Elements (NonMetals)
... Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small radius Unique properties of both group 1 and 17 Bond energy 431kJ/mol – very st ...
... Gas at room Temp B.P. –253°C (20K) and M.P.-259°C (14K) Insoluble in water: 2mL gas/ 1L of water Found in H2O, organic and biological molecules Most common element in universe H2 (H-H) isoelectronic with He H has a small radius Unique properties of both group 1 and 17 Bond energy 431kJ/mol – very st ...
$doc.title
... hydrogen atoms (and likewise the number of oxygen atoms), on the right side of the arrow. Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain chemical properties. Atoms are not visible under normal circumstances. Avogadro’s hypothesis allows us to relate the number of atoms (or molecules) to the mass ...
... hydrogen atoms (and likewise the number of oxygen atoms), on the right side of the arrow. Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain chemical properties. Atoms are not visible under normal circumstances. Avogadro’s hypothesis allows us to relate the number of atoms (or molecules) to the mass ...
The structure of Matter
... O Atoms will form either IONIC or COVALENT bonds. O The way that an atom bonds determines many of its properties. ...
... O Atoms will form either IONIC or COVALENT bonds. O The way that an atom bonds determines many of its properties. ...
Unit 1 Powerpoint
... Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with personal biases may or may not be in the public interest. But if enough of us underst ...
... Science aims to be objective, but scientists are human, too. Sometimes scientific data can be misinterpreted or misapplied by scientists who want to prove a particular point. Recommendations made by scientists with personal biases may or may not be in the public interest. But if enough of us underst ...
Practice Exam-Final Fall 2016 W-Ans
... 16. How many hydrogen atoms are there in 48.0 g of CH4? (a) 1.81x1023 (b) 7.22x1024 (c) 6.02x1023 (d) 1.20x1025 (e) 4.70x1025 Hint: According to the chemical formula, one mole of CH4 contains 1 mole of C atoms and 4 moles of hydrogen atoms. Thus, the mole of H = 4 x {mass of CH4/molar mass of CH4}. ...
... 16. How many hydrogen atoms are there in 48.0 g of CH4? (a) 1.81x1023 (b) 7.22x1024 (c) 6.02x1023 (d) 1.20x1025 (e) 4.70x1025 Hint: According to the chemical formula, one mole of CH4 contains 1 mole of C atoms and 4 moles of hydrogen atoms. Thus, the mole of H = 4 x {mass of CH4/molar mass of CH4}. ...
Chapter1011
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
... • Use valence bond theory to describe the bonding in the following (use clear 3-D pictures showing orbital overlap, etc) H2O NH3 CH4 PF3 --simple s bonds and lone pairs H2CNH --double bond like H2CCH2 ethene and H2CO formaldehyde) HCN --triple bond like HCCH ethyne and N2 nitrogen) ...
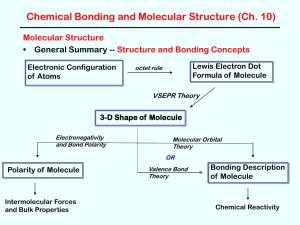
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
... Acids: anything giving H+ when dissolved in water Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not ...
Preparation and Properties of Hydrogen
... hydrogen will float. Because of the hydrogen molecule's small size, it will diffuse through many substances. Hydrogen gas is extremely flammable and will react with oxygen to form water with a release of a great deal of heat. The Hindenburg Zeppelin was destroyed in 1937 because of this reaction. He ...
... hydrogen will float. Because of the hydrogen molecule's small size, it will diffuse through many substances. Hydrogen gas is extremely flammable and will react with oxygen to form water with a release of a great deal of heat. The Hindenburg Zeppelin was destroyed in 1937 because of this reaction. He ...
Teacher Demo/Student Activity: Elephant`s Toothpaste
... compounds (e.g., carbon dioxide, CO2, has one more oxygen atom than carbon monoxide, CO) C3.2 name and write the formulae for simple ionic and molecular compounds (e.g., NaCl, NaOH, H2O, CO2) C3.3 write word equations and balanced chemical equations for simple chemical reactions (e.g., 2 H2 + O2 → 2 ...
... compounds (e.g., carbon dioxide, CO2, has one more oxygen atom than carbon monoxide, CO) C3.2 name and write the formulae for simple ionic and molecular compounds (e.g., NaCl, NaOH, H2O, CO2) C3.3 write word equations and balanced chemical equations for simple chemical reactions (e.g., 2 H2 + O2 → 2 ...
Click here to Ch 06.2 Covalent Bonding_Lewis Structures
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
... electrons, and for those that can fit more than eight electrons, into their outermost orbital. • Hydrogen forms bonds in which it is surrounded by only two electrons. • Boron has just three valence electrons, so it tends to form bonds in which it is surrounded by six electrons. ...
chapter_2_2009
... Components are distributed equally throughout. The process of making a solution is called dissolving. The solvent is the substance present in the largest amount. Frequently a liquid The solutes are the substances present in smaller amounts. ...
... Components are distributed equally throughout. The process of making a solution is called dissolving. The solvent is the substance present in the largest amount. Frequently a liquid The solutes are the substances present in smaller amounts. ...
Chapter 30 - The Chemical Basis of Animal Life
... When an atom either gains or loses electrons, it acquires an electrical charge and is called an ion (Gr. ion, going). If an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged because more positively charged protons are now in the nucleus than negatively charged electrons surrounding the ...
... When an atom either gains or loses electrons, it acquires an electrical charge and is called an ion (Gr. ion, going). If an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged because more positively charged protons are now in the nucleus than negatively charged electrons surrounding the ...
p-Block Elements, Part 1
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... Hydrogen forms ionic hydrides with the reactive s-block metals (groups 1 and 2) and forms covalent hydrides with the p-group metals, e.g. Al and Sn (group 13 and 14). Electronegativity = 2.1. The value is intermediate in the electronegativity scale that spans from 0.7 to 4.0. H can form hydrides ( ...
... Hydrogen forms ionic hydrides with the reactive s-block metals (groups 1 and 2) and forms covalent hydrides with the p-group metals, e.g. Al and Sn (group 13 and 14). Electronegativity = 2.1. The value is intermediate in the electronegativity scale that spans from 0.7 to 4.0. H can form hydrides ( ...
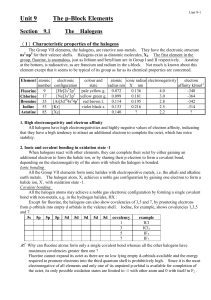
Unit 9 The p-Block Elements
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
... Electron affinity decreases numerically with increasing atomic number. This is because the outer electrons become more shielded from the nucleus as the atomic size increases, so the tendency to attract another electron decreases as the group is descended. (d) Suggest a reason why the electron affini ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
RESEARCH ARTICLE The statistics of electric field
... from which the reaction rate constants for dissociation and recombination have been determined [1, 2]. While these experiments provided valuable information on the kinetics of the reaction, their space and time resolution was not sufficient to clarify the atomistic details of the reaction. In princi ...
... from which the reaction rate constants for dissociation and recombination have been determined [1, 2]. While these experiments provided valuable information on the kinetics of the reaction, their space and time resolution was not sufficient to clarify the atomistic details of the reaction. In princi ...
1. Cl2 + 2Br- ® 2Cl- + Br2 formulae correct for elements 1 correct
... the (attractive) forces between molecules are weak (do not allow bonds or no forces, allow inter molecular forces are weak, do not allow they have weak forces / bonds) so little heat / energy is required before they can overcome forces / move freely / break out of solid structure / lattice (N.B. ...
... the (attractive) forces between molecules are weak (do not allow bonds or no forces, allow inter molecular forces are weak, do not allow they have weak forces / bonds) so little heat / energy is required before they can overcome forces / move freely / break out of solid structure / lattice (N.B. ...
Chem A Week 2 Matter Notes
... chromatography. It is the physical separation of a mixture into its individual components. It involves using a solvent to pass through the mixture. What solvent should I use? The solvent used depends upon the solubility of the mixture you are trying to separate. Examples are water, isopropyl alcohol ...
... chromatography. It is the physical separation of a mixture into its individual components. It involves using a solvent to pass through the mixture. What solvent should I use? The solvent used depends upon the solubility of the mixture you are trying to separate. Examples are water, isopropyl alcohol ...
1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
... Aluminum chloride, Al2Cl6 This forms an intermolecular Lewis acid-base dimer where one Cl atom on each AlCl3 donates a pair of electrons to the neighboring Al atom. Boron trifluoride, BF3 This forms partial pi bonds between the B and F atoms. Diborane, B2H6 B-H-B bridges are formed that use only two ...
BITSAT Chemistry
... constant pH of 9, the volume of 5 M KCN solution required to be together with water the boiled together with water, the boiling added to 10 ml of 2 M HCN solution is a ...
... constant pH of 9, the volume of 5 M KCN solution required to be together with water the boiled together with water, the boiling added to 10 ml of 2 M HCN solution is a ...
Document
... 82. Specifically a molecule with a partial positive charge on one end and a partially negative charge on the other end is called a ________ ...
... 82. Specifically a molecule with a partial positive charge on one end and a partially negative charge on the other end is called a ________ ...
H2O - WCCUSD.net
... § Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-‐PS1-‐2) ...
... § Each pure substance has characteristic physical and chemical properties (for any bulk quantity under given conditions) that can be used to identify it. (MS-‐PS1-‐2) ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.