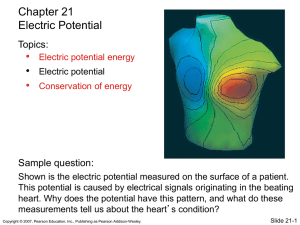
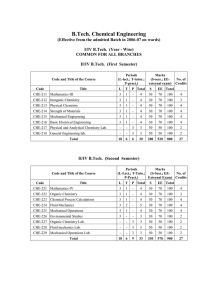
Physical Chemistry I – review guide
... • Material Equilibrium: No net chemical reactions are occurring in the system nor is there any net ...
... • Material Equilibrium: No net chemical reactions are occurring in the system nor is there any net ...
Chemistry - Beachwood City Schools
... Answers to Chapter 11 Study Questions 1. Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency. Energy is proportional to frequency. 2. The new idea in Bohr's model was that electrons can only exist in specific energy states. Bohr's model included an electron orbiting the nucleus as a planet does the su ...
... Answers to Chapter 11 Study Questions 1. Wavelength is inversely proportional to frequency. Energy is proportional to frequency. 2. The new idea in Bohr's model was that electrons can only exist in specific energy states. Bohr's model included an electron orbiting the nucleus as a planet does the su ...
The Logical Structure of Organic Chemistry and the Empirical
... simply that what one sees depends on how one looks, but rather that one constructs what one sees in terms of one’s interests and purposes of investigation. This is true even in cases where the objects of observation are given to an observer as visible phenomena or tangible physical substances. For i ...
... simply that what one sees depends on how one looks, but rather that one constructs what one sees in terms of one’s interests and purposes of investigation. This is true even in cases where the objects of observation are given to an observer as visible phenomena or tangible physical substances. For i ...
Chem - Andhra University
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
... Heat changes, Enthalpy, reversible changes, maximum work. Heat capacities at constant pressure and volume, adiabatic changes. Heat of Reaction, heat of Formation, Heat of Combustion, Thermo-chemical Laws, effect of temperature on Heat of Reaction. Second law of Thermodynamics, spontaneous processes, ...
TDB-5: Standards and conventions for TDB publications
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
... • The designators (cr), (am), (vit), and (s) are used for solid substances. (cr) is used when it is known that the compound is crystalline, (am) when it is known that it is amorphous, and (vit) for glassy substances. Otherwise, (s) is used. • In some cases, more than one crystalline form of the same ...
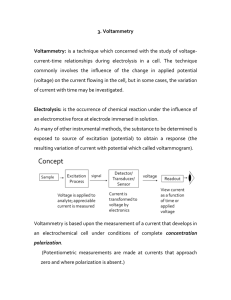
Diffusion current - Prof Dr Hisham E Abdellatef
... nature and concentration Of supporting electrolyte and the temperature are kept constant. Hence , upon determining the relative wave height or diffusion current of the unknown ion and with some standard or pilot ion added to the solution in known amount and comparing these with the ratio for known a ...
... nature and concentration Of supporting electrolyte and the temperature are kept constant. Hence , upon determining the relative wave height or diffusion current of the unknown ion and with some standard or pilot ion added to the solution in known amount and comparing these with the ratio for known a ...
Thermochemistry
... consider the matter involved to be a thermodynamic system which can be treated by the methods of equilibrium thermodynamics. The number of moles of the species νCO2 , νH2 , νCO and νH2 O become thermodynamic coordinates or functions along with those we are already acquainted with, M, p, V, U, H, S, ...
... consider the matter involved to be a thermodynamic system which can be treated by the methods of equilibrium thermodynamics. The number of moles of the species νCO2 , νH2 , νCO and νH2 O become thermodynamic coordinates or functions along with those we are already acquainted with, M, p, V, U, H, S, ...
Philosophy of Chemistry
... A central epistemological issue is whether chemical knowledge can be complete or not. Microstructural essentialists claim that a perfect microstructural description of any substance yields complete chemical knowledge. However, chemical properties are not manifest properties but dispositional relatio ...
... A central epistemological issue is whether chemical knowledge can be complete or not. Microstructural essentialists claim that a perfect microstructural description of any substance yields complete chemical knowledge. However, chemical properties are not manifest properties but dispositional relatio ...