Unit 3: 1 Equilibrium and the Constant, K
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
... environmental processes that are reversible, construct an explanation that connects the observations to the reversibility of the underlying chemical reactions or processes. [See SP 6.2; Essential knowledge 6.A.1] Learning objective 6.2 The student can, given a manipulation of a chemical reaction or ...
813. - Materials and Process Simulation Center
... We report reactive dynamics (RD) studies on: the decomposition of bulk hydrazine (N2H4); the decomposition of bulk monomethyl-hydrazine (CH3N2H3), hereafter referred to simply as methyl-hydrazine; the decomposition of hydrazine in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2); and decomposition hydrazine ...
... We report reactive dynamics (RD) studies on: the decomposition of bulk hydrazine (N2H4); the decomposition of bulk monomethyl-hydrazine (CH3N2H3), hereafter referred to simply as methyl-hydrazine; the decomposition of hydrazine in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2); and decomposition hydrazine ...
14.1 Dynamic Equilibrium, Keq , and the Mass Action Expression
... Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College ...
... Dr. Fred Omega Garces Chemistry 201 Miramar College ...
Chapter 15
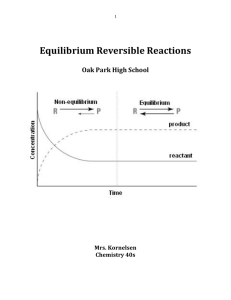
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
... of the reaction products is physically separated from a reaction mixture as a gas (the reaction of a metal carbonate with acid, for example, Figure 15.X), a single reaction arrow is used. The Equilibrium State In Chapter 12, we described the nature of a dynamic equilibrium between a liquid and its v ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... 15.2 The Equilibrium Constant, K 15.2a Equilibrium Constants The relationship between forward and reverse rate constants for an equilibrium system is shown in an equilibrium constant expression and quantified by an equilibrium constant (K). An equilibrium constant expression is written by rearrangi ...
... 15.2 The Equilibrium Constant, K 15.2a Equilibrium Constants The relationship between forward and reverse rate constants for an equilibrium system is shown in an equilibrium constant expression and quantified by an equilibrium constant (K). An equilibrium constant expression is written by rearrangi ...
Beverley John C. Beverley IE 500/PHI 598: Ontological Engineering
... clarity to the field. Moreover, it is clear that a well-developed ontology must begin with the foundations of the field of inquiry. It is with that in mind, and the lofty goals of terminological clarity, appropriate characterization of thermodynamic systems, and potential extensions into ...
... clarity to the field. Moreover, it is clear that a well-developed ontology must begin with the foundations of the field of inquiry. It is with that in mind, and the lofty goals of terminological clarity, appropriate characterization of thermodynamic systems, and potential extensions into ...
(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy
... • determine the number of moles of each species at equilibrium • divide moles by volume (in dm3) to get the equilibrium concentrations in mol dm-3 (If no volume is quoted, use a V; it will probably cancel out) • from the equation constructed in the first step, write out an expression for Kc. • subst ...
... • determine the number of moles of each species at equilibrium • divide moles by volume (in dm3) to get the equilibrium concentrations in mol dm-3 (If no volume is quoted, use a V; it will probably cancel out) • from the equation constructed in the first step, write out an expression for Kc. • subst ...














![(K c ) [A] - Knockhardy](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/011755527_1-914ea907d1ff7656ef398ad87316c94c-300x300.png)