Nuclear Stability
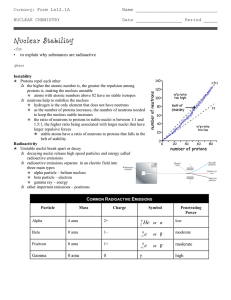
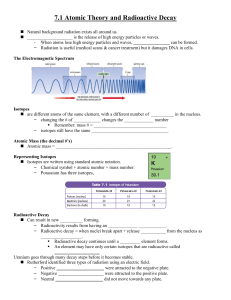
... protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons needed to keep the nucleus stable incr ...
... protons is, making the nucleus unstable p atoms with atomic numbers above 82 have no stable isotopes q neutrons help to stabilize the nucleus p hydrogen is the only element that does not have neutrons p as the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons needed to keep the nucleus stable incr ...
Teaching program
... with your class. Assume that your class wants to do Synchrotron and applications as its detailed study. You could start with Electric Power and then link the detailed study to the Interaction of light and ...
... with your class. Assume that your class wants to do Synchrotron and applications as its detailed study. You could start with Electric Power and then link the detailed study to the Interaction of light and ...
Infrared Spectrometry
... Now single channel infrared spectrometers are extinct, and multichannel infrared spectrometers have not yet been perfected. Fourier transform infrared spectrometers rule this region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The UV/Vis instruments discussed thus far work in the frequency domain. That is, the ...
... Now single channel infrared spectrometers are extinct, and multichannel infrared spectrometers have not yet been perfected. Fourier transform infrared spectrometers rule this region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The UV/Vis instruments discussed thus far work in the frequency domain. That is, the ...
Silicon Detectors in Particle Physics
... a) electrons used for particle detection (temporarily effects only) b) atoms of the detector permanent changes (defects) in the detector bulk. A displaced silicon atom produces an empty space in the lattice (Vacancy, V) and in another place an atom in an inter lattice space (Interstitial, I). ...
... a) electrons used for particle detection (temporarily effects only) b) atoms of the detector permanent changes (defects) in the detector bulk. A displaced silicon atom produces an empty space in the lattice (Vacancy, V) and in another place an atom in an inter lattice space (Interstitial, I). ...
Microsoft Word Format - University of Toronto Physics
... The radioactive source used in this experiment must not be touched in any way. If you suspect the source has been damaged, consult a Professor or Technologist immediately. The box containing the source, absorber, and detector must not be opened except under the supervision of a Professor or Tech ...
... The radioactive source used in this experiment must not be touched in any way. If you suspect the source has been damaged, consult a Professor or Technologist immediately. The box containing the source, absorber, and detector must not be opened except under the supervision of a Professor or Tech ...
Uses of Ionising and Non-Ionising Radiation
... radiation concentrates with it. Radiation detectors placed outside the body detect the radiation emitted and, with the aid of computers, build up an image of the inside of the body. When a radioactive chemical is used in this way it is not normally harmful, because: it has a short half-life and so d ...
... radiation concentrates with it. Radiation detectors placed outside the body detect the radiation emitted and, with the aid of computers, build up an image of the inside of the body. When a radioactive chemical is used in this way it is not normally harmful, because: it has a short half-life and so d ...
Gamma spectroscopy

Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, in such as the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just as in optical spectroscopy, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample.