Disordered Structures Lecture 1, Part 1
... • Amorphous metals • Produced by very rapid cooling from the melt • Some alloy glasses may be formed at less rapid cooling rates • Evaporation on a low temperature substrate • Liquid-like structure • RSP model with interatomic potential ...
... • Amorphous metals • Produced by very rapid cooling from the melt • Some alloy glasses may be formed at less rapid cooling rates • Evaporation on a low temperature substrate • Liquid-like structure • RSP model with interatomic potential ...
Atomic Structure - Hudson City School District
... attached to an electronegative atom of a different (oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) (has a partial negative charge. ...
... attached to an electronegative atom of a different (oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine) (has a partial negative charge. ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... A one Liter graduated cylinder has water added to it until the cylinder is completely filled. The water was then added to a 2.0 Liter cylinder and measured to be 1350 mL. The density of water is 1.0 g/mL. On the one Liter cylinder, the height from the one Liter mark to the top of the cylinder is 5.2 ...
... A one Liter graduated cylinder has water added to it until the cylinder is completely filled. The water was then added to a 2.0 Liter cylinder and measured to be 1350 mL. The density of water is 1.0 g/mL. On the one Liter cylinder, the height from the one Liter mark to the top of the cylinder is 5.2 ...
SAT Practice Test 3
... energy levels of the atom HCl is a proton donor Powdered zinc has a greater surface area NH3 is a polar substance Water boils when the vapor pressure of the water is equal to the atmospheric pressure In an exothermic reaction the products have less potential energy than the reactants Pressure and vo ...
... energy levels of the atom HCl is a proton donor Powdered zinc has a greater surface area NH3 is a polar substance Water boils when the vapor pressure of the water is equal to the atmospheric pressure In an exothermic reaction the products have less potential energy than the reactants Pressure and vo ...
Summary from Organic Chemistry Packet:
... • Recognize the terms cis-, trans- isomers – Unsaturated molecules – Orientation around the double bond ...
... • Recognize the terms cis-, trans- isomers – Unsaturated molecules – Orientation around the double bond ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
... Each group of elements embodied in the periodic table has their own unique properties. As for group II elements, they are classified as one of the s-block elements, also named as alkaline earth metals. In this essay, the variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds are illustrate ...
Here
... a. Add up all of the valence eb. Choose central atom c. Position other atoms around central d. Bind each atom singly to central and subtract e. Fill octet of surrounding atoms and subtract f. Attempt to fill octet of central atom g. Check for multiple bonds or ion formation h. Recount to 8 4. Single ...
... a. Add up all of the valence eb. Choose central atom c. Position other atoms around central d. Bind each atom singly to central and subtract e. Fill octet of surrounding atoms and subtract f. Attempt to fill octet of central atom g. Check for multiple bonds or ion formation h. Recount to 8 4. Single ...
EXAM 1 - gozips.uakron.edu
... (D) all of these are the same. (E) the temperatures can not be compared since they have different units. ...
... (D) all of these are the same. (E) the temperatures can not be compared since they have different units. ...
key to sample questions test 2
... r. A molecule with sp3d hybridization on the central atom always has a trigonal bipyramid geometry always has five pairs of electrons or bonded atoms around the central atom always has five bonds on the central atom always is a non planar molecule ...
... r. A molecule with sp3d hybridization on the central atom always has a trigonal bipyramid geometry always has five pairs of electrons or bonded atoms around the central atom always has five bonds on the central atom always is a non planar molecule ...
Autoionization in Liquid Water
... CPMD allows efficient classical nuclear dynamics simulations in condensed phases with forces determined at each time step by quantum chemistry calculations. From comparisons of force fields relevant for proton transfer (11) and dissociation (12) in water clusters, one expects CPMD [using the BLYP fu ...
... CPMD allows efficient classical nuclear dynamics simulations in condensed phases with forces determined at each time step by quantum chemistry calculations. From comparisons of force fields relevant for proton transfer (11) and dissociation (12) in water clusters, one expects CPMD [using the BLYP fu ...
Sample Exam 1 Key
... The actual number of moles was later determined to be 1.00. The above results are: a) both accurate and precise b) accurate but imprecise c) precise but inaccurate d) both inaccurate and imprecise 10. Aspirin has the formula C9H8O4. A compound is isolated from sea urchins that also has the formula C ...
... The actual number of moles was later determined to be 1.00. The above results are: a) both accurate and precise b) accurate but imprecise c) precise but inaccurate d) both inaccurate and imprecise 10. Aspirin has the formula C9H8O4. A compound is isolated from sea urchins that also has the formula C ...
Bonding Nomenclature Notes
... Two Types of Covalent Bonds 1. Polar Covalent Bond -one atom in a molecule is significantly more electronegative -This causes a slight positive and negative charge on a molecule. 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shared ...
... Two Types of Covalent Bonds 1. Polar Covalent Bond -one atom in a molecule is significantly more electronegative -This causes a slight positive and negative charge on a molecule. 2. Nonpolar Covalent Bond -electrons are shared ...
educator exam series
... Mathematical tables and electronic calculations may be used All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary For examiner’s use only: Questions Max. score Candidates score ...
... Mathematical tables and electronic calculations may be used All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary For examiner’s use only: Questions Max. score Candidates score ...
primes - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... (greater than 1) which cannot be divided by any smaller number except 1. We can call prime numbers the "elements" of arithmetic. Until a few hundred years ago, 1 was also called a prime number, but from the 19th century mathematicians started saying that 1 itself is not a prime number, and the small ...
... (greater than 1) which cannot be divided by any smaller number except 1. We can call prime numbers the "elements" of arithmetic. Until a few hundred years ago, 1 was also called a prime number, but from the 19th century mathematicians started saying that 1 itself is not a prime number, and the small ...
Document
... molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bigger number is called the coefficient and tells how many of a particular type of molecule there are. If there is a coeffi ...
... molecules and small numbers after certain atoms within a molecule. The little number is called the subscript and tells how many of a certain type of atom are in a molecule. The bigger number is called the coefficient and tells how many of a particular type of molecule there are. If there is a coeffi ...
chapter_2_2007
... with a positively charged hydrogen in solution. The strength of an acid or base is determined by how completely it will dissociate in water. – Strong acids release almost all of their hydrogen ions into water. – Strong bases release almost all of their hydroxide ions into water. ...
... with a positively charged hydrogen in solution. The strength of an acid or base is determined by how completely it will dissociate in water. – Strong acids release almost all of their hydrogen ions into water. – Strong bases release almost all of their hydroxide ions into water. ...
Ch 11 Review - mvhs
... HF has a higher melting point because intermolecular hydrogen bonding is important. CsI and LiF have still higher melting points because ionic lattice forces must be overcome to break up the crystals, and the ionic forces are stronger than van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds. SiC is an example o ...
... HF has a higher melting point because intermolecular hydrogen bonding is important. CsI and LiF have still higher melting points because ionic lattice forces must be overcome to break up the crystals, and the ionic forces are stronger than van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds. SiC is an example o ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
Chemical Bonding Quiz
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
... Study Guide: Chemical Bonding Quiz Students should be able to understand and apply the following Chemical Bonding concepts: ...
Note
... D. because the ions are oppositely charged, they attract each other negatively charged ions are attracted to nearby ions of the opposite charge so that individual molecules do not exist F. instead the ions form ionic crystals/solids that tend to dissociate in water and other polar solvents, have hig ...
... D. because the ions are oppositely charged, they attract each other negatively charged ions are attracted to nearby ions of the opposite charge so that individual molecules do not exist F. instead the ions form ionic crystals/solids that tend to dissociate in water and other polar solvents, have hig ...
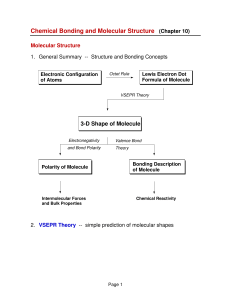
3-D Shape of Molecule
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
... 2. Molecular Orbitals for simple diatomic molecules (H2 and He2) in H2 the 1s atomic orbitals on the two H atoms are combined into: a bonding MO -- σ1s and an antibonding MO -- σ*1s MO energy level diagram for H2 (only the bonding MO is filled): ...
Chapter 8
... Multiple Covalent Bonds In many molecules, atoms attain a noblegas configuration by sharing more then one pair of electrons between 2 atoms. C, N, O and S most often form multiple bonds. ...
... Multiple Covalent Bonds In many molecules, atoms attain a noblegas configuration by sharing more then one pair of electrons between 2 atoms. C, N, O and S most often form multiple bonds. ...
Exam 1 Review
... What is a London dispersion force? How strong is it compared to other forces? Which compound has the highest boiling point? Which can undergo hydrogen bonding? What is the definition of boiling point? What is the triple point? What does supercritical mean? Topics that will likely be on the test: Cha ...
... What is a London dispersion force? How strong is it compared to other forces? Which compound has the highest boiling point? Which can undergo hydrogen bonding? What is the definition of boiling point? What is the triple point? What does supercritical mean? Topics that will likely be on the test: Cha ...
IGCSE Revision document
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
... Sodium chloride NaCl is a ____________. There are __________ bonds between the two the same/ different numbers of electrons. elements _________ and _________. When these atoms bond one ____________ from the • Isotopes are atoms of the same element with ___________ atom is donated to the ____________ ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.