Proposal and testing of dual-beam dynamic light
... First, it provides a microscopic probe to study the local properties of rheologically inhomogeneous samples. Second, it requires only a minuscule sample volume, making the technique particularly useful for biological samples that are difficult to obtain in large quantities. To fully utilize these ad ...
... First, it provides a microscopic probe to study the local properties of rheologically inhomogeneous samples. Second, it requires only a minuscule sample volume, making the technique particularly useful for biological samples that are difficult to obtain in large quantities. To fully utilize these ad ...
Sensitivity of Cirrus Bidirectional Reflectance to Vertical
... but irregular aggregates. The edges of these irregular ice crystals seem to be rounded, perhaps due to the effect of sublimation. Roughness can also be noted from the replicator images of the irregular ice crystals. In both images, it is apparent that the particles increase in size and the shapes be ...
... but irregular aggregates. The edges of these irregular ice crystals seem to be rounded, perhaps due to the effect of sublimation. Roughness can also be noted from the replicator images of the irregular ice crystals. In both images, it is apparent that the particles increase in size and the shapes be ...
Broadband Semiconductor Light Source for Optical Sensing
... Recently, this technology is applied positively in the field of medical diagnosis, and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)1), blood glucose level check 2), measurement of oxygen concentration in blood are studied. These studies are intended to image the state of insides of the living organisms or the ...
... Recently, this technology is applied positively in the field of medical diagnosis, and OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)1), blood glucose level check 2), measurement of oxygen concentration in blood are studied. These studies are intended to image the state of insides of the living organisms or the ...
Sorting by Periodic Potential Energy Landscapes: Optical
... the data in Fig. 2 as q(a) = 2(1 − vmin /u). Similarly, the separation between the depleted region ahead of the traps and the position of maximum occupancy is 2σ(a). From the histograms in Fig. 2(c) and (d), we obtain q(a) = 1.6 ± 0.1 and 0.9 ± 0.2, and σ(a) = 0.85 ± 0.07 µm and 0.58 ± 0.07 µm for t ...
... the data in Fig. 2 as q(a) = 2(1 − vmin /u). Similarly, the separation between the depleted region ahead of the traps and the position of maximum occupancy is 2σ(a). From the histograms in Fig. 2(c) and (d), we obtain q(a) = 1.6 ± 0.1 and 0.9 ± 0.2, and σ(a) = 0.85 ± 0.07 µm and 0.58 ± 0.07 µm for t ...
reflection and planar mirrors
... image are focused by the eye’s lens to produce a real image on the back surface of the eye. This is the image we “see.” 3e. Description of Plane Mirror Images. The image of an object in front of a plane mirror is virtual, upright, of the same size, and an equal distance from the mirror. The ratio of ...
... image are focused by the eye’s lens to produce a real image on the back surface of the eye. This is the image we “see.” 3e. Description of Plane Mirror Images. The image of an object in front of a plane mirror is virtual, upright, of the same size, and an equal distance from the mirror. The ratio of ...
State University of New York at New Paltz
... that given distance than the shorter wavelengths (see the wavelength diagram above). The number of waves over a given distance increases as the energy level increases. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths so they have the least amount of energy and the least number of waves over a given distance ...
... that given distance than the shorter wavelengths (see the wavelength diagram above). The number of waves over a given distance increases as the energy level increases. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths so they have the least amount of energy and the least number of waves over a given distance ...
Isolated hexaphenyl nanofibers as optical waveguides
... state, from which it relaxes predominantly into the first vibrationally excited level of the electronic ground state S 0 . A typical spectrum of the resulting luminescence at a transition wavelength of 425.5 nm measured at the tip of an individual fiber is shown in Fig. 2. Due to the homogeneity of ...
... state, from which it relaxes predominantly into the first vibrationally excited level of the electronic ground state S 0 . A typical spectrum of the resulting luminescence at a transition wavelength of 425.5 nm measured at the tip of an individual fiber is shown in Fig. 2. Due to the homogeneity of ...
To determine the wavelength of a monochromatic source of light
... 2. Light source and slit is arranged in order to get the maximum light incident on the slit. 3. The centre of slit, biprism and eye piece is arranged at same height as shown in Figure.1. 4. The slit and biprism edge are made vertical and in line parallel to the bench. 5. Observe the interference fri ...
... 2. Light source and slit is arranged in order to get the maximum light incident on the slit. 3. The centre of slit, biprism and eye piece is arranged at same height as shown in Figure.1. 4. The slit and biprism edge are made vertical and in line parallel to the bench. 5. Observe the interference fri ...
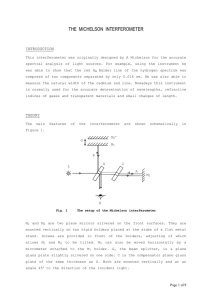
Michelson Interferometer
... at their focal points on the eye retina. Since for fixed d and λ and different values of m, a system of dark and bright circle concentric fringes each corresponding to a constant θ will be observed, such interference fringes are therefore known as fringes of equal inclination. They are localized at ...
... at their focal points on the eye retina. Since for fixed d and λ and different values of m, a system of dark and bright circle concentric fringes each corresponding to a constant θ will be observed, such interference fringes are therefore known as fringes of equal inclination. They are localized at ...
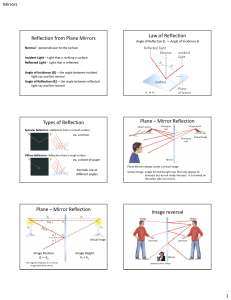
Physics for Scientists & Geometric Optics
... ! Images formed by plane mirrors appear to be reversed because the light rays incident on the surface of the mirror are reflected back on the other side of the normal di do ! A mirror image looks correct vertically ...
... ! Images formed by plane mirrors appear to be reversed because the light rays incident on the surface of the mirror are reflected back on the other side of the normal di do ! A mirror image looks correct vertically ...
Coherence properties of sunlight
... degree of coherence of the f ield generated by an incoherent source takes on its far-zone behavior at distances immediately beyond the near zone of the source and well before one reaches the traditionally def ined far-zone limit. We have performed calculations of the degree of coherence for sources ...
... degree of coherence of the f ield generated by an incoherent source takes on its far-zone behavior at distances immediately beyond the near zone of the source and well before one reaches the traditionally def ined far-zone limit. We have performed calculations of the degree of coherence for sources ...
Experience with optical partial discharge detection M. M ,
... The UV channel works within the so-called sun blind range from 240 nm to 280 nm of ...
... The UV channel works within the so-called sun blind range from 240 nm to 280 nm of ...
Effective refractive index for determining ray propagation in an
... A number of methods have been developed to solve for the single-scattering properties of micron-sized nonspherical particles that are present in nature (e.g., ice crystals within cirrus clouds) [1]. When a particle is much larger than the incident wavelength, the ray-tracing technique based on the p ...
... A number of methods have been developed to solve for the single-scattering properties of micron-sized nonspherical particles that are present in nature (e.g., ice crystals within cirrus clouds) [1]. When a particle is much larger than the incident wavelength, the ray-tracing technique based on the p ...
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.