Interference2
... When white light is used the center fringe at C is white since all waves will constructively interfere here while the fringes on the both side of C are colored because the fringe width () depends on wavelength of light. ...
... When white light is used the center fringe at C is white since all waves will constructively interfere here while the fringes on the both side of C are colored because the fringe width () depends on wavelength of light. ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... color light has a different wavelength and frequency. The speed of light can be calculated by multiplying the wavelength with the frequency. Violet has the shortest wavelength and red has the longest wavelength. When an object appears a certain color it is due to the absorption of all colors but the ...
... color light has a different wavelength and frequency. The speed of light can be calculated by multiplying the wavelength with the frequency. Violet has the shortest wavelength and red has the longest wavelength. When an object appears a certain color it is due to the absorption of all colors but the ...
pptx - Caltech GPS
... Solution depends on the distribution of mass and velocity in the cloud before its collapse to form the sun One simple solution supposes all constituent masses arrived at the sun with a velocity equal to the escape velocity from the Sun today: ...
... Solution depends on the distribution of mass and velocity in the cloud before its collapse to form the sun One simple solution supposes all constituent masses arrived at the sun with a velocity equal to the escape velocity from the Sun today: ...
HW #8 Solutions
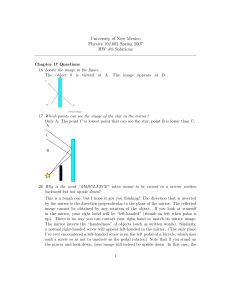
... Only A. The point C is lowest point that can see the star; point B is lower than C. ...
... Only A. The point C is lowest point that can see the star; point B is lower than C. ...
Name
... vapor (gas), going up into the atmosphere. Condensation - Warm air rises and loses energy (cools down. Water vapor forms liquid water droplets that create clouds. Precipitation – When warm air loses energy (is cooled), water droplets can no longer hold in clouds and will fall as rain (above 32oF), s ...
... vapor (gas), going up into the atmosphere. Condensation - Warm air rises and loses energy (cools down. Water vapor forms liquid water droplets that create clouds. Precipitation – When warm air loses energy (is cooled), water droplets can no longer hold in clouds and will fall as rain (above 32oF), s ...
Meteorology Unit Test Study Guide
... 13. During a sea breeze the land heats up faster than the water in the day time. 14. Radiation is heat transfer in waves. 15. Convection occurs when warm things rise and cool things sink. 16. Conduction happens when heat transfers because two things are touching each other. 17. Explain why clouds c ...
... 13. During a sea breeze the land heats up faster than the water in the day time. 14. Radiation is heat transfer in waves. 15. Convection occurs when warm things rise and cool things sink. 16. Conduction happens when heat transfers because two things are touching each other. 17. Explain why clouds c ...
Homework #1
... meaning the Sun was at the zenith in the sky at this time. Being in Alexandria, which was located more or less due north of Syene, he could measure the length of a shadow cast by an obelisk at the same time, noon on the summer solstice. This measurement, along with the height of the obelisk, gave hi ...
... meaning the Sun was at the zenith in the sky at this time. Being in Alexandria, which was located more or less due north of Syene, he could measure the length of a shadow cast by an obelisk at the same time, noon on the summer solstice. This measurement, along with the height of the obelisk, gave hi ...
Photosynthesis
... The light independent reactions are also known as the ________________ cycle.* Plants use both water and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Which of these is the source of the oxygen plants give off?* carbon dioxide water The hydrogen ion gradient that forms during the light dependent reactions i ...
... The light independent reactions are also known as the ________________ cycle.* Plants use both water and carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Which of these is the source of the oxygen plants give off?* carbon dioxide water The hydrogen ion gradient that forms during the light dependent reactions i ...
exam solutions
... (c) If you reflect an unpolarized beam from a glass plate at the polarization angle, the reflected light is linearly polarized. (d) In an optically dense material, interference between an incoming beam and the secondary wave it creates is constructive in the forward direction. (e) In specular reflec ...
... (c) If you reflect an unpolarized beam from a glass plate at the polarization angle, the reflected light is linearly polarized. (d) In an optically dense material, interference between an incoming beam and the secondary wave it creates is constructive in the forward direction. (e) In specular reflec ...
weather test study guide
... 17. At what temperature does water freeze or melt? 0˚Celsius or 32˚ Fahrenheit 18. At what temperature does water boil? 100˚Celsius or 212˚ Fahrenheit Be able to do the following things. 1. Draw and label the water cycle. 2. Recognize pictures that represent evaporation, condensation, and precipitat ...
... 17. At what temperature does water freeze or melt? 0˚Celsius or 32˚ Fahrenheit 18. At what temperature does water boil? 100˚Celsius or 212˚ Fahrenheit Be able to do the following things. 1. Draw and label the water cycle. 2. Recognize pictures that represent evaporation, condensation, and precipitat ...
5th Grade Energy Study Guide
... into another (think about a straw in a cup of water, it looks/appears bent). 27. _______________ The bouncing of light waves off a surface, such as a mirror 28. _______________ Curves inward. 29. _______________ Bulges outward. 30. _______________ is a form of energy that travels in waves and in str ...
... into another (think about a straw in a cup of water, it looks/appears bent). 27. _______________ The bouncing of light waves off a surface, such as a mirror 28. _______________ Curves inward. 29. _______________ Bulges outward. 30. _______________ is a form of energy that travels in waves and in str ...
Total intensity and quasi-elastic light
... probe which unlike electron microscopy, is nondestructive [ 13. For smaller microbes like many spherical plant viruses, the simpler Rayleigh-Gans-Debye (as opposed to Lorenz-Mie) theory is applicable and it is possible from total intensity light scattering to use for example the ‘Zimm Plot’ method f ...
... probe which unlike electron microscopy, is nondestructive [ 13. For smaller microbes like many spherical plant viruses, the simpler Rayleigh-Gans-Debye (as opposed to Lorenz-Mie) theory is applicable and it is possible from total intensity light scattering to use for example the ‘Zimm Plot’ method f ...
2010-2011 Updated Science L to J Vocabulary List
... 28. Pangaea supercontinent that included all the landmasses on Earth 29. Deposition the process in which eroded sediment is deposited in a new location 30. Desertification-the expansion of desert-like conditions in areas where the natural plant cover has been destroyed 31. Conduction- process that m ...
... 28. Pangaea supercontinent that included all the landmasses on Earth 29. Deposition the process in which eroded sediment is deposited in a new location 30. Desertification-the expansion of desert-like conditions in areas where the natural plant cover has been destroyed 31. Conduction- process that m ...
presentation source
... light with different colors, additive effect of colors, complimentary colors light reflects from surfaces the laws of reflection: (1) the angles the incident and reflected rays make with the normal to the surface are equal (2) the reflected ray lies in the same plane as the normal and incident ray m ...
... light with different colors, additive effect of colors, complimentary colors light reflects from surfaces the laws of reflection: (1) the angles the incident and reflected rays make with the normal to the surface are equal (2) the reflected ray lies in the same plane as the normal and incident ray m ...
Light Rays
... We can understand the formation of an image with the fundamentals of ray optics. ...
... We can understand the formation of an image with the fundamentals of ray optics. ...
Light - FT HELP
... the wave nature of light, and are a little more difficult to explain. Scientists have also found that gravity can bend light, but it takes a very large object with strong gravity such as a star to bend light very much, so it's not an effect you see every day! This is called REFRACTION, and it's how ...
... the wave nature of light, and are a little more difficult to explain. Scientists have also found that gravity can bend light, but it takes a very large object with strong gravity such as a star to bend light very much, so it's not an effect you see every day! This is called REFRACTION, and it's how ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.