Partially coherent image formation with x
... Unlike conventional refractive lenses, the focusing properties of zone plates are based on diffraction. This implies that the focal length of a zone plate lens strongly depends on the wavelength and that multiple diffraction orders exist. In most cases only the first diffraction order is used. The d ...
... Unlike conventional refractive lenses, the focusing properties of zone plates are based on diffraction. This implies that the focal length of a zone plate lens strongly depends on the wavelength and that multiple diffraction orders exist. In most cases only the first diffraction order is used. The d ...
PDF Link
... function, t(xʹ, yʹ), which defines the sample field via Us(xʹ, yʹ) = t(xʹ, yʹ)ei(kxxʹ + kyyʹ) when illuminated by a plane wave with wavevector (kx, ky), for example, and is the quantity of interest in our discussion of resolution. ...
... function, t(xʹ, yʹ), which defines the sample field via Us(xʹ, yʹ) = t(xʹ, yʹ)ei(kxxʹ + kyyʹ) when illuminated by a plane wave with wavevector (kx, ky), for example, and is the quantity of interest in our discussion of resolution. ...
Lecture 16 - Purdue Physics
... • Point light sources produce umbras. • Multiple point sources or extended light sources penumbras. ...
... • Point light sources produce umbras. • Multiple point sources or extended light sources penumbras. ...
Integrated Optics: Guiding and manipulating light for device
... primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical components. Integrated optics is the miniaturised version of bulk optical functional blocks w ...
... primary parameters namely intensity, frequency or wavelength, polarisation and phase. It travels in a straight line unless the space-time itself is curved or the path is altered by means of external optical components. Integrated optics is the miniaturised version of bulk optical functional blocks w ...
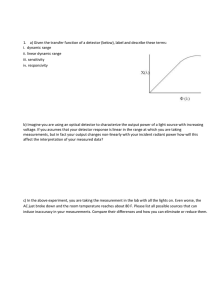
a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and
... AC just broke down and the room temperature reaches about 80 F. Please list all possible sources that can induce inaccuracy in your measurements. Compare their differences and how you can eliminate or reduce them. ...
... AC just broke down and the room temperature reaches about 80 F. Please list all possible sources that can induce inaccuracy in your measurements. Compare their differences and how you can eliminate or reduce them. ...
Ch14 Review
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
RESOLVING POWER AND MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION
... (target) to be processed. Other means are X-rays, electron beams or neutrons. The power of imaging is due to the fact that structurizing a 2-D area becomes possible in one exposure, at the same time the control of the imaging parameters allows selecting the image size, e.g. by demagnifying. However, ...
... (target) to be processed. Other means are X-rays, electron beams or neutrons. The power of imaging is due to the fact that structurizing a 2-D area becomes possible in one exposure, at the same time the control of the imaging parameters allows selecting the image size, e.g. by demagnifying. However, ...
HW #8 Solutions
... Light reflect off of a transparent material (like glass) is decreased in amplitude– some of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is ...
... Light reflect off of a transparent material (like glass) is decreased in amplitude– some of the light intensity is transmitted through the material. Since intensity is power per unit area, energy conservation requires that the reflected plus transmitted intensity (plus absorbed intensity, if any) is ...
Thermal Analysis Infrared Microscopy During device functioning, the
... Characterizing mechanical properties of the materials used for manufacturing semiconductors could be a consititutive part of the failure analysis. This is true mainly for semiconductor devices with moving mechanical parts, for example MEMS. The mechanical properties are valuable inputs for the desig ...
... Characterizing mechanical properties of the materials used for manufacturing semiconductors could be a consititutive part of the failure analysis. This is true mainly for semiconductor devices with moving mechanical parts, for example MEMS. The mechanical properties are valuable inputs for the desig ...
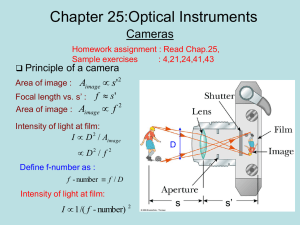
Lecture 25: Optical Instruments
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
... Resolution of Single-Slit and Circular Apertures Resolution of single-slit aperture The ability of an optical system such as the eye, a microscope, or a telescope to distinguish between closely spaced objects is limited because of wave nature of light. - Light from two independent sources which a ...
PDF
... absorption/emission transition dipoles of elongated dye molecules follow n̂srd, and the polarized confocal imaging visualizes the 3D director patterns.2 However, this approach requires doping a specially selected dye that at small concentrations would provide strong contrast without affecting the LC ...
... absorption/emission transition dipoles of elongated dye molecules follow n̂srd, and the polarized confocal imaging visualizes the 3D director patterns.2 However, this approach requires doping a specially selected dye that at small concentrations would provide strong contrast without affecting the LC ...
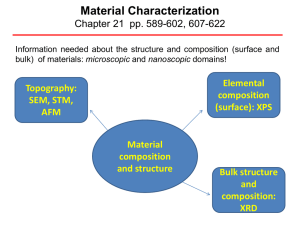
Material Characterization
... sample.[4] Information is acquired by monitoring the current as the tip's position scans across the surface, and is usually displayed in image form. STM can be a challenging technique, as it requires extremely clean and stable surfaces, sharp tips, excellent vibration control, and ...
... sample.[4] Information is acquired by monitoring the current as the tip's position scans across the surface, and is usually displayed in image form. STM can be a challenging technique, as it requires extremely clean and stable surfaces, sharp tips, excellent vibration control, and ...
simple positive stain with three easy to find dyes - Microscopy-UK
... illumination system. If we want something more special, well there are other illumination techniques. This article is related to brightfield microscopy because the samples are observed with this illumination. If the samples are less than a micron in size such as bacteria, they are difficult to see w ...
... illumination system. If we want something more special, well there are other illumination techniques. This article is related to brightfield microscopy because the samples are observed with this illumination. If the samples are less than a micron in size such as bacteria, they are difficult to see w ...
Measurement of Surface Quality 1. Lyot Test 2. FECO 3. Nomarski
... range can be determined. Two disadvantages are 1) we are getting data only along a line and 2) the sample being measured must have a high reflectivity. ...
... range can be determined. Two disadvantages are 1) we are getting data only along a line and 2) the sample being measured must have a high reflectivity. ...
The University of Georgia Department of Physics and Astronomy
... 6. Optical computers require microscopic optical switches to turn signals on and off. One device for doing so is the Mach-Zender interferometer shown in the figure. Light from a infrared laser (λ = 1.00µm) is split into two waves that travel equal distances around the arms of the interferometer. One ...
... 6. Optical computers require microscopic optical switches to turn signals on and off. One device for doing so is the Mach-Zender interferometer shown in the figure. Light from a infrared laser (λ = 1.00µm) is split into two waves that travel equal distances around the arms of the interferometer. One ...
View
... • Production of a magnified image of the lamp filament that is focused at the level of the aperture plane of the condensor. • Opening or closing this diaphragm controls the angle of the light cone that reaches the specimen, which is determining the image resolution along with the numerical aperture ...
... • Production of a magnified image of the lamp filament that is focused at the level of the aperture plane of the condensor. • Opening or closing this diaphragm controls the angle of the light cone that reaches the specimen, which is determining the image resolution along with the numerical aperture ...
Wide-field extended-resolution fluorescence
... with periodic corrugations in the metal layer [3], and that magnification can similarly be achieved [4]. While super-resolution on the order of λ/4 can be obtained with these methods, the sample must be placed at a specific location that is virtually impossible for most biomedical applications. Furt ...
... with periodic corrugations in the metal layer [3], and that magnification can similarly be achieved [4]. While super-resolution on the order of λ/4 can be obtained with these methods, the sample must be placed at a specific location that is virtually impossible for most biomedical applications. Furt ...
DG Papazoglou et al.
... are lead to a better understanding of the physical process. Our results clearly support a photochemical mechanism for low repetition rate laser sources! D.G. Papazoglou et al., Opt. Lett. 31, 1441 (2006) , D. G. Papazoglou et al., Opt. Lett., 32, 2055 (2007), D.G. Papazoglou et al., (invited) to app ...
... are lead to a better understanding of the physical process. Our results clearly support a photochemical mechanism for low repetition rate laser sources! D.G. Papazoglou et al., Opt. Lett. 31, 1441 (2006) , D. G. Papazoglou et al., Opt. Lett., 32, 2055 (2007), D.G. Papazoglou et al., (invited) to app ...
Zach Stephen Richard Worhatch Royce Grewer
... This is done so that different objectives can be used on the same microscope, making it easier to find what you want to focus on. ...
... This is done so that different objectives can be used on the same microscope, making it easier to find what you want to focus on. ...
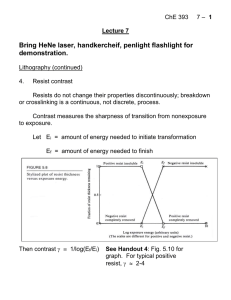
ChE 393 Course Notes
... well-defined molecule in the excited state that lives briefly before it decays into the largely repulsive ground state. Electronic diagram: ...
... well-defined molecule in the excited state that lives briefly before it decays into the largely repulsive ground state. Electronic diagram: ...
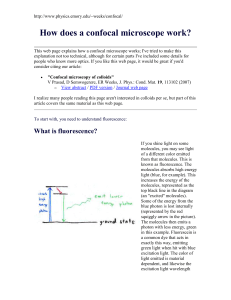
How does a confocal microscope work
... of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the lens, but which nonetheless get imaged by the lenses of the microscope. (Note that the red ...
... of one lens to another point. This is represented by the blue rays of light in the above picture. The red rays of light represent light from another point in the sample, which is not at the focal point of the lens, but which nonetheless get imaged by the lenses of the microscope. (Note that the red ...
Lecture 3
... http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/darkfield/cardioid/index.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/darkfieldreflect.html reflected DF ...
... http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/java/darkfield/cardioid/index.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/darkfieldreflect.html reflected DF ...
1. a) 25% b)86% 2. For my opinion, I think the way to make
... measure the solutions at the parts per million levels which equivalent to one gram of element per 100kg of solution. It is suitable to be used for wide range of analysis. This technique is based on the fact that ground state metals absorb light at specific wavelengths. Metal ions of a solutions are ...
... measure the solutions at the parts per million levels which equivalent to one gram of element per 100kg of solution. It is suitable to be used for wide range of analysis. This technique is based on the fact that ground state metals absorb light at specific wavelengths. Metal ions of a solutions are ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.