAN RAJA PEREMPUAN, IPOH
... 1. State the meaning of relative atomic mass based on C- 12 scale 2. State why C 12 is used as a standard for determining relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass 3. Caculate the relative molecular mass of substances. A student is able to 1. Define a mole as the amount of matter that contain ...
... 1. State the meaning of relative atomic mass based on C- 12 scale 2. State why C 12 is used as a standard for determining relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass 3. Caculate the relative molecular mass of substances. A student is able to 1. Define a mole as the amount of matter that contain ...
a ΔG - KFUPM Resources v3
... What happens when one of the potential driving forces behind a chemical reaction is favorable and the other is not? In other words, what is the situation when enthalpy and entropy compete with each other? Gibbs free energy (or simply free energy) is another thermodynamic quantity that reflects t ...
... What happens when one of the potential driving forces behind a chemical reaction is favorable and the other is not? In other words, what is the situation when enthalpy and entropy compete with each other? Gibbs free energy (or simply free energy) is another thermodynamic quantity that reflects t ...
Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... Standard: 3.1.C.A2 – Describe how changes in energy affect the rate of chemical reactions. Standard: 3.2.C.A1 – Explain the relationship of an elements position on the periodic table to its atomic number, ionization energy, electro-negativity, atomic size, and classification of elements. Anchor: CHE ...
... Standard: 3.1.C.A2 – Describe how changes in energy affect the rate of chemical reactions. Standard: 3.2.C.A1 – Explain the relationship of an elements position on the periodic table to its atomic number, ionization energy, electro-negativity, atomic size, and classification of elements. Anchor: CHE ...
Kinetics and Equilibrium ___ 1. In a chemical reaction the use of a
... ___ 2. Given the reaction: CO2(s) <======> CO2(g). As the CO2(s) changes to CO 2(g) the entropy of the system (1) decreases; (2) increases; (3) remains the same.. ___ 3. Given the reaction at equilibrium: X(g) + Y(g) <======> 2Z(g). As the pressure on the system increases, the temperature remaining ...
... ___ 2. Given the reaction: CO2(s) <======> CO2(g). As the CO2(s) changes to CO 2(g) the entropy of the system (1) decreases; (2) increases; (3) remains the same.. ___ 3. Given the reaction at equilibrium: X(g) + Y(g) <======> 2Z(g). As the pressure on the system increases, the temperature remaining ...
CH3511: PHYSICAL CHEMISTRY LAB I Lab 6
... In this experiment, the molar heat of fusion and the freezing point depression constant of water will be calculated. The system being studied is an aqueous solution of varying salts. Multiple systems containing different concentrations (ranging from 0.0179 m to 0.8961 m) of the salts magnesium chlor ...
... In this experiment, the molar heat of fusion and the freezing point depression constant of water will be calculated. The system being studied is an aqueous solution of varying salts. Multiple systems containing different concentrations (ranging from 0.0179 m to 0.8961 m) of the salts magnesium chlor ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... The diameter of the atom is determined by the range of the electrons in their travels around the nucleus and is approximately 10-8 cm. The diameter of the nucleus is roughly 10,000 times smaller, approximately 10-13 to 10-12 cm. Because the nucleus is composed of neutrons and protons that are about ...
... The diameter of the atom is determined by the range of the electrons in their travels around the nucleus and is approximately 10-8 cm. The diameter of the nucleus is roughly 10,000 times smaller, approximately 10-13 to 10-12 cm. Because the nucleus is composed of neutrons and protons that are about ...
Department of Chemistry School of Natural Sciences
... electronic balances and volumetric glassware, preparation of solutions, chemical measurements using pH. ...
... electronic balances and volumetric glassware, preparation of solutions, chemical measurements using pH. ...
The Periodic Electronegativity Table
... Since r0 is characteristic of each atom, characteristic energies are predicted for atomic valence-state electrons. It is the atomic equivalent of the Fermi energy of an electron at the surface of the Fermi sea in condensed phases, and in that sense represents the chemical potential of the valence el ...
... Since r0 is characteristic of each atom, characteristic energies are predicted for atomic valence-state electrons. It is the atomic equivalent of the Fermi energy of an electron at the surface of the Fermi sea in condensed phases, and in that sense represents the chemical potential of the valence el ...
4.2- Reaction Stoichiometry Reaction Stoichiometry
... ions and their solutions are good conductor of electricity ionic compounds and strong acids ...
... ions and their solutions are good conductor of electricity ionic compounds and strong acids ...
введение в общую introductio to the general ch ведение в общую
... traditional examples of such physical processes: melting of the ice and crystallization of the water, boiling of the water and condensation of the vapor. Chemical processes are described by chemical reactions. A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical s ...
... traditional examples of such physical processes: melting of the ice and crystallization of the water, boiling of the water and condensation of the vapor. Chemical processes are described by chemical reactions. A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical s ...
The Shale Gas Revolution: A Methane-to
... By comparison, 2012 Ethylene Capacity = 24,000 kta Plenty of methane available for chemical use EES — 7 ...
... By comparison, 2012 Ethylene Capacity = 24,000 kta Plenty of methane available for chemical use EES — 7 ...