Name: (1 of 2) Math Set # 13 Protons, Neutrons, Electrons Proton
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
... An ionic bond is created between metals and nonmetals. This is because a metal in group 1 or 2 gives up electrons easily and nonmetals in groups 16 through 18 accept electrons easily. An ionic bond results in two or more ions being attracted to each other. The total charge of the molecule must be ze ...
3.091 – Introduction to Solid State Chemistry Lecture Notes No
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
... by electronic rearrangements must be in a lower energy state than the atoms were prior to interaction, prior to bond formation. Since atoms of each of the elements have different electronic structures, the variety of possible chemical bonds (differing from each other in at least some small way) is c ...
lewis dot diagrams (structures) for atoms and ions predicting
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
1)A neutral atom has no overall charge, and ion is a
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
... 5)a)Create graph, will be gone over in class. b)These are the smallest atoms on each of their respective rows, and electrons are being removed from filled orbitals, which have strong stability, which takes a lot of energy to do. c)The valence electrons experience a smaller nuclear force of attractio ...
Polarity of Molecules
... structure of atoms to the electronic structure and geometries of molecules Two models: Valence Bond (VB) Model Molecular Orbital (MO) Model ...
... structure of atoms to the electronic structure and geometries of molecules Two models: Valence Bond (VB) Model Molecular Orbital (MO) Model ...
Chemical bonding
... Guidelines for Lewis Structures • The lesser amount of an element gets placed in the middle of the molecule (everything bonds to it) • Hydrogen NEVER gets placed in the middle ...
... Guidelines for Lewis Structures • The lesser amount of an element gets placed in the middle of the molecule (everything bonds to it) • Hydrogen NEVER gets placed in the middle ...
History and Current Status of the Plastics Industry
... Polymer chains with atoms other than carbon – Usually polymer chains with C and N, O, S, F, and Cl • PVC has Cl; Nylon has O and N; Polyurethane has O and N • PET has O and benzene ring; PC has O and benzene ring ...
... Polymer chains with atoms other than carbon – Usually polymer chains with C and N, O, S, F, and Cl • PVC has Cl; Nylon has O and N; Polyurethane has O and N • PET has O and benzene ring; PC has O and benzene ring ...
Ch 2 ppt - Houston ISD
... Weak Chemical Bonds • Most of the strongest bonds in organisms are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each other Copyrigh ...
... Weak Chemical Bonds • Most of the strongest bonds in organisms are covalent bonds that form a cell’s molecules • Weak chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds and hydrogen bonds, are also important • Weak chemical bonds reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each other Copyrigh ...
Molecular Modeling Activity for Carbohydrates
... 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccharide molecules are needed to form one sucrose molecule? ________ The production of a disaccharide is a chemical reaction called a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a r ...
... 10. How many times larger is the number of hydrogen atoms than oxygen atoms in a disaccharide? ________ 11. How many monosaccharide molecules are needed to form one sucrose molecule? ________ The production of a disaccharide is a chemical reaction called a dehydration synthesis reaction. In such a r ...
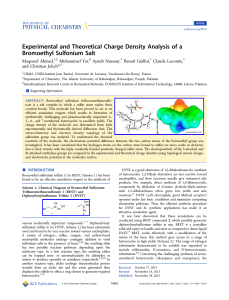
Experimental and Theoretical Charge Density Analysis of a
... intervals. To improve the quality of the data a second data set was later collected using the same crystal at the same temperature but using different exposure times in the experiment. In the first experiment, the exposure time was 10 and 25 s for low- and high-resolution data. In the second experimen ...
... intervals. To improve the quality of the data a second data set was later collected using the same crystal at the same temperature but using different exposure times in the experiment. In the first experiment, the exposure time was 10 and 25 s for low- and high-resolution data. In the second experimen ...
Review 1
... made of silver but does not want it damaged during the analysis. The chemist decides to determine the density, knowing that silver has a density of 10.5 g/ml. The figurine is put into a graduated cylinder that contains 32.6 ml of water. The reading while the figurine is in the water is 60.1 ml. The ...
... made of silver but does not want it damaged during the analysis. The chemist decides to determine the density, knowing that silver has a density of 10.5 g/ml. The figurine is put into a graduated cylinder that contains 32.6 ml of water. The reading while the figurine is in the water is 60.1 ml. The ...
Chemistry in Biology
... B.Types of Chemical Bonds 1. Covalent bond—forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons •A molecule is a compound in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. •Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. ...
... B.Types of Chemical Bonds 1. Covalent bond—forms when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons •A molecule is a compound in which the atoms are held together by covalent bonds. •Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
Formula and The Mole
... 7. Draw the structural formulae for the two monomers form which nylon 6,6 is made. 8. What type of polymer is nylon 6,6? ...
... 7. Draw the structural formulae for the two monomers form which nylon 6,6 is made. 8. What type of polymer is nylon 6,6? ...
Bonding Notes
... opposite charges of the two ions that attract for one another. Notice that a total number of eight valence electrons are used . This is called the octet rule! The octet rule means that each atom participating in a ionic bond must achieve eight electrons in its outermost energy level, thus eight dots ...
... opposite charges of the two ions that attract for one another. Notice that a total number of eight valence electrons are used . This is called the octet rule! The octet rule means that each atom participating in a ionic bond must achieve eight electrons in its outermost energy level, thus eight dots ...
Chapter 2 Expanded Notes
... salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ions. The bond will only form between opposite charges, but may form between multiple atoms. The overall driving force for this is that atoms want to be electrically neutral. But they gain or lose ele ...
... salts. Ionic bonds are formed by the mutual attraction of opposite charges of positive and negative ions. The bond will only form between opposite charges, but may form between multiple atoms. The overall driving force for this is that atoms want to be electrically neutral. But they gain or lose ele ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... A. The natural tendency is to achieve the lowest possible Potential Energy state and thus behave “like” a Noble gas element. B. Energy is released in bond formation between atoms. C. Energy is required in the breaking of a bond between atoms. 1. The energy to make or break a bond is referred to as b ...
... A. The natural tendency is to achieve the lowest possible Potential Energy state and thus behave “like” a Noble gas element. B. Energy is released in bond formation between atoms. C. Energy is required in the breaking of a bond between atoms. 1. The energy to make or break a bond is referred to as b ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
... Remember Lewis Dot Diagrams from Chem 20?? This means carbon can bond extensively and can bond together to form chains effectively = called Polymerism Carbon covalently bonds by sharing 4 pairs of electrons. These bonds may be single, double or triple, all producing stable compounds Compound ...
15anespp
... The four orbitals (an s and three p’s) combine or HYBRIDISE to give four new orbitals. All four orbitals are equivalent. Because one s and three p orbitals are used, it is called sp3 hybridisation ...
... The four orbitals (an s and three p’s) combine or HYBRIDISE to give four new orbitals. All four orbitals are equivalent. Because one s and three p orbitals are used, it is called sp3 hybridisation ...
ch14 lecture 7e
... Silicone polymers are synthetic substances consisting of alternating Si and O atoms. They are used in a wide variety of applications. ...
... Silicone polymers are synthetic substances consisting of alternating Si and O atoms. They are used in a wide variety of applications. ...
thermocompression
... temperature and high impact force, and the ball/wedge method. No ultrasonic is used during bonding. Use in special application such as bonding of GaAs devices •The joining together of two materials, without an intermediate material, by the application of pressure and heat in the absence of an electr ...
... temperature and high impact force, and the ball/wedge method. No ultrasonic is used during bonding. Use in special application such as bonding of GaAs devices •The joining together of two materials, without an intermediate material, by the application of pressure and heat in the absence of an electr ...
2 - FacultyWeb
... • Formed by sharing of two or more valence shell electrons • Allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time ...
... • Formed by sharing of two or more valence shell electrons • Allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time ...
Organic Chemistry 2014 finalzzz
... If we know how many bonding e-’s an atom has, we can predict what structure a molecular compound will have Atom ...
... If we know how many bonding e-’s an atom has, we can predict what structure a molecular compound will have Atom ...
Hydrogen bond
A hydrogen bond is the electrostatic attraction between polar molecules that occurs when a hydrogen (H) atom bound to a highly electronegative atom such as nitrogen (N), oxygen (O) or fluorine (F) experiences attraction to some other nearby highly electronegative atom.These hydrogen-bond attractions can occur between molecules (intermolecular) or within different parts of a single molecule (intramolecular). The hydrogen bond (5 to 30 kJ/mole) is stronger than a van der Waals interaction, but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.Intermolecular hydrogen bonding is responsible for the high boiling point of water (100 °C) compared to the other group 16 hydrides that have no hydrogen bonds. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is partly responsible for the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins and nucleic acids. It also plays an important role in the structure of polymers, both synthetic and natural.In 2011, an IUPAC Task Group recommended a modern evidence-based definition of hydrogen bonding, which was published in the IUPAC journal Pure and Applied Chemistry. This definition specifies that The hydrogen bond is an attractive interaction between a hydrogen atom from a molecule or a molecular fragment X–H in which X is more electronegative than H, and an atom or a group of atoms in the same or a different molecule, in which there is evidence of bond formation. An accompanying detailed technical report provides the rationale behind the new definition.