Biology 177: Principles of Modern Microscopy
... manipulate) • Most illuminate opposite objective so have to pass through specimen • If prism on same side then more complicated alignment ...
... manipulate) • Most illuminate opposite objective so have to pass through specimen • If prism on same side then more complicated alignment ...
Isotropic Diffraction-Limited Focusing Using a Single Objective Lens
... coherent manner through two objective lenses facing each other, as depicted in Fig. 1(b), so that the illumination is almost spherical [8]. The constructive interference of the two focused light fields produces an intensity peak whose axial dimension is 3 times narrower than that obtained with a sin ...
... coherent manner through two objective lenses facing each other, as depicted in Fig. 1(b), so that the illumination is almost spherical [8]. The constructive interference of the two focused light fields produces an intensity peak whose axial dimension is 3 times narrower than that obtained with a sin ...
Miniaturized modules for light sheet microscopy with low chromatic
... In recent years, light sheet microscopy has proven to be a valuable method for 3D imaging of biological specimens (Huisken et al., 2004; Santi, 2011). In contrast to established methods, e.g. confocal laser scanning microscopy (Pawley, 1990; Webb, 1996) or structured illumination microscopy (Neil et ...
... In recent years, light sheet microscopy has proven to be a valuable method for 3D imaging of biological specimens (Huisken et al., 2004; Santi, 2011). In contrast to established methods, e.g. confocal laser scanning microscopy (Pawley, 1990; Webb, 1996) or structured illumination microscopy (Neil et ...
James Powenski - Optical Computing
... superior when characterisitc resistance is included. V (C + C d ) > D R0 Rτ ...
... superior when characterisitc resistance is included. V (C + C d ) > D R0 Rτ ...
Waves & Oscillations Geometric Optics Physics 42200 3/20/2016
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
... – Given an optical system, what are the properties of the image that is formed (if any)? – What configuration of optical elements (if any) will produce an image with certain desired characteristics? ...
Spectrophotometry and its Applications in Microbiology
... will leak out. Because the proteins, salts, and small molecules that make up the cytoplasm of a cell are soluble, they will not contribute to the light scattering of the sample. Thus damage to the cells will result in a decrease in Optical Density of the sample. Pieces of cells that reform after exp ...
... will leak out. Because the proteins, salts, and small molecules that make up the cytoplasm of a cell are soluble, they will not contribute to the light scattering of the sample. Thus damage to the cells will result in a decrease in Optical Density of the sample. Pieces of cells that reform after exp ...
n - LSU Physics
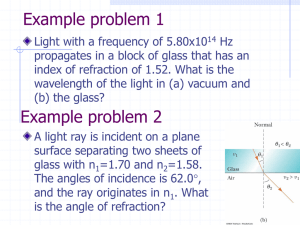
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... Fluorescein Dye- illuminated with a blue wavelength of light and emits in the green. ...
... Fluorescein Dye- illuminated with a blue wavelength of light and emits in the green. ...
lecture22
... Example: In a double-slit experiment, it is observed that the distance between adjacent maxima on a remote screen is 1.0 cm. What happens to the distance between adjacent maxima when the slit separation is cut in half? A) It increases to 2.0 cm. B) It increases to 4.0 cm. C) It decreases to 0.50 cm ...
... Example: In a double-slit experiment, it is observed that the distance between adjacent maxima on a remote screen is 1.0 cm. What happens to the distance between adjacent maxima when the slit separation is cut in half? A) It increases to 2.0 cm. B) It increases to 4.0 cm. C) It decreases to 0.50 cm ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
... materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adjust the group velocity υg of a pulse. Large normal dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increas ...
... materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adjust the group velocity υg of a pulse. Large normal dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increas ...
BL Web - The Bioluminescence Web Page
... that you are likely to encounter are non-luminous, but there is one deep-sea species which puts off a sparkling display of luminescence when disturbed. The main planktonic invertebrates (as distinct from protists) that don’t luminesce are the heteropods and pteropods (although many other molluscs ca ...
... that you are likely to encounter are non-luminous, but there is one deep-sea species which puts off a sparkling display of luminescence when disturbed. The main planktonic invertebrates (as distinct from protists) that don’t luminesce are the heteropods and pteropods (although many other molluscs ca ...
Wave optics
... Can the lower drawing be used to determine the angles for the a bright fringes, where the waves incident shown also originate from light, positions a/2 apart? ...
... Can the lower drawing be used to determine the angles for the a bright fringes, where the waves incident shown also originate from light, positions a/2 apart? ...
used to cook Infrared - “heat waves” Visible Light
... Depth of Field: Range of object distances over which image is sufficiently well focused, i.e., range for which blur circle is less than the resolution of the imaging sensor. ...
... Depth of Field: Range of object distances over which image is sufficiently well focused, i.e., range for which blur circle is less than the resolution of the imaging sensor. ...
light reflection plane mirror
... light is represented as straight lines called rays ray diagrams are drawings that show the path that light takes after it leaves its source light travels in straight lines until it strikes something some materials absorb light and other materials reflect light Regular Reflection light rays ...
... light is represented as straight lines called rays ray diagrams are drawings that show the path that light takes after it leaves its source light travels in straight lines until it strikes something some materials absorb light and other materials reflect light Regular Reflection light rays ...
Spectrometry 1 R
... which are mutually perpendicular and which radiate out from a source • It is therefore a form of electromagnetic radiation. • Electric and magnetic fields are propagated through space as wave functions which may be characterized by wavelength, λ (the distance from one part of the wave to the corresp ...
... which are mutually perpendicular and which radiate out from a source • It is therefore a form of electromagnetic radiation. • Electric and magnetic fields are propagated through space as wave functions which may be characterized by wavelength, λ (the distance from one part of the wave to the corresp ...
Interference
... Single Slit Diffraction... • A single slit can interfere with itself! simulate this • Equation for Nodes: n W sin ...
... Single Slit Diffraction... • A single slit can interfere with itself! simulate this • Equation for Nodes: n W sin ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... (Aspergillus oryzae),9 and Vishnyakov and Levin observed human red blood cells and lymphocites. 8-9 Note that quantitative RI data are found only in Refs. 8-9. In a recent paper,12 we have shown for the first time to our knowledge the quantitative 3D distribution of RI of a semi-transparent object, ...
... (Aspergillus oryzae),9 and Vishnyakov and Levin observed human red blood cells and lymphocites. 8-9 Note that quantitative RI data are found only in Refs. 8-9. In a recent paper,12 we have shown for the first time to our knowledge the quantitative 3D distribution of RI of a semi-transparent object, ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refraction angles 2() for a given 1 ...
... This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refraction angles 2() for a given 1 ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance Spectroscopy
... Largest Refractor • Great Refractor at Yerkes Observatory (run by the University of Chicago) • Completed in 1897 • 1.02 m aperture ...
... Largest Refractor • Great Refractor at Yerkes Observatory (run by the University of Chicago) • Completed in 1897 • 1.02 m aperture ...
Particles and Waves in Electron Optics and Microscopy, Vol 194.... Imaging and Electron Physics
... Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics merges two long-running serials, Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics and Advances in Optical and Electron Microscopy. The series features extended articles on the physics of electron devices (especially semiconductor devices), particle optics at high ...
... Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics merges two long-running serials, Advances in Electronics and Electron Physics and Advances in Optical and Electron Microscopy. The series features extended articles on the physics of electron devices (especially semiconductor devices), particle optics at high ...
Optical Polarimetry
... determined by the angle of the lens itself. This light is then passed through a solution of an optically active compound, which results in a rotation of the plane of oscillation. A second polarizing lens (prism) is used in conjunction with a detector to find the angle of rotation. The magnitude of t ...
... determined by the angle of the lens itself. This light is then passed through a solution of an optically active compound, which results in a rotation of the plane of oscillation. A second polarizing lens (prism) is used in conjunction with a detector to find the angle of rotation. The magnitude of t ...
Microscopy - PSSurvival.com
... microscopy) lie in three areas; ◾ This technique can only image dark or strongly refracting objects effectively. ◾ Diffraction limits resolution to approximately 0.2 micrometres (see: microscope). This limits the practical magnification limit to ~1500x. ◾ Out of focus light from points outside the f ...
... microscopy) lie in three areas; ◾ This technique can only image dark or strongly refracting objects effectively. ◾ Diffraction limits resolution to approximately 0.2 micrometres (see: microscope). This limits the practical magnification limit to ~1500x. ◾ Out of focus light from points outside the f ...
Wang_Project_Summery
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
... inferred) enters the light shack through a series of guide mirrors. Taking this visible light beam, using a series of optical devices, I will focus the beam and direct it into a light-tight box where the photo detector sits. Using a special computer to gather data from the photon counter, we will be ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.