Unit 7 Reaction Rates and Equilibrium Notes
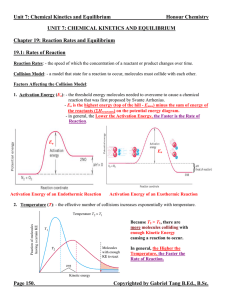
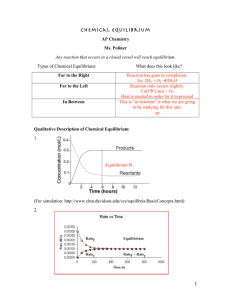
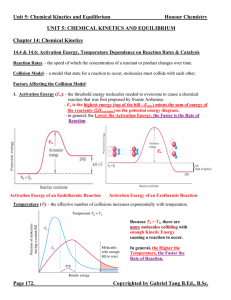
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: - a qualitative method to predict the shift on an equilibrium system if it is disturbed by means of changing concentration, pressure and temperature. - the equilibrium will shift in the direction that minimizes the change imposed on the system. 1. Effects of a Change in Con ...
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: - a qualitative method to predict the shift on an equilibrium system if it is disturbed by means of changing concentration, pressure and temperature. - the equilibrium will shift in the direction that minimizes the change imposed on the system. 1. Effects of a Change in Con ...
Effect of phospholipid and (phospho)lipase - Annales UMCS
... properties are important in such systems because are they connected with their biocompatibility. It seems interesting to consider the possibility of functionalizing the model dispersions with the membrane-active biomolecules as the systems of biological significance with the desired biocompatibility ...
... properties are important in such systems because are they connected with their biocompatibility. It seems interesting to consider the possibility of functionalizing the model dispersions with the membrane-active biomolecules as the systems of biological significance with the desired biocompatibility ...
Unit 5: Chemical Kinetics and Equilibrium
... Homogeneous Equilibria: - an equilibrium system where all chemical species are in the same phase. Equilibrium Constant (K): - the symbol for equilibrium constant when the expression deals with concentrations is simply K or Kc. When the expression deals with pressures, it is symbolized as KP. - for e ...
... Homogeneous Equilibria: - an equilibrium system where all chemical species are in the same phase. Equilibrium Constant (K): - the symbol for equilibrium constant when the expression deals with concentrations is simply K or Kc. When the expression deals with pressures, it is symbolized as KP. - for e ...
Predicting point defect equilibria across oxide hetero-interfaces
... responsible for the formation of the core zone at the interface which exhibit very different defect concentrations in comparison with the extended space charge zone. Attempts have been made to establish interfacial defect chemistry theoretically.9,11,37 These theories consider equilibrium defect reac ...
... responsible for the formation of the core zone at the interface which exhibit very different defect concentrations in comparison with the extended space charge zone. Attempts have been made to establish interfacial defect chemistry theoretically.9,11,37 These theories consider equilibrium defect reac ...
Stoichiometry and the Mole
... How big is a mole? It is very large. Suppose you had a mole of dollar bills that need to be counted. If everyone on earth (about 6 billion people) counted one bill per second, it would take about 3.2 million years to count all the bills. A mole of sand would fill a cube about 32 km on a side. A mole ...
... How big is a mole? It is very large. Suppose you had a mole of dollar bills that need to be counted. If everyone on earth (about 6 billion people) counted one bill per second, it would take about 3.2 million years to count all the bills. A mole of sand would fill a cube about 32 km on a side. A mole ...
Electric Potential - Little Shop of Physics
... energy at point C is (Uelec)C = 6 mJ because it took 6 mJ of work to move it to point C. What if we were to repeat this experiment with a different charge—say, q = 20 nC? According to Coulomb’s law, the electric force on this charge due to the source charges will be twice that on the 10 nC charge. C ...
... energy at point C is (Uelec)C = 6 mJ because it took 6 mJ of work to move it to point C. What if we were to repeat this experiment with a different charge—say, q = 20 nC? According to Coulomb’s law, the electric force on this charge due to the source charges will be twice that on the 10 nC charge. C ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... 7. Chemical energy: Energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances. 8. Chemical Equilibrium: A chemical state in which no net change can be observed. 9. Colligative properties: Properties of solutions which depend on the number of solute particles in solution and not on the nature ...
... 7. Chemical energy: Energy stored within the structural units of chemical substances. 8. Chemical Equilibrium: A chemical state in which no net change can be observed. 9. Colligative properties: Properties of solutions which depend on the number of solute particles in solution and not on the nature ...