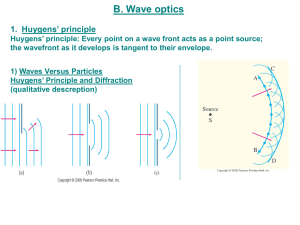
Light Sources
... passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatia ...
... passing through the aperture. (The smaller the aperture, the more it spreads out.) • If we want to image the aperture on an image plane (resist), we can collect the light using a lens and focus it on the image plane. • But the finite diameter of the lens means some information is lost (higher spatia ...
Optics and Optoelectronics
... 1. Ray optics and its limit. Light reflection and refraction. Index of refraction. Total internal reflection. Light reflection and refraction at a plane surfaces. 2. Light reflection and refraction at a spherical surfaces. Convex and concave mirrors. Formation of images by spherical mirrors. Thin le ...
... 1. Ray optics and its limit. Light reflection and refraction. Index of refraction. Total internal reflection. Light reflection and refraction at a plane surfaces. 2. Light reflection and refraction at a spherical surfaces. Convex and concave mirrors. Formation of images by spherical mirrors. Thin le ...
lecture20
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
... As the wavelets propagate from each point, they propagate more slowly in the medium of higher index of refraction. This leads to a bend in the wavefront and therefore in the ray. The frequency of the light does not change, but the wavelength does as it travels into a new medium. ...
Microscopy
... In the third lab, we learned about the basic configuration of the compound microscope. In general, an object you wish to image is 3-dimensional. Although you may wish to image one plane of a specimen, out-of-plane light will cause distortion of your image and make it look blurry. The confocal micros ...
... In the third lab, we learned about the basic configuration of the compound microscope. In general, an object you wish to image is 3-dimensional. Although you may wish to image one plane of a specimen, out-of-plane light will cause distortion of your image and make it look blurry. The confocal micros ...
Microscopy - Frank`s Hospital Workshop
... white light, i.e. illuminated from below and observed from above. Limitations include low contrast of most biological samples and low apparent resolution due to the blur of out of focus material. The simplicity of the technique and the minimal sample preparation required are significant advantages. ...
... white light, i.e. illuminated from below and observed from above. Limitations include low contrast of most biological samples and low apparent resolution due to the blur of out of focus material. The simplicity of the technique and the minimal sample preparation required are significant advantages. ...
Class 12 Optics
... Method: A laser rig (see below picture) is set up where the light is bouncing between mirrors placed on either wall, and at the top so that the laser beam is reflected back upon itself. To view the light, water or chalk dust were sprayed over where the light was passing. Observation: When there was ...
... Method: A laser rig (see below picture) is set up where the light is bouncing between mirrors placed on either wall, and at the top so that the laser beam is reflected back upon itself. To view the light, water or chalk dust were sprayed over where the light was passing. Observation: When there was ...
Single Pixel Cameras wall panels
... of the head, but interestingly, each image is spatially identical. In other words, even though the detectors are in different positions, they do not provide different perspectives. Instead, the location of the detectors determines the apparent illumination in each image, and the perspective of the i ...
... of the head, but interestingly, each image is spatially identical. In other words, even though the detectors are in different positions, they do not provide different perspectives. Instead, the location of the detectors determines the apparent illumination in each image, and the perspective of the i ...
Forensic Science
... objects under investigation are observed side-by-side in a circular field that is equally divided into two parts. •Modern firearms examination began with the introduction of the comparison microscope, with its ability to give the firearms examiner a side-by-side magnified view of bullets. The Stereo ...
... objects under investigation are observed side-by-side in a circular field that is equally divided into two parts. •Modern firearms examination began with the introduction of the comparison microscope, with its ability to give the firearms examiner a side-by-side magnified view of bullets. The Stereo ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy -TEM
... Optical Phase Contrast microscope (useful for biological specimen which absorb little radiation but have different diffraction index with respect to surrounding medium, thus inducing a phase shift) ...
... Optical Phase Contrast microscope (useful for biological specimen which absorb little radiation but have different diffraction index with respect to surrounding medium, thus inducing a phase shift) ...
Light: “God is light, and in him is no darkness at all.” I John
... 1. the light emitted by a lamp 2. heavenly light such as surrounds angels when they appear on earth 3. anything emitting light: star, fire because it is light and sheds light; a lamp or torch 4. me ...
... 1. the light emitted by a lamp 2. heavenly light such as surrounds angels when they appear on earth 3. anything emitting light: star, fire because it is light and sheds light; a lamp or torch 4. me ...
LM Ch 8: Bright Field
... another. Some oils are fluorescent and this would be disastrous if you were doing fluorescence microscopy. Some oils will etch various plastics; you should test this if you use plastic materials to mount your specimens. Remember that the NA of a lens is partly based on the refractive index of the im ...
... another. Some oils are fluorescent and this would be disastrous if you were doing fluorescence microscopy. Some oils will etch various plastics; you should test this if you use plastic materials to mount your specimens. Remember that the NA of a lens is partly based on the refractive index of the im ...
report - CREATE project
... autocorrelation function with nonlinear crystal placed at the microscope output (Fig. 2a). The first imaging test was performed with a piece of paper. We verified that paper absorbs 745 nm through two photon absorption and emits visible light.In order to compare functions of the signal intensity ver ...
... autocorrelation function with nonlinear crystal placed at the microscope output (Fig. 2a). The first imaging test was performed with a piece of paper. We verified that paper absorbs 745 nm through two photon absorption and emits visible light.In order to compare functions of the signal intensity ver ...
Brightfield contrast methods
... How can you specifically alter the phase of the light that is scattered by the specimen? • Using the diffraction gradient as a model for the specimen, the Abbe theory shows that at the back focal plane of the objective, the diffracted (scattered) light is spatially separated from the undiffracted ( ...
... How can you specifically alter the phase of the light that is scattered by the specimen? • Using the diffraction gradient as a model for the specimen, the Abbe theory shows that at the back focal plane of the objective, the diffracted (scattered) light is spatially separated from the undiffracted ( ...
Two-Photon Excited Fluorescence Microscopy - Spectra
... generated everywhere along the optical axis. Upon twophoton absorption at 800 nm, fluorescence is observed exclusively at the focal point of the objective. By using high numerical aperture objectives, fluorescence induced by twophoton absorption can be confined to only a few hundred nanometers of pa ...
... generated everywhere along the optical axis. Upon twophoton absorption at 800 nm, fluorescence is observed exclusively at the focal point of the objective. By using high numerical aperture objectives, fluorescence induced by twophoton absorption can be confined to only a few hundred nanometers of pa ...
Light Tree.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... WDM wide area networks employ tunable lasers and filters at access nodes and optical/electronic switches at routing nodes. An access node may transmit signals on different wavelengths, which are coupled into the fiber using wavelength multiplexers. An optical signal passing through an optical wavele ...
... WDM wide area networks employ tunable lasers and filters at access nodes and optical/electronic switches at routing nodes. An access node may transmit signals on different wavelengths, which are coupled into the fiber using wavelength multiplexers. An optical signal passing through an optical wavele ...
Document
... Feynman “Lectures on Physics” Ch. 30. Diffraction No one has ever been able to define the difference between interference and diffraction satisfactorily … there is no specific, important physical difference between them … roughly speaking … when there are only a few sources, say two, interfering, t ...
... Feynman “Lectures on Physics” Ch. 30. Diffraction No one has ever been able to define the difference between interference and diffraction satisfactorily … there is no specific, important physical difference between them … roughly speaking … when there are only a few sources, say two, interfering, t ...
White-light diffraction tomography of unlabelled live cells
... has been applied to live cells27–30. This type of reconstruction has a complex set-up because of the requirement to either scan the illumination angle or rotate the specimen about a fixed axis. As a result, this method is limited to shallow depths of field31. Importantly, without additional efforts su ...
... has been applied to live cells27–30. This type of reconstruction has a complex set-up because of the requirement to either scan the illumination angle or rotate the specimen about a fixed axis. As a result, this method is limited to shallow depths of field31. Importantly, without additional efforts su ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
Bright Field Microscopy
... Bright Field Microscopy Some specimens are considered amplitude objects because they absorb light partially or completely, and can thus be readily observed using conventional brightfield microscopy. ...
... Bright Field Microscopy Some specimens are considered amplitude objects because they absorb light partially or completely, and can thus be readily observed using conventional brightfield microscopy. ...
Tabletop nanometer extreme ultraviolet imaging in an
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
... (SEM) images, and also removes all negative effects of nonuniform illumination of the sample or imperfect knowledge of the sample position as it is scanned [17]. The result is a general and extensible imaging technique that can provide a comprehensive and definitive characterization of how light at ...
Conroy2005-SurfaceMetrology.pdf
... techniques with modern electronics, computers, and software has produced extremely powerful measurement tools. Typically are two different techniques commonly used in interferometry, phase shifting and scanning white light. Phase-shifting interferometry has proven to be extremely powerful and many c ...
... techniques with modern electronics, computers, and software has produced extremely powerful measurement tools. Typically are two different techniques commonly used in interferometry, phase shifting and scanning white light. Phase-shifting interferometry has proven to be extremely powerful and many c ...
Light and Optics Unit
... know the ray model of light understand and apply the terms transparent, translucent, and opaque understand and apply the terms specular and diffuse reflection Reflection from a Plane Mirror understand and apply the terms angle of incidence, angle of reflection, normal, incident ray, reflec ...
... know the ray model of light understand and apply the terms transparent, translucent, and opaque understand and apply the terms specular and diffuse reflection Reflection from a Plane Mirror understand and apply the terms angle of incidence, angle of reflection, normal, incident ray, reflec ...
Rev.Sci.Instrum.
... inhomogeneity is imparted to the properties of the reflected light. The most well-known imaging technique for visualizing this is Brewster angle microscopy ~BAM!,10,11 which has been successfully employed for characterizing the phase diagrams and the morphology of Langmuir films. BAM is based on the ...
... inhomogeneity is imparted to the properties of the reflected light. The most well-known imaging technique for visualizing this is Brewster angle microscopy ~BAM!,10,11 which has been successfully employed for characterizing the phase diagrams and the morphology of Langmuir films. BAM is based on the ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.