Chemical Reactions - 2012 Book Archive
... of iodine is 126.90 g/mol. When we deal with elements such as iodine and sulfur, which occur as a diatomic molecule (I2) and a polyatomic molecule (S8), respectively, molar mass usually refers to the mass of 1 mol of atoms of the element—in this case I and S, not to the mass of 1 mol of molecules of ...
... of iodine is 126.90 g/mol. When we deal with elements such as iodine and sulfur, which occur as a diatomic molecule (I2) and a polyatomic molecule (S8), respectively, molar mass usually refers to the mass of 1 mol of atoms of the element—in this case I and S, not to the mass of 1 mol of molecules of ...
Chapter 16
... three components at all, that is, for the system to be in chemical equilibrium. It appears that although we know the temperature, pressure, and composition (thus the state) of the system, we are unable to predict whether the system is in chemical equilibrium. In this chapter we develop the necessary ...
... three components at all, that is, for the system to be in chemical equilibrium. It appears that although we know the temperature, pressure, and composition (thus the state) of the system, we are unable to predict whether the system is in chemical equilibrium. In this chapter we develop the necessary ...
W. H. Freeman Publishers - Physical Chemistry for the Life Sciences
... and incorporate some of the complications that the original model ignored. Thus, models provide the initial framework for discussions, and reality is progressively captured rather like a building is completed, decorated, and furnished. One example is the nuclear model of an atom, and in particular a ...
... and incorporate some of the complications that the original model ignored. Thus, models provide the initial framework for discussions, and reality is progressively captured rather like a building is completed, decorated, and furnished. One example is the nuclear model of an atom, and in particular a ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 3: Chemistry in Society
... Balanced equations show the mole ratio(s) of reactants and products. Using the balanced equation and the gram formula masses (GFM), mass to mass calculations can be performed. ...
... Balanced equations show the mole ratio(s) of reactants and products. Using the balanced equation and the gram formula masses (GFM), mass to mass calculations can be performed. ...
Chemical Reaction Equations
... 2) Dissociate all high-solubility ionic compounds, and ionize all strong acids to show the complete ionic equation 3) Cancel identical entities that appear on both the reactant and ...
... 2) Dissociate all high-solubility ionic compounds, and ionize all strong acids to show the complete ionic equation 3) Cancel identical entities that appear on both the reactant and ...
Document
... equilibrium is not true? A) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in a manner to restore equilibrium. B) Equilibrium in molecular systems is dynamic, with two opposing processes balancing one another. C) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given reaction mixture i ...
... equilibrium is not true? A) A system that is disturbed from an equilibrium condition responds in a manner to restore equilibrium. B) Equilibrium in molecular systems is dynamic, with two opposing processes balancing one another. C) The value of the equilibrium constant for a given reaction mixture i ...
unit-4-notes-1_enthalpy-and-entropy
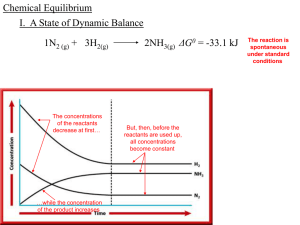
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
... and no NO2. The forward reaction rate was high at the start, but the reverse reaction rate eventually "caught up", the rates became equal and equilibrium was established. Can you guess what would happen if we had started with pure NO2 instead (no N2O4 )? The reverse rate would start out high and the ...
English A4 - FLIRmedia.com
... identifier. The FLIR Griffin G510 enables military and civil responders to easily sample all phases of matter, including solid, liquid, and vapor, to rapidly identify chemical hazards in the field. The versatile Griffin G510 represents a new-generation of portable GC/MS capability, with multiple int ...
... identifier. The FLIR Griffin G510 enables military and civil responders to easily sample all phases of matter, including solid, liquid, and vapor, to rapidly identify chemical hazards in the field. The versatile Griffin G510 represents a new-generation of portable GC/MS capability, with multiple int ...
Chapter 8 - Chemical Equations and Reactions
... balancing equations by inspection, continued 3. Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Balance the different types of atoms one at a time. • First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. • Balance p ...
... balancing equations by inspection, continued 3. Balance the formula equation according to the law of conservation of mass. • Balance the different types of atoms one at a time. • First balance the atoms of elements that are combined and that appear only once on each side of the equation. • Balance p ...
Ch 21 - Keene ISD
... must measure the amount of work it takes to move the charge from point A to that other point. ...
... must measure the amount of work it takes to move the charge from point A to that other point. ...