View PDF
... What about ruled vs holographic gratings? For ruled gratings, blaze wavelength is where you get highest reflectivity Typically use holographic grating when groove density of 1200 g/mm or higher is required in UV-VIS-NIR applications ...
... What about ruled vs holographic gratings? For ruled gratings, blaze wavelength is where you get highest reflectivity Typically use holographic grating when groove density of 1200 g/mm or higher is required in UV-VIS-NIR applications ...
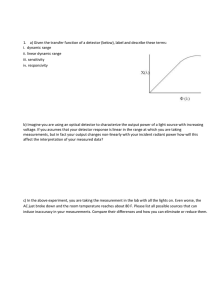
a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and
... 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity ...
... 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity ...
Excited Elements - Light Emission Spectroscopy
... gas-filled glass tube. Gases under low pressure and excited by an electrical discharge give off light in characteristic wavelengths. The emitted light is passed through a spectroscope, which breaks light into its components for analysis. A gas viewed through a spectroscope, such as the one shown in ...
... gas-filled glass tube. Gases under low pressure and excited by an electrical discharge give off light in characteristic wavelengths. The emitted light is passed through a spectroscope, which breaks light into its components for analysis. A gas viewed through a spectroscope, such as the one shown in ...
Document
... detectors to detect them Calorimetry does not work – muons only leave small energy in the calorimeter (said to be “minimum ionization particles”) Muons are detected outside calorimeters and additional shielding, where all other particles (except neutrinos) have already been stopped As this is far ...
... detectors to detect them Calorimetry does not work – muons only leave small energy in the calorimeter (said to be “minimum ionization particles”) Muons are detected outside calorimeters and additional shielding, where all other particles (except neutrinos) have already been stopped As this is far ...
RADIOMETRY - gamma
... Radiant Exitance, a property of the light source, is the total radiant flux from the source divided by the surface area of the source. Its unit of measure is watt/m2, simplified as watt/cm2. This type of measurement only applies to extended light sources and is useful for making efficiency measureme ...
... Radiant Exitance, a property of the light source, is the total radiant flux from the source divided by the surface area of the source. Its unit of measure is watt/m2, simplified as watt/cm2. This type of measurement only applies to extended light sources and is useful for making efficiency measureme ...
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - An introduction
... variations in the band bending and, thus, the work function will vary from point to point. This variation in surface potential produces a broadening of the XPS peaks. -Excitation process such as the shake-up/shake-off processes or vibrational broadening. ...
... variations in the band bending and, thus, the work function will vary from point to point. This variation in surface potential produces a broadening of the XPS peaks. -Excitation process such as the shake-up/shake-off processes or vibrational broadening. ...
Student 5
... What conclusions were made about the atom from Rutherford’s gold leaf experiment? Rutherford fired a beam of alpha particles at thin gold foil. The alpha particles were from a radioactive source, in an evacuated container. A scintillation detector then rotated around the container was used to pick u ...
... What conclusions were made about the atom from Rutherford’s gold leaf experiment? Rutherford fired a beam of alpha particles at thin gold foil. The alpha particles were from a radioactive source, in an evacuated container. A scintillation detector then rotated around the container was used to pick u ...
e + + e
... C) Neutrons – during reactions with nuclei (strong interaction) further particles (also charged) are emmited D) Neutrina – only weak interaction → only very small cross sections of interaction with matter. These interactions, which convert kinetic particle energy to electrons created by ionization, ...
... C) Neutrons – during reactions with nuclei (strong interaction) further particles (also charged) are emmited D) Neutrina – only weak interaction → only very small cross sections of interaction with matter. These interactions, which convert kinetic particle energy to electrons created by ionization, ...
File - Ms M - EARL MARRIOTT SECONDARY
... Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleus as radiation. Radioactive atoms release energy until they become stable, often as different atoms. An element may have only certain isotopes that are radioactive. These are called radioisotopes. Rutherford identified three types of radiation using ...
... Radioactive decay releases energy from the nucleus as radiation. Radioactive atoms release energy until they become stable, often as different atoms. An element may have only certain isotopes that are radioactive. These are called radioisotopes. Rutherford identified three types of radiation using ...
Wales Research and Diagnostic Positron Emission Tomography
... • SynApSPECT (Synthetic Aperture SPECT) includes: base with interchangeable apertures – incl’ multiple pinhole apertures proprietary reconstruction software better resolution than the size of the pinholes high sensitivity; significant reduction in acquisition time or delivered dose. two focal length ...
... • SynApSPECT (Synthetic Aperture SPECT) includes: base with interchangeable apertures – incl’ multiple pinhole apertures proprietary reconstruction software better resolution than the size of the pinholes high sensitivity; significant reduction in acquisition time or delivered dose. two focal length ...
Field and particle pictures advance notice article - Specimen
... 10 Fig. 1 is obtained. This is exactly what would be expected: each decay liberates the same amount of energy, and conservation of momentum allows only one way for the sharing of this energy. Nearly all the energy is given to the alpha particles, which all emerge with the same energy of 5.4 MeV. ...
... 10 Fig. 1 is obtained. This is exactly what would be expected: each decay liberates the same amount of energy, and conservation of momentum allows only one way for the sharing of this energy. Nearly all the energy is given to the alpha particles, which all emerge with the same energy of 5.4 MeV. ...
A full Monte Carlo simulation code for silicon strip detectors
... We have developed a new MC full simulation code that includes all the physical processes taking place in a SSD The MC code can be used with different detector geometries and front-end electronics The temperature dependence of the physical processes is taken into account, thus allowing a study ...
... We have developed a new MC full simulation code that includes all the physical processes taking place in a SSD The MC code can be used with different detector geometries and front-end electronics The temperature dependence of the physical processes is taken into account, thus allowing a study ...
The Influence of Detector Active Area on Sensitivity and Noise
... sensitivity of any point on the detector, including the case, the wire connections (which also have some radiation sensitivity), etc. In short, no statement of "true responsivity" should be made without reference to experimental data. ...
... sensitivity of any point on the detector, including the case, the wire connections (which also have some radiation sensitivity), etc. In short, no statement of "true responsivity" should be made without reference to experimental data. ...
PPT
... For spectroscopy it is placed at the image plane of a spectrometer to allow a range of wavelengths to be detected simultaneously. In this regard it can be thought of as an electronic version of photographic film. Array detectors are especially useful for recording the full uv-vis absorption spectra ...
... For spectroscopy it is placed at the image plane of a spectrometer to allow a range of wavelengths to be detected simultaneously. In this regard it can be thought of as an electronic version of photographic film. Array detectors are especially useful for recording the full uv-vis absorption spectra ...
Notes - Science With Horne
... The total of the atomic masses (superscripts) on the left side of the equation must equal the sum of the atomic masses on the right side. After completing the equation by writing all the nuclear particles in an atomic notation, a coefficient may be necessary to balance the reaction. Use a particle o ...
... The total of the atomic masses (superscripts) on the left side of the equation must equal the sum of the atomic masses on the right side. After completing the equation by writing all the nuclear particles in an atomic notation, a coefficient may be necessary to balance the reaction. Use a particle o ...
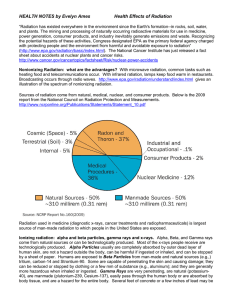
Health Effects of Radiation
... more hazardous when inhaled or ingested. Gamma Rays are very penetrating, are natural (potassium40), are manmade (plutonium-239, Cesium-137), easily pass through the human body or are absorbed by body tissue, and are a hazard for the entire body. Several feet of concrete or a few inches of lead may ...
... more hazardous when inhaled or ingested. Gamma Rays are very penetrating, are natural (potassium40), are manmade (plutonium-239, Cesium-137), easily pass through the human body or are absorbed by body tissue, and are a hazard for the entire body. Several feet of concrete or a few inches of lead may ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.