Hands-on Activities with LEDs and Light
... Nevertheless it is necessary a theoretical framework as an introductory fundamental lesson-material for LEDs and their way of light emission ...
... Nevertheless it is necessary a theoretical framework as an introductory fundamental lesson-material for LEDs and their way of light emission ...
Scouting_Atmosphere
... Ridges: Warm air, usually moving from equator to pole. Associated with: tranquil weather, lighter winds, clearer skies, this is summer’s “heat dome”. Troughs: Cold air, usually moving from pole to equator. Associated with: disturbed weather, stronger winds, clouds, precipitation and “weather systems ...
... Ridges: Warm air, usually moving from equator to pole. Associated with: tranquil weather, lighter winds, clearer skies, this is summer’s “heat dome”. Troughs: Cold air, usually moving from pole to equator. Associated with: disturbed weather, stronger winds, clouds, precipitation and “weather systems ...
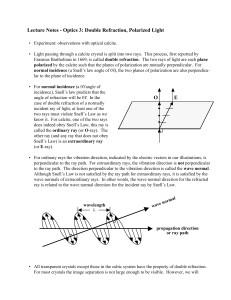
Lecture Notes - Optics 3: Double Refraction, Polarized Light E O
... observe other optical properties that result from the double refraction. For hexagonal and tetragonal crystals, there will be one O-ray and one E-ray. For orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic crystals, there will be two E-rays. In general, the refractive indices for non-cubic crystals depend on v ...
... observe other optical properties that result from the double refraction. For hexagonal and tetragonal crystals, there will be one O-ray and one E-ray. For orthorhombic, monoclinic, and triclinic crystals, there will be two E-rays. In general, the refractive indices for non-cubic crystals depend on v ...
METR215-lec1-introduction - Department of Meteorology and
... they have little effect on weather and other atmospheric processes. The variable components, which make up far less than 1 percent of the atmosphere, have a much greater influence on both short-term weather and long-term climate. For example, variations in water vapor in the atmosphere are familiar ...
... they have little effect on weather and other atmospheric processes. The variable components, which make up far less than 1 percent of the atmosphere, have a much greater influence on both short-term weather and long-term climate. For example, variations in water vapor in the atmosphere are familiar ...
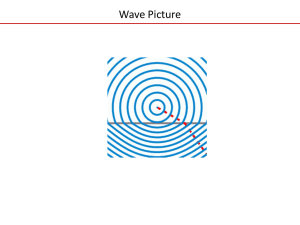
9-5 Huygens principle
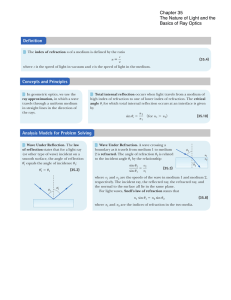
... Restatement of Fermat’s Principle Define the “optical path length” (OPL) to be the effective distance traveled by a light ray (if it travels through a dense material of index n the effective distance is n times greater than the actual distance) Small variations in the path taken by a light ray must ...
... Restatement of Fermat’s Principle Define the “optical path length” (OPL) to be the effective distance traveled by a light ray (if it travels through a dense material of index n the effective distance is n times greater than the actual distance) Small variations in the path taken by a light ray must ...
Introduction to light 2
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
Study guide_2
... 15. How is the retina like a “movie screen”? 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Troug ...
... 15. How is the retina like a “movie screen”? 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Troug ...
Meteorology MentorScienceOlympiad
... 39. Fog formed by cooling of the earth’s surface at night is A. Radiation fog B. Advection fog C. Steam fog D. Frontal Fog 40. Clouds that develop due to convective uplift are termed A. Stratiform B. Noctilucent C. Cumulus D. Lenticular 41. These are high clouds composed of ice crystals A. Cumulus B ...
... 39. Fog formed by cooling of the earth’s surface at night is A. Radiation fog B. Advection fog C. Steam fog D. Frontal Fog 40. Clouds that develop due to convective uplift are termed A. Stratiform B. Noctilucent C. Cumulus D. Lenticular 41. These are high clouds composed of ice crystals A. Cumulus B ...
Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... gradual changing density of the air throughout the atmosphere. Images of objects, close to the horizon, appear at a higher elevation that the real objects are. Atmospheric refraction is hardly noticeable at high viewing angles (e.g., near zenith). ...
... gradual changing density of the air throughout the atmosphere. Images of objects, close to the horizon, appear at a higher elevation that the real objects are. Atmospheric refraction is hardly noticeable at high viewing angles (e.g., near zenith). ...
PhysicsTutor
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
... from the top surface of the film with light reflected from the film-glass interface. • The number of phase jumps is the same for recombining beams (air to soap and soap to glass). • Find the optical path length difference between the two beams, phase shift of 2. ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.