PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
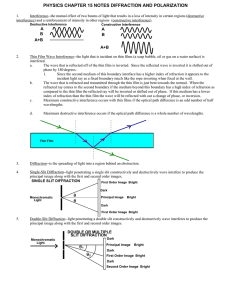
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
Light waves Review
... b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...
... b) use of additive rather than subtractive colors. c) wavelengths of visible light that reaches your eyes. d) speed with which visible light reaches it. a) ...
An introduction to Optics
... two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's ...
... two media, or equivalently, to the opposite ratio of the indices of refraction (n2 / n1): In optics, refraction is a phenomenon that often occurs when waves travel from a medium with a given refractive index to a medium with another at an oblique angle. At the boundary between the media, the wave's ...
1 Optical Phenomena
... going through that substance. For example, blue light, with a shorter wavelength, bends more than red light when passing into a refracting material. The process of separating polychromatic light into its components is called dispersion. When white light enters a prism, the blue component light is ...
... going through that substance. For example, blue light, with a shorter wavelength, bends more than red light when passing into a refracting material. The process of separating polychromatic light into its components is called dispersion. When white light enters a prism, the blue component light is ...
Word Know Not sure Definition Mineral Physical properties color
... Evaporation takes place as the air moves in this direction ...
... Evaporation takes place as the air moves in this direction ...
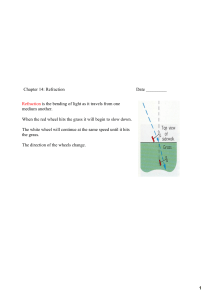
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
... dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. ...
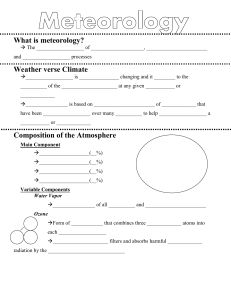
What is meteorology? The ________________ of ___________
... Have ________ below ___________________ A. Stratus ___________ layer of _____________ that cover ________ of the _____ B. Stratocumulus _____________ bottom that _____________ as long _____________________ or _____________________________ C. Nimbostratus ______________ clouds covering most of th ...
... Have ________ below ___________________ A. Stratus ___________ layer of _____________ that cover ________ of the _____ B. Stratocumulus _____________ bottom that _____________ as long _____________________ or _____________________________ C. Nimbostratus ______________ clouds covering most of th ...
Homework Questions - science
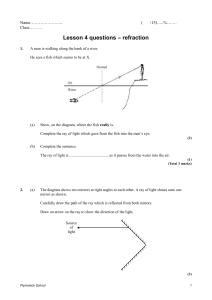
... The diagram shows two mirrors at right angles to each other. A ray of light shines onto one mirror as shown. Carefully draw the path of the ray which is reflected from both mirrors. Draw an arrow on the ray to show the direction of the light. Source of light ...
... The diagram shows two mirrors at right angles to each other. A ray of light shines onto one mirror as shown. Carefully draw the path of the ray which is reflected from both mirrors. Draw an arrow on the ray to show the direction of the light. Source of light ...
PDF
... Light changes speed when going from one medium into another (e.g. air to glass) If it hits the surface at an angle it will bend. What is this known as? A ...
... Light changes speed when going from one medium into another (e.g. air to glass) If it hits the surface at an angle it will bend. What is this known as? A ...
Unit Study Guide - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... electromagnetic spectrum – the entire range of radiant energy, from radio waves through visible light to gamma rays incandescence – the process of emitting light because of high temperatures opaque - describes a material that does not allow any light to be transmitted; all of the light energy is eit ...
... electromagnetic spectrum – the entire range of radiant energy, from radio waves through visible light to gamma rays incandescence – the process of emitting light because of high temperatures opaque - describes a material that does not allow any light to be transmitted; all of the light energy is eit ...
concave lens
... through it (a). The translucent lamp shade allows light to pass through, although the lightbulb source itself is not visible (b). The opaque tarp covers the statue, preventing the statue from being seen (c). ...
... through it (a). The translucent lamp shade allows light to pass through, although the lightbulb source itself is not visible (b). The opaque tarp covers the statue, preventing the statue from being seen (c). ...
Integrated Optics: Guiding and manipulating light for device
... Study of light and its associated phenomenon has always been a subject of great curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-ti ...
... Study of light and its associated phenomenon has always been a subject of great curiosity. The light behaves as wave and also as particle called photon. It has four primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-ti ...
Message from the Secretary-General Dr.Petteri Taalas of the World
... masterpieces of musical impressionism. Photographers are particularly fascinated by clouds, including those who enthusiastically contributed to the WMO 2017 calendar illustrating this year’s World Meteorological Day Theme of “Understanding clouds.” Clouds are also embedded in cultural symbols and ha ...
... masterpieces of musical impressionism. Photographers are particularly fascinated by clouds, including those who enthusiastically contributed to the WMO 2017 calendar illustrating this year’s World Meteorological Day Theme of “Understanding clouds.” Clouds are also embedded in cultural symbols and ha ...
II. Optical properties of glass
... incoming light waves of a range of the wavelengths. Often selective optical filters can be utilized to alter or enhance the brightness and contrast of digital images. Guided light wave transmission via frequency selective waveguides involves the emerging field of fiber optics and its ability of cert ...
... incoming light waves of a range of the wavelengths. Often selective optical filters can be utilized to alter or enhance the brightness and contrast of digital images. Guided light wave transmission via frequency selective waveguides involves the emerging field of fiber optics and its ability of cert ...
Weather Interpretation File
... Before any outdoor activity, you should check the weather conditions from a reputable weather predicting source, such as the bureau of meteorology (BOM), or your nearest National Parks and Wildlife Service who should have regular updates. As well as this, you should be able to recognise some common ...
... Before any outdoor activity, you should check the weather conditions from a reputable weather predicting source, such as the bureau of meteorology (BOM), or your nearest National Parks and Wildlife Service who should have regular updates. As well as this, you should be able to recognise some common ...
Atmosphere Troposphere Stratosphere Ozone Layer
... partially melted or a raindrop turns back into ice as it is falling through the air. This happens when the layers of the atmosphere it passes through have different temperatures than the temperature where it was formed. (Sleet is usually tiny clear pellets) ...
... partially melted or a raindrop turns back into ice as it is falling through the air. This happens when the layers of the atmosphere it passes through have different temperatures than the temperature where it was formed. (Sleet is usually tiny clear pellets) ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Wave number: number of wave in a centimeter.from25000 for violet light, to 13.000 for red light. Ⅱ. Rays and Waves The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray method. ﹡ The fi ...
... Wave number: number of wave in a centimeter.from25000 for violet light, to 13.000 for red light. Ⅱ. Rays and Waves The path along which light travels are known as rays in a homogeneous medium, they are straight lines. ﹡The location and brightness of an image can be determined by ray method. ﹡ The fi ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.