Chapter 29. The Electric Potential
... If 2H+O=>H2O released E=1 eV of “chemical energy,” what is the total energy release in joules and how high would that lift one kg subject to earth gravity? The number of molecules formed = the number of protons in one gm = the inverse of the proton mass (1.67e-24 gm) = Avogadro’s number N=6e23. The ...
... If 2H+O=>H2O released E=1 eV of “chemical energy,” what is the total energy release in joules and how high would that lift one kg subject to earth gravity? The number of molecules formed = the number of protons in one gm = the inverse of the proton mass (1.67e-24 gm) = Avogadro’s number N=6e23. The ...
Chemical Dynamics, Thermochemistry, and Quantum Chemistry
... monitoring the temperature for a 5 to 10 minute period following this jump. Do not stop monitoring temperature until the slope of the temperature versus time curve is reasonably constant (i.e. each time step the temperature changes by a constant increment). ...
... monitoring the temperature for a 5 to 10 minute period following this jump. Do not stop monitoring temperature until the slope of the temperature versus time curve is reasonably constant (i.e. each time step the temperature changes by a constant increment). ...
CHEMISTRY Academic Standards Statement
... 2.1.4 Chemical thermodynamics, equilibrium and kinetics i. Different chemical species have different energies. Most chemical changes are accompanied by a net change of energy of the system. ii. Energy is conserved in chemical changes: breaking chemical bonds requires energy; formation of chemical bo ...
... 2.1.4 Chemical thermodynamics, equilibrium and kinetics i. Different chemical species have different energies. Most chemical changes are accompanied by a net change of energy of the system. ii. Energy is conserved in chemical changes: breaking chemical bonds requires energy; formation of chemical bo ...
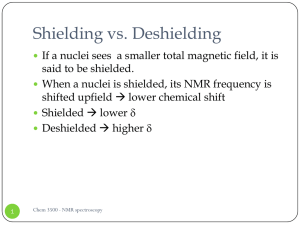
Shielding vs. Deshielding
... chemistry is a property of the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of the substituents based on relevant resonance structures and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric ...
... chemistry is a property of the substituents or functional groups in a chemical compound. The effect is used in a qualitative way and describes the electron withdrawing or releasing properties of the substituents based on relevant resonance structures and is symbolized by the letter M. The mesomeric ...
ppt - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: A system in equilibrium that is subjected to a stress will react in a way that tends to counteract the stress At equilibrium, the macroscopic properties of a system remain constant When you perturb the equilibrium, the system will counteract the ...
... Le Châtelier’s Principle: A system in equilibrium that is subjected to a stress will react in a way that tends to counteract the stress At equilibrium, the macroscopic properties of a system remain constant When you perturb the equilibrium, the system will counteract the ...
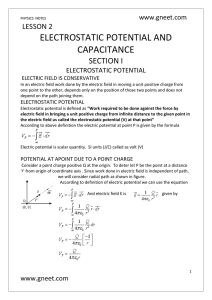
Electric Potential Maps and Voltage
... energy of a unit volume of the fluid, thus we see that our hydrodynamic voltage has the dimensions of energy per unit volume. Electric voltage is a quantity with the dimensions of energy per unit charge that in different situations is represented by a series of terms like the terms in Bernoulli’s hy ...
... energy of a unit volume of the fluid, thus we see that our hydrodynamic voltage has the dimensions of energy per unit volume. Electric voltage is a quantity with the dimensions of energy per unit charge that in different situations is represented by a series of terms like the terms in Bernoulli’s hy ...
Kinetics of Oxygen Reduction in Aprotic Li–O2 Cells: A Model
... presents the simulated Tafel plots for a wide range of τ. In Figure 2a and b, τ has been color-coded from blue for a very large desorption time constant (1010 s), to magenta for sufficiently small τ (10−4 s). A linear trend is obtained over the full range of potential (current) for extreme values of τ ...
... presents the simulated Tafel plots for a wide range of τ. In Figure 2a and b, τ has been color-coded from blue for a very large desorption time constant (1010 s), to magenta for sufficiently small τ (10−4 s). A linear trend is obtained over the full range of potential (current) for extreme values of τ ...
The enthalpy change
... Many chemical reactions are reversible. In these reactions, there is both a forward reaction (where reactants are made into products) and a reverse reaction (where product molecules break down to form reactants). The Haber process, the industrial route to the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and h ...
... Many chemical reactions are reversible. In these reactions, there is both a forward reaction (where reactants are made into products) and a reverse reaction (where product molecules break down to form reactants). The Haber process, the industrial route to the formation of ammonia from nitrogen and h ...