
R1B p4 - CenSSIS - Northeastern University
... microscopic examination of optically thick transparent objects. A number of phase imaging modalities have been developed to address this need. If a stack of images is acquired through focusing, the image at a given focal plane is contaminated by out-of-focus information coming from other planes [1]. ...
... microscopic examination of optically thick transparent objects. A number of phase imaging modalities have been developed to address this need. If a stack of images is acquired through focusing, the image at a given focal plane is contaminated by out-of-focus information coming from other planes [1]. ...
Biology 177: Principles of Modern Microscopy
... • Practically zero working distance and small depth of field. • Extremely long scan times for high resolution images or large specimen areas. ...
... • Practically zero working distance and small depth of field. • Extremely long scan times for high resolution images or large specimen areas. ...
How I discovered phase contrast
... The opposing microscopists, however, said these experiments only showed how the microscope may be used, or rather misused, by the physicist for interference experiments which have nothing to do with the ordinary proper use of the instrument. A long story could be told about the violent controversies ...
... The opposing microscopists, however, said these experiments only showed how the microscope may be used, or rather misused, by the physicist for interference experiments which have nothing to do with the ordinary proper use of the instrument. A long story could be told about the violent controversies ...
FYS0460 / FYSZ460 Ohjelmatyö Elektronisuhkulitografia
... Working in laboratory and in cleanroom conditions ...
... Working in laboratory and in cleanroom conditions ...
4Pi Microscopy
... lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye, it is not surprising that the majority of recent 3D-imaging appl ...
... lenses for STED, the axial resolution was improved down to 30 to 50 nm (Dyba and Hell, 2002; Dyba et al., 2003). However, as STED is still in its infancy and, unlike I5M and 4Pi microscopy, relies on the specific properties of the dye, it is not surprising that the majority of recent 3D-imaging appl ...
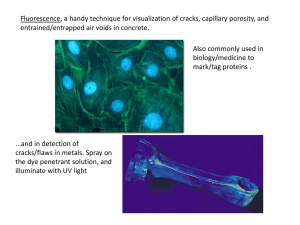
Fluorescence
... The blue filters purchased for your microscopes are not ideal, they are too small. So, there isn’t enough light to cause the dye to glow bright green. To compensate for this, you will use the converging lens below the microscope stage to concentrate the light. This won’t be sufficient for the low p ...
... The blue filters purchased for your microscopes are not ideal, they are too small. So, there isn’t enough light to cause the dye to glow bright green. To compensate for this, you will use the converging lens below the microscope stage to concentrate the light. This won’t be sufficient for the low p ...
Introduction to Light and Optics
... Light is a form of energy visible to the naked eye It is an electromagnetic wave ...
... Light is a form of energy visible to the naked eye It is an electromagnetic wave ...
Optics01
... described the law of reflection. He believed that vision involves rays going from the eyes to the object seen 965-1020Ibn-al-Haitham ~1267Roger Bacon (England) speed of light is finite and that it is propagated through a medium in a manner analogous to the propagation of sound 1303Bernard of Gordon ...
... described the law of reflection. He believed that vision involves rays going from the eyes to the object seen 965-1020Ibn-al-Haitham ~1267Roger Bacon (England) speed of light is finite and that it is propagated through a medium in a manner analogous to the propagation of sound 1303Bernard of Gordon ...
Instrumental Analysis as Applied to Architectural Materials
... The light may be either reflected by the sample or transmitted through the sample. The image generated is magnified through lenses. Optical microscopy is used to analyze coatings, stones, and mortar and to identify constituents such as minerals (crystals). Microscopy is typically qualitative but may ...
... The light may be either reflected by the sample or transmitted through the sample. The image generated is magnified through lenses. Optical microscopy is used to analyze coatings, stones, and mortar and to identify constituents such as minerals (crystals). Microscopy is typically qualitative but may ...
repeat
... For each of the molecules shown below, indicate on the diagram itself, in the space provided next to each group attached to the stereocentre, its priority, by writing the numbers 1, 2, 3, or 4 (1 being the highest and 4 the lowest priority). Then indicate whether the configuration of the stereocentr ...
... For each of the molecules shown below, indicate on the diagram itself, in the space provided next to each group attached to the stereocentre, its priority, by writing the numbers 1, 2, 3, or 4 (1 being the highest and 4 the lowest priority). Then indicate whether the configuration of the stereocentr ...
Biomedical imaging in the undergraduate physics curriculum
... Despite the broad subject matter, our course is taught by one instructor (unlike similar courses that have been described recently2) and is offered for just two units/credits (1.5 lecture hours per week). The two-unit format reduces the depth at which material can be covered but also makes the cours ...
... Despite the broad subject matter, our course is taught by one instructor (unlike similar courses that have been described recently2) and is offered for just two units/credits (1.5 lecture hours per week). The two-unit format reduces the depth at which material can be covered but also makes the cours ...
Resolution questions with solutions
... In this experiment, the light from point source P has a wavelength of 500 nm and the width of the central maximum of intensity on the screen is 10.0 mm. When light of unknown wavelength λ is used, the width of the central maximum of intensity is 13.0 mm. Determine the value of λ. ...
... In this experiment, the light from point source P has a wavelength of 500 nm and the width of the central maximum of intensity on the screen is 10.0 mm. When light of unknown wavelength λ is used, the width of the central maximum of intensity is 13.0 mm. Determine the value of λ. ...
Biology 3235: Resolution and magnification of a light microscopes
... 0.25 will resolve details as small as 1.2 µm when using green light (λ = 500 nm). With a100× objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue li ...
... 0.25 will resolve details as small as 1.2 µm when using green light (λ = 500 nm). With a100× objective (NA = 1.3), you could resolve details as small as 0.23 µm using green light. Note that shorter wavelengths of light also provide for greater resolution; smaller details can be resolved with blue li ...
Size Estimation of Protein Clusters in the Nanometer Range by
... contains three peaks, one centered at zero frequency stemming from the envelope (sinc2) and two peaks at +/- the modulation frequency (cos2). Theory [10] showed that the intensities and the positions of these “Fourier”peaks contain all the important parameters of the AID. The parameters extracted in ...
... contains three peaks, one centered at zero frequency stemming from the envelope (sinc2) and two peaks at +/- the modulation frequency (cos2). Theory [10] showed that the intensities and the positions of these “Fourier”peaks contain all the important parameters of the AID. The parameters extracted in ...
Chapter 1: Introduction to Microbiology
... l Absorption: The light rays neither pass through nor bounce off an object but are taken up by the ...
... l Absorption: The light rays neither pass through nor bounce off an object but are taken up by the ...
Image processing in Spectral Domain Optical Coherence
... A depth profile is formed by the detection of the interference pattern between the reference and sample arm as the reference arm is scanned. ...
... A depth profile is formed by the detection of the interference pattern between the reference and sample arm as the reference arm is scanned. ...
Microscopy Overview
... magnification is M, the longitudinal magnification is approximately equal to M2. However, it can be shown that it is impossible to devise an instrument that can produce a perfect 3-D image of a 3-D object, because to have a perfect transverse image the system must satisfy Abbe's sine condition, but ...
... magnification is M, the longitudinal magnification is approximately equal to M2. However, it can be shown that it is impossible to devise an instrument that can produce a perfect 3-D image of a 3-D object, because to have a perfect transverse image the system must satisfy Abbe's sine condition, but ...
Super-resolution Microscopy
... fluoresce. The emission signal from each fluorophore molecule still generates a diffraction-limited spot; however, because the population of the fluorophores is so sparse the spots can be independently resolved. Such resolvable individual molecules are imaged, localized (using computational tools) a ...
... fluoresce. The emission signal from each fluorophore molecule still generates a diffraction-limited spot; however, because the population of the fluorophores is so sparse the spots can be independently resolved. Such resolvable individual molecules are imaged, localized (using computational tools) a ...
tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz
... that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A and B. The wavelength of the light is 520 nm. Using the fringe pattern shown in the drawing, determin ...
... that form a thin wedge of air as shown in fig. 1. An observer looking down through the glass plate sees the fringe pattern shown in the lower part of the drawing, with the dark fringes at the ends A and B. The wavelength of the light is 520 nm. Using the fringe pattern shown in the drawing, determin ...
Document
... At the image plane, we now have two types of high-frequency fields, phase shifted by /2 and not, which generate high contrast fringes (bright or dark halos, depending on the sign of the phase shift filter). The existence of the halo indicates the failure of our assumption for a perfect 2D Fourie ...
... At the image plane, we now have two types of high-frequency fields, phase shifted by /2 and not, which generate high contrast fringes (bright or dark halos, depending on the sign of the phase shift filter). The existence of the halo indicates the failure of our assumption for a perfect 2D Fourie ...
Microscope
... resolution to about 0.1 m. However, UV light is invisible to the human eye, so the image must be recorded on a photographic plate or fluorescent screen. Because this light is absorbed by glass, all lenses must be made of quartz, such microscopes are too expensive for routine use. ...
... resolution to about 0.1 m. However, UV light is invisible to the human eye, so the image must be recorded on a photographic plate or fluorescent screen. Because this light is absorbed by glass, all lenses must be made of quartz, such microscopes are too expensive for routine use. ...
Advantages of Infinity-Corrected Optics in FT
... small flaws are magnified by long beam paths and additional optical components. An infinity-corrected system will reduce or eliminate many of the aberrations, because spherical mirrors, which can be precisely ground and polished, can be used in place of aspherical mirrors. In general, a collimated b ...
... small flaws are magnified by long beam paths and additional optical components. An infinity-corrected system will reduce or eliminate many of the aberrations, because spherical mirrors, which can be precisely ground and polished, can be used in place of aspherical mirrors. In general, a collimated b ...
Photo Contest Winners Member Lens:
... streams of liquid into a ceramic bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integ ...
... streams of liquid into a ceramic bowl, where they combine to form white light. “This image beautifully demonstrates total internal reflection and three-color mixing, creating a visceral, interactive tutorial for optical fiber technology, modern display technology, Rayleigh scattering, and even integ ...
diffraction and interference
... Eyepiece lens acts like magnifier Meye = N/do N/feye Lenses subject to chromatic aberration Different colors focus differently Many telescopes are reflecting telescopes to avoid this ...
... Eyepiece lens acts like magnifier Meye = N/do N/feye Lenses subject to chromatic aberration Different colors focus differently Many telescopes are reflecting telescopes to avoid this ...
Panoramic 180˚ H Hybrid
... MADE IN THE USA - LIFETIME WARRANTY All products are covered by a lifetime warranty with advanced replacement. All Axton lights are designed and manufactured in the USA. ...
... MADE IN THE USA - LIFETIME WARRANTY All products are covered by a lifetime warranty with advanced replacement. All Axton lights are designed and manufactured in the USA. ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.













![tutorial #10 [wave nature of light] .quiz](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/020410144_1-db052accb2aa8cded167524d89755606-300x300.png)





