Chemical Process Modeling in Modelica
... Real zeta; equation outlet[1].f = zeta*inlet[1].f; outlet[1].H = zeta*inlet[1].H; end Divider; ...
... Real zeta; equation outlet[1].f = zeta*inlet[1].f; outlet[1].H = zeta*inlet[1].H; end Divider; ...
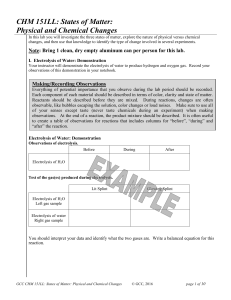
CHM 151LL: States of Matter: Physical and Chemical Changes
... boiling point a liquid will boil and become a gas. If we decrease the temperature, which decreases the molecular motion, a gas will condense into a liquid at the boiling point, and a liquid will freeze to become a solid at the melting point (which can also be called the freezing point). A few substa ...
... boiling point a liquid will boil and become a gas. If we decrease the temperature, which decreases the molecular motion, a gas will condense into a liquid at the boiling point, and a liquid will freeze to become a solid at the melting point (which can also be called the freezing point). A few substa ...
Chapter 10: Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
... • The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a perfect crystal of any pure substance approaches zero as the temperature approaches absolute zero. • Because S is explicitly known (= 0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. • The entropy of one mole of a chemical substance ...
... • The third law of thermodynamics states that the entropy of a perfect crystal of any pure substance approaches zero as the temperature approaches absolute zero. • Because S is explicitly known (= 0) at 0 K, S values at other temps can be calculated. • The entropy of one mole of a chemical substance ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
7.1 Describing Reactions
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
... reactants. This principle is the law of conservation of mass. When charcoal burns, the mass of the carbon dioxide produced is equal to the mass of the charcoal and oxygen that reacted. ...
What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry
... and computer skills. Because the field of chemistry is very broad, you will need to clarify your employment direction early on and gain practical experience through internships and volunteer work. A bachelor’s degree in chemistry is usually required for entry-level chemist positions. An undergraduat ...
... and computer skills. Because the field of chemistry is very broad, you will need to clarify your employment direction early on and gain practical experience through internships and volunteer work. A bachelor’s degree in chemistry is usually required for entry-level chemist positions. An undergraduat ...
Chemical Equations - Salem Community Schools
... • You may have also noticed that the word energy is not always written in the equation. • It is used only if it is important to know whether energy is released or absorbed. ...
... • You may have also noticed that the word energy is not always written in the equation. • It is used only if it is important to know whether energy is released or absorbed. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... We consider an isolated macroscopic system, which contains only a pure substance, without any internal walls limiting the motion of molecules, for instance, a pure gas in a vessel. Only a few parameters are needed to completely characterize an equilibrium state of such a simple system (Fig. 2.3b). T ...
... We consider an isolated macroscopic system, which contains only a pure substance, without any internal walls limiting the motion of molecules, for instance, a pure gas in a vessel. Only a few parameters are needed to completely characterize an equilibrium state of such a simple system (Fig. 2.3b). T ...
Folie 1
... • At C (about 60 bar for CO2), the piston suddenly slides in without any further rise in pressure. Just to the left of C a liquid appears, and there are two phases separated by a sharply defined surface. • As the volume is decreased from C through D to E, the amount of liquid increases. There is no ...
... • At C (about 60 bar for CO2), the piston suddenly slides in without any further rise in pressure. Just to the left of C a liquid appears, and there are two phases separated by a sharply defined surface. • As the volume is decreased from C through D to E, the amount of liquid increases. There is no ...
H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
... This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + C Activated complex Transition state ...
spontaneous processes
... irreversible process: getting back what you started with requires more than just an “undo” -- we can restore the original system, but the surroundings will have changed ...
... irreversible process: getting back what you started with requires more than just an “undo” -- we can restore the original system, but the surroundings will have changed ...