Phase Contrast
... (Differential Interference Contrast after Nomarski) High Contrast and high resolution Control of condenser aperture for optimum contrast Changes GRADIENTS into brightness differences ...
... (Differential Interference Contrast after Nomarski) High Contrast and high resolution Control of condenser aperture for optimum contrast Changes GRADIENTS into brightness differences ...
Light Microscopy Excerpt from Chapter 1
... Although illumination of the specimen is important, the microscope objective is the single most critical component of the microscope. Its properties largely determine depth of focus, resolution, and contrast of the specimen. The eyepiece and/or other so-called transfer optical devices simply magnify ...
... Although illumination of the specimen is important, the microscope objective is the single most critical component of the microscope. Its properties largely determine depth of focus, resolution, and contrast of the specimen. The eyepiece and/or other so-called transfer optical devices simply magnify ...
Microscopy 1: Optical
... To provide a magnified image To observe features that are beyond the resolution of the human eyes (~100mm) ─ directly by light (optical) microscope using visible light ─ other microscopy imaging techniques use some other interaction probe and response signal (usually electrons) to provide the co ...
... To provide a magnified image To observe features that are beyond the resolution of the human eyes (~100mm) ─ directly by light (optical) microscope using visible light ─ other microscopy imaging techniques use some other interaction probe and response signal (usually electrons) to provide the co ...
Final Exam
... a) What is the distance from the central axis to the first zero of the light intensity? b) How far in mm from the central axis is the fourth bright fringe? c) Now consider that a 1-mm glass slide (n = 1.52) is inserted behind the top slit. How much will the fringe pattern move along the y-axis? Is i ...
... a) What is the distance from the central axis to the first zero of the light intensity? b) How far in mm from the central axis is the fourth bright fringe? c) Now consider that a 1-mm glass slide (n = 1.52) is inserted behind the top slit. How much will the fringe pattern move along the y-axis? Is i ...
Scanning transmission soft x-ray microscopy at beamline X
... preservation in biological specimens8. This system has also been used for demonstrations of tomographic imaging, including a reconstruction of a frozen hydrated fibroblast at approximately 100x100x250 nm resolution9. Recent studies with the cryoSTXM by T. Beetz of Stony Brook have centered on a more ...
... preservation in biological specimens8. This system has also been used for demonstrations of tomographic imaging, including a reconstruction of a frozen hydrated fibroblast at approximately 100x100x250 nm resolution9. Recent studies with the cryoSTXM by T. Beetz of Stony Brook have centered on a more ...
The Resolving Power Of a Microscope and Telescope
... 1. sin θ must be large. To achieve this, the objective lens is kept as close to the specimen as possible. 2. A higher refractive index (n) medium must be used. Oil immersion microscopes use oil to increase the refractive index. Typically for use in biology studies this is limited to 1.6 to match the ...
... 1. sin θ must be large. To achieve this, the objective lens is kept as close to the specimen as possible. 2. A higher refractive index (n) medium must be used. Oil immersion microscopes use oil to increase the refractive index. Typically for use in biology studies this is limited to 1.6 to match the ...
A Brief History of the Microscope and its Significance
... The second set of technical advances came in the form of scanned image microscopy. First, two very different types of illumination must be explained: Bright-field (wide-field) illumination and point scanning. To explain these terms, more definitions are needed. Bright-field microscopy involves direc ...
... The second set of technical advances came in the form of scanned image microscopy. First, two very different types of illumination must be explained: Bright-field (wide-field) illumination and point scanning. To explain these terms, more definitions are needed. Bright-field microscopy involves direc ...
refl and refr, mirrors
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
... we see images where light appears to come from Consider how light from your eye reflects from a mirror to get to ...
Optical, Confocal, and 4Pi Microscopy
... Table of Figures Figure 1. Basic Optical Microscope (Free Info Society) ............................................................... 4 Figure 2. Optical Path in a Standard Compound Microscope (Hecht 214) ................................... 5 Figure 3. Resolution Equation (Rack) .................. ...
... Table of Figures Figure 1. Basic Optical Microscope (Free Info Society) ............................................................... 4 Figure 2. Optical Path in a Standard Compound Microscope (Hecht 214) ................................... 5 Figure 3. Resolution Equation (Rack) .................. ...
How to turn your microscope into a phase contrast microscope
... professional phase contrast devices, but it can serve its purpose quite well. Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the si ...
... professional phase contrast devices, but it can serve its purpose quite well. Note that, in the absence of any object with shifted phases, the image will always be dark. If there is an object, we will see light, but that does not reveal whether the phase shift is positive or negative. To make the si ...
Chapter 3: Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
... between two separate points, that lie close to each other, as separate and distinct. (structures less than 0.2um cannot be resolved with the compound light microscope) ...
... between two separate points, that lie close to each other, as separate and distinct. (structures less than 0.2um cannot be resolved with the compound light microscope) ...
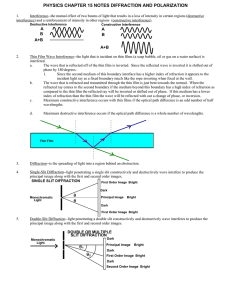
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When the refracted ray comes to the second boundary if the medium beyond this boundary has a high index of ...
... incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When the refracted ray comes to the second boundary if the medium beyond this boundary has a high index of ...
The petrographic microscope
... The petrographic microscope A petrographic microscope is used to observe a series of characteristics in a mineral which reflect its properties and allow us to identify it. The petrographic microscope is a compound microscope which can work with plane polarised light, meaning that it has some peculia ...
... The petrographic microscope A petrographic microscope is used to observe a series of characteristics in a mineral which reflect its properties and allow us to identify it. The petrographic microscope is a compound microscope which can work with plane polarised light, meaning that it has some peculia ...
Slide 1
... source to generate a three-dimensional image – Computer can focus the laser on single layers of the specimen – Cells are (i) either stained with fluorescent dyes, or (ii) different layers in specimen are assigned colors to generate false color images – Different layers are then be compiled for a 3-D ...
... source to generate a three-dimensional image – Computer can focus the laser on single layers of the specimen – Cells are (i) either stained with fluorescent dyes, or (ii) different layers in specimen are assigned colors to generate false color images – Different layers are then be compiled for a 3-D ...
chem 360 Quiz 1 answers
... The device is designed so that beams of light which enter and exit parallel travel different distances. Constructive interference occurs if the extra distance traveled = nλ The constructive interference means that wavelength of light will be transmitted (filter)– or come off at that particular angle ...
... The device is designed so that beams of light which enter and exit parallel travel different distances. Constructive interference occurs if the extra distance traveled = nλ The constructive interference means that wavelength of light will be transmitted (filter)– or come off at that particular angle ...
A short introduction to light and electron microscopy
... the wavelength of the light itself. The diffraction of light by small structural elements in a specimen is the principal process governing image formation in the light microscope. Diffraction and image formation Diffraction and interference are the key principles that determine how a microscope form ...
... the wavelength of the light itself. The diffraction of light by small structural elements in a specimen is the principal process governing image formation in the light microscope. Diffraction and image formation Diffraction and interference are the key principles that determine how a microscope form ...
Microscopes:
... Phase –contrast. Several different forms of phase-contrast are available. Conventional phase is advantageous for looking at live semen, as well as semen “fixed” in an appropriate liquid fixative (e.g. Formal-saline or PBS-Gluteraldehyde). The additional contrast provided by phase means that differen ...
... Phase –contrast. Several different forms of phase-contrast are available. Conventional phase is advantageous for looking at live semen, as well as semen “fixed” in an appropriate liquid fixative (e.g. Formal-saline or PBS-Gluteraldehyde). The additional contrast provided by phase means that differen ...
Depth-of-Focus in Microscopy
... The depth-of-focus (∆z) of a microscope system has been described by a number of authors. Unfortunately, these descriptions do not agree. In general, the authors propose that ∆z should be a function of the wavelength of light, λ , the numerical aperture of the objective lens NA, the index of refract ...
... The depth-of-focus (∆z) of a microscope system has been described by a number of authors. Unfortunately, these descriptions do not agree. In general, the authors propose that ∆z should be a function of the wavelength of light, λ , the numerical aperture of the objective lens NA, the index of refract ...
Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
SWIR (Short Wave Infrared) to Visible Image Up
... A second design option is to use a Liquid Crystal Optical Spatial Light Modulator (LC-OSLM) configuration. In this apparatus, the photoexcited charge carriers induce a localized electric field in the LC, so that the SWIR serves as the writing light. The reading light is a green light that is reflect ...
... A second design option is to use a Liquid Crystal Optical Spatial Light Modulator (LC-OSLM) configuration. In this apparatus, the photoexcited charge carriers induce a localized electric field in the LC, so that the SWIR serves as the writing light. The reading light is a green light that is reflect ...
Phase contrast microscopy (PCM) represents a major breakthrough
... Figure 10. Bright field (a) and phase contrast (b) image of an unstained neuron. The powerful capability of PCM is illustrated in Fig. 10. Phase contrast microscopy is significantly more effective in enhancing contrast than the dark field method. Instead of removing the unscattered light completely ...
... Figure 10. Bright field (a) and phase contrast (b) image of an unstained neuron. The powerful capability of PCM is illustrated in Fig. 10. Phase contrast microscopy is significantly more effective in enhancing contrast than the dark field method. Instead of removing the unscattered light completely ...
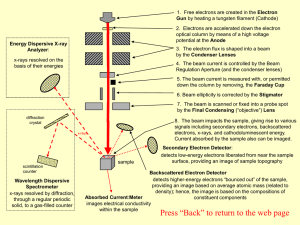
No Slide Title
... 4. The beam current is controlled by the Beam Regulation Aperture (and the condenser lenses) 5. The beam current is measured with, or permitted down the column by removing, the Faraday Cup 6. Beam ellipticity is corrected by the Stigmator 7. The beam is scanned or fixed into a probe spot by the Fina ...
... 4. The beam current is controlled by the Beam Regulation Aperture (and the condenser lenses) 5. The beam current is measured with, or permitted down the column by removing, the Faraday Cup 6. Beam ellipticity is corrected by the Stigmator 7. The beam is scanned or fixed into a probe spot by the Fina ...
Optics Review
... be 3 cm tall? How tall is the object? (tough question!) 14. A 19-cm tall object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens that has a focal length of 14 cm. How far from the lens will the image be formed? How tall is the image? Describe the characteristics of the image. (tough question!) 15. Determine t ...
... be 3 cm tall? How tall is the object? (tough question!) 14. A 19-cm tall object is placed 21 cm from a converging lens that has a focal length of 14 cm. How far from the lens will the image be formed? How tall is the image? Describe the characteristics of the image. (tough question!) 15. Determine t ...
Microbial physiology
... Fluorescence: when a molecule is excited by light at a shorter wavelength, and emits light at a longer wavelength Auto fluorescence: some substances, such as chlorophyll, are naturally fluorescent Fluorescence Microscope: a microscope that excites and detects fluorescent materials Fluorescent Dyes: ...
... Fluorescence: when a molecule is excited by light at a shorter wavelength, and emits light at a longer wavelength Auto fluorescence: some substances, such as chlorophyll, are naturally fluorescent Fluorescence Microscope: a microscope that excites and detects fluorescent materials Fluorescent Dyes: ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.