I. Introduction - ER Publications
... Optical wireless system and FSO links provide higher performance to the communication system.FSO links improve data rate transmission and overall SNR of the system for deep-space communication applications. The most important parameter for an optical system is low weight and coast of system are impr ...
... Optical wireless system and FSO links provide higher performance to the communication system.FSO links improve data rate transmission and overall SNR of the system for deep-space communication applications. The most important parameter for an optical system is low weight and coast of system are impr ...
Physics 44
... first pass through a narrow slit. Then, the light that passes through the grating or prism is an image of the slit and so an image of the slit will be seen at each wavelength. Since the slit is narrow, there will be minimal overlap of the images at neighboring wavelengths. The separate wavelengths c ...
... first pass through a narrow slit. Then, the light that passes through the grating or prism is an image of the slit and so an image of the slit will be seen at each wavelength. Since the slit is narrow, there will be minimal overlap of the images at neighboring wavelengths. The separate wavelengths c ...
Two-state Optical Filter Based on Micromechanical
... The two-state CDOE can be viewed as grating light valves operated in a high (m > 1) diffraction order. Reducing the light intensity at one wavelength will increase the intensity at the neighboring wavelengths (side-bands). The principle is shown in Figure 1 with four sub-elements, and diffraction or ...
... The two-state CDOE can be viewed as grating light valves operated in a high (m > 1) diffraction order. Reducing the light intensity at one wavelength will increase the intensity at the neighboring wavelengths (side-bands). The principle is shown in Figure 1 with four sub-elements, and diffraction or ...
2.2 Basic Optical Laws and Definitions
... ¾ Condition of wave propagation : All points on the same phase front (wave front) of a plane wave must be in phase ¾ That means: Phase change between the two different tracings with same phase front must be an integer multiple of 2π ¾ Wavefront : The surfaces joining all points of equal phase are kn ...
... ¾ Condition of wave propagation : All points on the same phase front (wave front) of a plane wave must be in phase ¾ That means: Phase change between the two different tracings with same phase front must be an integer multiple of 2π ¾ Wavefront : The surfaces joining all points of equal phase are kn ...
The retrieval of ozone`s absorption coefficient in the stratosphere
... comes to multiple scattering environments with complex geometric configurations [7]. Ultimately, the Fourier series depicts another attempt to solve the ETR. Although it is mathematically complicated, it only concludes that it is possible to apply Fourier series in the radiative transfer calculation ...
... comes to multiple scattering environments with complex geometric configurations [7]. Ultimately, the Fourier series depicts another attempt to solve the ETR. Although it is mathematically complicated, it only concludes that it is possible to apply Fourier series in the radiative transfer calculation ...
Resource Doc File - Dayton Regional Stem Center
... NOTE: The Guided Research is used to get the students accustomed to the vocabulary and information they will be learning about in this STEM lesson. Therefore the grading of this assignment is very subjective. As a suggestion, a student could receive a score of 20 points for completing the entire ass ...
... NOTE: The Guided Research is used to get the students accustomed to the vocabulary and information they will be learning about in this STEM lesson. Therefore the grading of this assignment is very subjective. As a suggestion, a student could receive a score of 20 points for completing the entire ass ...
Optical Instruments
... (Fig. 4.9). The incident rays from the collimator are falling more obliquely on the prism. The telescope is focussed so that the image is sharp and there is no parallax between the image and the cross-wires. In this case the rays coming out of the prism become more parallel. Keeping the position of ...
... (Fig. 4.9). The incident rays from the collimator are falling more obliquely on the prism. The telescope is focussed so that the image is sharp and there is no parallax between the image and the cross-wires. In this case the rays coming out of the prism become more parallel. Keeping the position of ...
Experiment VI Polarized Light
... about 180o. If the variation in beam intensity is less than about 10%, then no further alignment will be needed. Otherwise set the polarizer at 0o and rotate the quarter wave plate for the lowest power reading on the Logger Pro plot. Again, rotate the “analyzing polarizer” back and forth, just to ch ...
... about 180o. If the variation in beam intensity is less than about 10%, then no further alignment will be needed. Otherwise set the polarizer at 0o and rotate the quarter wave plate for the lowest power reading on the Logger Pro plot. Again, rotate the “analyzing polarizer” back and forth, just to ch ...
Surface-plasmon-polariton-induced suppressed
... the metal disk array, compared with the closed film, will transmit more light. However, we emphasize that the measurement demonstrates less light transmitted through the array of gold disks. When p or r is varied, the resonant wavelength changes slightly, as does the transmittance. The resonant wave ...
... the metal disk array, compared with the closed film, will transmit more light. However, we emphasize that the measurement demonstrates less light transmitted through the array of gold disks. When p or r is varied, the resonant wavelength changes slightly, as does the transmittance. The resonant wave ...
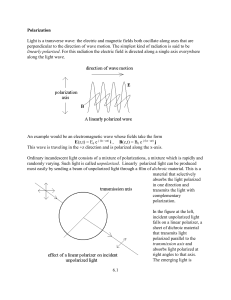
Polarization
... Laser light (peak wavelength = 650 nm) is passed through two polarizers. As the second polarizer (the analyzer) is rotated by hand, the relative light intensity is recorded as a function of the angle between the axes of polarization of the two polarizers. The angle is obtained using a Rotary Motion ...
... Laser light (peak wavelength = 650 nm) is passed through two polarizers. As the second polarizer (the analyzer) is rotated by hand, the relative light intensity is recorded as a function of the angle between the axes of polarization of the two polarizers. The angle is obtained using a Rotary Motion ...
prezantacia aj
... much smaller core that only allows light rays to travel along one mode inside the fiber. Every fiber-optic cable used for networking consists of two glass fibers encased in separate sheaths. One fiber carries transmitted data from device A to device B. The second fiber carries data from device B to ...
... much smaller core that only allows light rays to travel along one mode inside the fiber. Every fiber-optic cable used for networking consists of two glass fibers encased in separate sheaths. One fiber carries transmitted data from device A to device B. The second fiber carries data from device B to ...
LM Ch 4: Optics
... because the ray is striking the lens at an angle far from the normal do to the curvature of the lens. We will discuss Snell’s law of refraction later. A second ray hitting the lens somewhere between the first two will be refracted more than the center ray but less than the peripheral ray. This pheno ...
... because the ray is striking the lens at an angle far from the normal do to the curvature of the lens. We will discuss Snell’s law of refraction later. A second ray hitting the lens somewhere between the first two will be refracted more than the center ray but less than the peripheral ray. This pheno ...
ETM4106Tutorial3
... which give an attenuation of 0.8 dB each. Determine the minimum mean optical power, which must be launched into the fiber in order to maintain a mean optical power level of 0.30 W at the detector. Ans. 703 W. Q.4 Determine the theoretical attenuation in decibels per km due to the Rayleight scatt ...
... which give an attenuation of 0.8 dB each. Determine the minimum mean optical power, which must be launched into the fiber in order to maintain a mean optical power level of 0.30 W at the detector. Ans. 703 W. Q.4 Determine the theoretical attenuation in decibels per km due to the Rayleight scatt ...
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors
... which the reflecting surface is caved in Another name for the concave mirror is a CONVERGING MIRROR. ...
... which the reflecting surface is caved in Another name for the concave mirror is a CONVERGING MIRROR. ...
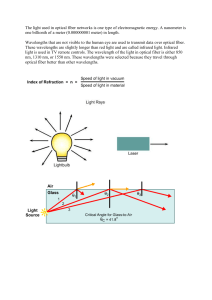
Atmospheric optics

Atmospheric optics deals with how the unique optical properties of the Earth's atmosphere cause a wide range of spectacular optical phenomena. The blue color of the sky is a direct result of Rayleigh scattering which redirects higher frequency (blue) sunlight back into the field of view of the observer. Because blue light is scattered more easily than red light, the sun takes on a reddish hue when it is observed through a thick atmosphere, as during a sunrise or sunset. Additional particulate matter in the sky can scatter different colors at different angles creating colorful glowing skies at dusk and dawn. Scattering off of ice crystals and other particles in the atmosphere are responsible for halos, afterglows, coronas, rays of sunlight, and sun dogs. The variation in these kinds of phenomena is due to different particle sizes and geometries.Mirages are optical phenomena in which light rays are bent due to thermal variations in the refraction index of air, producing displaced or heavily distorted images of distant objects. Other optical phenomena associated with this include the Novaya Zemlya effect where the sun appears to rise earlier or set later than predicted with a distorted shape. A spectacular form of refraction occurs with a temperature inversion called the Fata Morgana where objects on the horizon or even beyond the horizon, such as islands, cliffs, ships or icebergs, appear elongated and elevated, like ""fairy tale castles"".Rainbows are the result of a combination of internal reflection and dispersive refraction of light in raindrops. Because rainbows are seen on the opposite side of the sky as the sun, rainbows are more prominent the closer the sun is to the horizon due to their greater distance apart.