Chapter 2
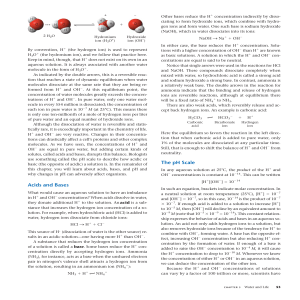
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... All covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons; however, the electrons that are shared are not shared equally in all cases. Unequal sharing results when a pair of shared electrons spends more time ...
... All covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons; however, the electrons that are shared are not shared equally in all cases. Unequal sharing results when a pair of shared electrons spends more time ...
Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... human blood and many other biological solutions. One of these is carbonic acid (H2CO3), formed when CO2 reacts with water in blood plasma. As mentioned earlier, carbonic acid dissociates to yield a bicarbonate ion (HCO3") and a hydrogen ion (H!): ...
... human blood and many other biological solutions. One of these is carbonic acid (H2CO3), formed when CO2 reacts with water in blood plasma. As mentioned earlier, carbonic acid dissociates to yield a bicarbonate ion (HCO3") and a hydrogen ion (H!): ...
Hydrogen Sulfide in Nitrogen 0.0001% to 5.0%
... rate of product from the cylinder. Use a check valve or trap in the discharge line to prevent hazardous back flow into the cylinder. Protect cylinders from physical damage. Store in cool, dry, well-ventilated area of non-combustible construction away from heavy traffic areas and emergency exits. Do ...
... rate of product from the cylinder. Use a check valve or trap in the discharge line to prevent hazardous back flow into the cylinder. Protect cylinders from physical damage. Store in cool, dry, well-ventilated area of non-combustible construction away from heavy traffic areas and emergency exits. Do ...
Atomic Theories and Models - MrD-Home
... The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ______ yet properly balanced because the atoms of the elements on the product side do not ______ the atoms of each element on the reactant side of the equation. The _________________________, which states that matter can neither be ____ ...
... The chemical equation for the reaction of methane and oxygen is ______ yet properly balanced because the atoms of the elements on the product side do not ______ the atoms of each element on the reactant side of the equation. The _________________________, which states that matter can neither be ____ ...
Chapter 2 - OrgSites.com
... 26. The R-groups of amino acids are important in determining the structure and function of proteins. R-group Elements (element groups) How this property could affect structure/function of properties that appear to give them part of protein that the amino acid is in (e.g. their properties hyrodophili ...
... 26. The R-groups of amino acids are important in determining the structure and function of proteins. R-group Elements (element groups) How this property could affect structure/function of properties that appear to give them part of protein that the amino acid is in (e.g. their properties hyrodophili ...
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and
... factories, automobiles, power plants and other waste vents. In addition, fossil fuel resources doesn't guarantee a sustainable future of energy which indicates even more the importance of finding alternative, sustainable, eco-friendly and cost-effective sources. For this purpose, this study was cond ...
... factories, automobiles, power plants and other waste vents. In addition, fossil fuel resources doesn't guarantee a sustainable future of energy which indicates even more the importance of finding alternative, sustainable, eco-friendly and cost-effective sources. For this purpose, this study was cond ...
Chemical Equations
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compound. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
... Reaction Types: Synthesis or Composition • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compound. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction ...
How to balance chemical equations File
... That should do it. Do a check to be sure: You have 2 nitrogen atoms on the left and 2 nitrogen atoms on the right. You have 6 hydrogen atoms on the left and 6 hydrogen atoms on the right. The equation is balanced. You can read the equation this way: 1 nitrogen molecule reacts with 3 hydrogen molecul ...
... That should do it. Do a check to be sure: You have 2 nitrogen atoms on the left and 2 nitrogen atoms on the right. You have 6 hydrogen atoms on the left and 6 hydrogen atoms on the right. The equation is balanced. You can read the equation this way: 1 nitrogen molecule reacts with 3 hydrogen molecul ...
Word and Skeleton Equations Practice (ws Fall 2010)
... hydrogen, H2(g); nitrogen, N2(g); oxygen O2(g); fluorine, F2(g); chlorine Cl2(g); bromine, Br2(l); and iodine, I2(s). 1. Gaseous hydrogen and oxygen react to form gaseous water. 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid ...
... hydrogen, H2(g); nitrogen, N2(g); oxygen O2(g); fluorine, F2(g); chlorine Cl2(g); bromine, Br2(l); and iodine, I2(s). 1. Gaseous hydrogen and oxygen react to form gaseous water. 2. Solid sodium metal reacts with liquid water to form an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide and hydrogen gas. 3. Solid ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... Properties of Water - the boiling point and melting points are higher in water than other similar substances – the need to break the hydrogen bonds - it requires a great deal of energy to raise the temperature of water – strong intermolecular forces - has a concave meniscus and shows capillary actio ...
... Properties of Water - the boiling point and melting points are higher in water than other similar substances – the need to break the hydrogen bonds - it requires a great deal of energy to raise the temperature of water – strong intermolecular forces - has a concave meniscus and shows capillary actio ...
(S-Benzylthiuronium) Chloranilate Supramolecular Crystal Structure
... populated areas of SBT-cations. Each CA-dianion forms eight hydrogen bonds with the amine protons of six SBT-cations, through its oxygen atoms. In this way, an extended H-bond network, containing infinite chains of alternative R42(8) and R22(9) cyclic patterns, is obtained. The whole arrangement lea ...
... populated areas of SBT-cations. Each CA-dianion forms eight hydrogen bonds with the amine protons of six SBT-cations, through its oxygen atoms. In this way, an extended H-bond network, containing infinite chains of alternative R42(8) and R22(9) cyclic patterns, is obtained. The whole arrangement lea ...
8F Compounds and Mixtures
... 2. Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to make magnesium chloride and hydrogen. magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen ...
... 2. Magnesium reacts with hydrochloric acid to make magnesium chloride and hydrogen. magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen ...
AP Chap 2
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
... In biological elements, remember electrons are filled in shells in the following order: ...
9791/02 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... In 2011 xenon dioxide, XeO2, was synthesised for the first time (reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society). Xenon dioxide exists as a polymer in which the oxygen atoms are bonded to xenon in a square planar arrangement. Work out the number of ...
... In 2011 xenon dioxide, XeO2, was synthesised for the first time (reported in the Journal of the American Chemical Society). Xenon dioxide exists as a polymer in which the oxygen atoms are bonded to xenon in a square planar arrangement. Work out the number of ...
Compounds
... 1. How many sulfur atoms are in 0.25 moles of Sulfur? 2. How many moles of boron are in 3.79x1024 atoms of Boron? 3. What is the molar mass of N2O5? 4. How many grams are in 1.34 moles of Aspirin (C9H8O4)? 5. How many grams are in a 10 L tank of Propane (C3H8) at STP? 6. How many atoms of sulfur are ...
... 1. How many sulfur atoms are in 0.25 moles of Sulfur? 2. How many moles of boron are in 3.79x1024 atoms of Boron? 3. What is the molar mass of N2O5? 4. How many grams are in 1.34 moles of Aspirin (C9H8O4)? 5. How many grams are in a 10 L tank of Propane (C3H8) at STP? 6. How many atoms of sulfur are ...
File
... • Chlorine accepts extra electron to be more stable Cl(Note: there is a size change when atoms form ions.) After such a transfer, the chlorine atom has net negative charge, while sodium atom has net positive charge. In sodium chloride (NaCl), all sodium and chloride atoms exist as ions. ...
... • Chlorine accepts extra electron to be more stable Cl(Note: there is a size change when atoms form ions.) After such a transfer, the chlorine atom has net negative charge, while sodium atom has net positive charge. In sodium chloride (NaCl), all sodium and chloride atoms exist as ions. ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
Equilibrium Constant- Keq
... c) Calculate the equilibrium constant d) Describe the percent reaction. 4. Hydrogen Chloride is produced from hydrogen and chlorine gases. At equilibrium, the hydrogen concentration is 0.12 mol/L and chlorine is 0.10 mol/L. Find the concentration of the hydrogen chloride if the equilibrium constant ...
... c) Calculate the equilibrium constant d) Describe the percent reaction. 4. Hydrogen Chloride is produced from hydrogen and chlorine gases. At equilibrium, the hydrogen concentration is 0.12 mol/L and chlorine is 0.10 mol/L. Find the concentration of the hydrogen chloride if the equilibrium constant ...
7 - Mona Shores Blogs
... 47. When the species F¯, Na+, and Ne are arranged in order of increasing energy for the removal of an electron, what is the correct order? (A) F¯ < Na+ < Ne (B) F¯ < Ne < Na+ (C) Na+ < Ne < F¯ (D) Ne < F¯ < Na+ 48. Which electronic transition in a hydrogen atom occurs with an energy that corresponds ...
... 47. When the species F¯, Na+, and Ne are arranged in order of increasing energy for the removal of an electron, what is the correct order? (A) F¯ < Na+ < Ne (B) F¯ < Ne < Na+ (C) Na+ < Ne < F¯ (D) Ne < F¯ < Na+ 48. Which electronic transition in a hydrogen atom occurs with an energy that corresponds ...
Lecture 11 - AP Chem Solutions
... 2) A potassium hydroxide solution is mixed with a solution of zinc nitrate. The potassium ion is always soluble as it is a Group 1A element. Nitrate is also soluble with everything. Thus, K+ and NO3- must be spectator ions. Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Æ Zn(OH)2(s) 3) A solution of lead (II) nitrate is pour ...
... 2) A potassium hydroxide solution is mixed with a solution of zinc nitrate. The potassium ion is always soluble as it is a Group 1A element. Nitrate is also soluble with everything. Thus, K+ and NO3- must be spectator ions. Zn2+(aq) + 2 OH-(aq) Æ Zn(OH)2(s) 3) A solution of lead (II) nitrate is pour ...
12.3 - heoldduscience
... materials that end up as useful products. It is important for sustainable development and economical reasons that industrial reactions have High Atom Economy. ...
... materials that end up as useful products. It is important for sustainable development and economical reasons that industrial reactions have High Atom Economy. ...
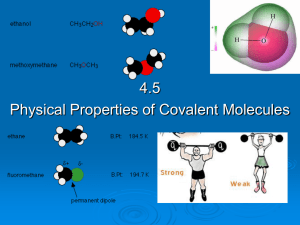
4.5 Physical properties of molecular covalent
... Physical properties are governed by the intermolecular forces a) van der Waals (non-polar covalent molecules) b) permanent dipole-permanent dipole (the strongest IMF found in polar covalent molecules) c) hydrogen bonds (found in polar covalent molecules with O-H, F-H and N-H bonds) All molecules con ...
... Physical properties are governed by the intermolecular forces a) van der Waals (non-polar covalent molecules) b) permanent dipole-permanent dipole (the strongest IMF found in polar covalent molecules) c) hydrogen bonds (found in polar covalent molecules with O-H, F-H and N-H bonds) All molecules con ...
makeup2
... (B) the atoms in CO2 are bound by covalent bonds while SiO2 is an ionic compound (C) van der Waals' forces are stronger in SiO2 (D) CO2 consists of discrete molecules while in SiO2 atoms are joined by a network of covalent bonds 69. 2.00 moles of NO and an undetermined amount of O2 are placed in a o ...
... (B) the atoms in CO2 are bound by covalent bonds while SiO2 is an ionic compound (C) van der Waals' forces are stronger in SiO2 (D) CO2 consists of discrete molecules while in SiO2 atoms are joined by a network of covalent bonds 69. 2.00 moles of NO and an undetermined amount of O2 are placed in a o ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.