what is light? - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... 29.12 Total Internal Reflection Optical Fibers Optical fibers, sometimes called light pipes, are transparent fibers that pipe light from one place to another. They do this by a series of total internal reflections. Optical fibers are useful for getting light to inaccessible places. Mechanics and ma ...
... 29.12 Total Internal Reflection Optical Fibers Optical fibers, sometimes called light pipes, are transparent fibers that pipe light from one place to another. They do this by a series of total internal reflections. Optical fibers are useful for getting light to inaccessible places. Mechanics and ma ...
Photo = Illusion
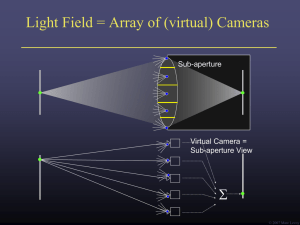
... Wigner Distributions and How They Relate to the Light Field Zhengyun Zhang and Marc Levoy, ICCP 2009 (best paper) Augmenting Light Field to Model Wave Optics Effects , Se Baek Oh, Barbastathis, Raskar (in Preparation) Quasi light fields: extending the light field to coherent radiation , Anthony Acca ...
... Wigner Distributions and How They Relate to the Light Field Zhengyun Zhang and Marc Levoy, ICCP 2009 (best paper) Augmenting Light Field to Model Wave Optics Effects , Se Baek Oh, Barbastathis, Raskar (in Preparation) Quasi light fields: extending the light field to coherent radiation , Anthony Acca ...
5 The Basics of Confocal Microscopy
... fixed specimens ranging in thickness up to 100 micrometers. In fact the confocal microscope is often capable of revealing the presence of single molecule (Peterman, Sosa et al., 2004). Modern confocal microscopes have kept the key elements of Minsky’s design: the pinhole apertures and point by point ...
... fixed specimens ranging in thickness up to 100 micrometers. In fact the confocal microscope is often capable of revealing the presence of single molecule (Peterman, Sosa et al., 2004). Modern confocal microscopes have kept the key elements of Minsky’s design: the pinhole apertures and point by point ...
Chapter 8a Wave Optics
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
... Example 2: two microscope slides each 7.5cm long are in contact along one pair of edges while the other edges are held apart by a piece of paper 0.012mm thick. Calculate the spacing of interference fringes under illumination by light of 632nm wavelength at near normal incidence. Solution: let the a ...
CHAPTER 2: Experimental
... temperatures viz. 75, 100, 125 and 185°C for two hours. The precipitate obtained was washed with methanol and acetone to remove unreacted species and dried under ambient conditions. The same procedure was followed for the synthesis of other lanthanide ions doped samples. 2.5 Synthesis of gallate nan ...
... temperatures viz. 75, 100, 125 and 185°C for two hours. The precipitate obtained was washed with methanol and acetone to remove unreacted species and dried under ambient conditions. The same procedure was followed for the synthesis of other lanthanide ions doped samples. 2.5 Synthesis of gallate nan ...
Reflection of Light
... • Most objects that you can see are nonluminous (you can see them because they reflect light to your eyes). • Most non-luminous objects have rough surfaces and will reflect light in a manner that reveals their shape, colour, and texture. • Some non-luminous objects reflect light is such a way that ...
... • Most objects that you can see are nonluminous (you can see them because they reflect light to your eyes). • Most non-luminous objects have rough surfaces and will reflect light in a manner that reveals their shape, colour, and texture. • Some non-luminous objects reflect light is such a way that ...
No Slide Title
... most common and emit intense light at 253.7 nm (and certain other wavelengths). Because of the limited emission spectra, of the lamp wavelengths are not adjustable. Because of the intensity of the radiation, fixed wavelength detectors can be up to 20 times more sensitive than variable wavelength det ...
... most common and emit intense light at 253.7 nm (and certain other wavelengths). Because of the limited emission spectra, of the lamp wavelengths are not adjustable. Because of the intensity of the radiation, fixed wavelength detectors can be up to 20 times more sensitive than variable wavelength det ...
Slide 1
... The light collected is almost (not perfect) linear proportional to the Etendue of system (smaller one of the Etendues of light source and photodiode) Experiment II: f and Etendue constant, M (p and q) is changed The light intensity collected remains constant. Conclusion: Light collection efficienc ...
... The light collected is almost (not perfect) linear proportional to the Etendue of system (smaller one of the Etendues of light source and photodiode) Experiment II: f and Etendue constant, M (p and q) is changed The light intensity collected remains constant. Conclusion: Light collection efficienc ...
Optical Molasses
... First demonstrated in 1985 by S. Chu Laser cooling first became popular in 1970’s This led to the idea of the Doppler limit ...
... First demonstrated in 1985 by S. Chu Laser cooling first became popular in 1970’s This led to the idea of the Doppler limit ...
Techniques to Improve 3D Optical Imaging
... animal thereby reducing the amount of tissue light propagates through. A direct comparison showing that compression increases signal levels is shown. Reconstructions for a compressed and uncompressed animal models will be shown co-registered to μCT data for cross validation. Sensitivity of fluoresce ...
... animal thereby reducing the amount of tissue light propagates through. A direct comparison showing that compression increases signal levels is shown. Reconstructions for a compressed and uncompressed animal models will be shown co-registered to μCT data for cross validation. Sensitivity of fluoresce ...
From a flat mirror, designer light — Harvard School of Engineering
... who was co-principal investigator for this work. "The reflected beam can bounce backward instead of forward. You can create negative refraction. There is a new angle of total internal reflection." Moreover, the frequency (color), amplitude (brightness), and polarization of the light can also be cont ...
... who was co-principal investigator for this work. "The reflected beam can bounce backward instead of forward. You can create negative refraction. There is a new angle of total internal reflection." Moreover, the frequency (color), amplitude (brightness), and polarization of the light can also be cont ...
Optical diffraction tomography for high resolution live cell imaging
... techniques do not provide quantitative maps of phase change. More advanced phase microscopy techniques have been developed to record quantitative phase images of specimen-induced phase changes [3-7]. These techniques can either provide average refractive index of cells or cell thickness [8-11], but ...
... techniques do not provide quantitative maps of phase change. More advanced phase microscopy techniques have been developed to record quantitative phase images of specimen-induced phase changes [3-7]. These techniques can either provide average refractive index of cells or cell thickness [8-11], but ...
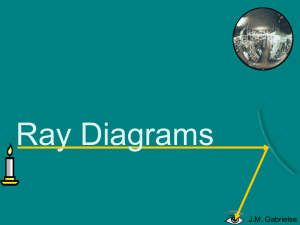
Ray Diagrams
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Reflection-mode scanning near-field optical microscopy: Influence
... actual contact!. This depends on the length of protrusions, generally grains in the metal coating at the tip apex which act as shear-force sensors, as these protrusions come into the point of shear-force contact when the optical aperture is still some distance away from the surface and ~2! the angul ...
... actual contact!. This depends on the length of protrusions, generally grains in the metal coating at the tip apex which act as shear-force sensors, as these protrusions come into the point of shear-force contact when the optical aperture is still some distance away from the surface and ~2! the angul ...
Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... 8. When light is passing from a medium with a high index of refraction to one with a lower index of refraction at the critical angle, what is the angle of refraction? 90o 9. If the light is incident at a greater angle what happens? total internal reflection 10. Describe the lenses (number and type) ...
... 8. When light is passing from a medium with a high index of refraction to one with a lower index of refraction at the critical angle, what is the angle of refraction? 90o 9. If the light is incident at a greater angle what happens? total internal reflection 10. Describe the lenses (number and type) ...
Non-linear Optical Microscopy and Spectroscopy for
... This is a method where the measured signal is analysed with respect to itself at a later time. It is used for analysing the diffusion and the number of large molecules at low concentrations, and is often used in biological environments. In this thesis, the combination of FCS and TPLSM is used for the ...
... This is a method where the measured signal is analysed with respect to itself at a later time. It is used for analysing the diffusion and the number of large molecules at low concentrations, and is often used in biological environments. In this thesis, the combination of FCS and TPLSM is used for the ...
Red Tide Specifications
... OFLV Variable Longpass Order-sorting Filters block second- and third-order light. These filters are optional. ...
... OFLV Variable Longpass Order-sorting Filters block second- and third-order light. These filters are optional. ...
Activity: Emission spectroscopy and smart sensors
... A “Red Tide” CCD detector based spectrometer, A CCD is an acronym for a charge coupled device: Here a linear array of silicon sensors that responds to light. In the spectrometer light is broken down into component wavelengths by an interferometer and the output at each wavelength sensed by the CCD s ...
... A “Red Tide” CCD detector based spectrometer, A CCD is an acronym for a charge coupled device: Here a linear array of silicon sensors that responds to light. In the spectrometer light is broken down into component wavelengths by an interferometer and the output at each wavelength sensed by the CCD s ...
Microscopes - Photonics Research Group
... eyepiece, albeit with residual error of the secondary spectrum and appreciable curvature of field. Early high-resolution compound microscopes were equipped with an (oilimmersible) Abbe condenser whose iris diaphragm, placed at the front focal plane of the condenser, could be off-centered to achieve ...
... eyepiece, albeit with residual error of the secondary spectrum and appreciable curvature of field. Early high-resolution compound microscopes were equipped with an (oilimmersible) Abbe condenser whose iris diaphragm, placed at the front focal plane of the condenser, could be off-centered to achieve ...
BPM Blatt 7
... sphere with a higher refractive index than its background.The relative thickness of the two representative rays (black arrows)symbolizes intensity. The rays are refracted, giving rise to the reaction forces shown acting through the sphere’s center (gray arrows). The brighter right ray conveys more f ...
... sphere with a higher refractive index than its background.The relative thickness of the two representative rays (black arrows)symbolizes intensity. The rays are refracted, giving rise to the reaction forces shown acting through the sphere’s center (gray arrows). The brighter right ray conveys more f ...
11.1 law of reflection and curved mirrors
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
Lens Types
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
... from the object to the lens, z2 is the length from the lens to the focal point, and f is the focal length the equation to find the magnification is , M=-(z2/z1) You would place a sensor at the focal point to get a focused image Convex have a + focal length (image is on the other side of light) Conca ...
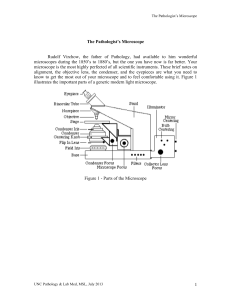
The Pathologist`s Microscope
... specimen; close the condenser iris until you see good contrast without fringes. What good does alignment do? All of the optical corrections of the microscope are designed around Köhler alignment. Due to the effects of diffraction, a misaligned microscope produces false images that may not be recogni ...
... specimen; close the condenser iris until you see good contrast without fringes. What good does alignment do? All of the optical corrections of the microscope are designed around Köhler alignment. Due to the effects of diffraction, a misaligned microscope produces false images that may not be recogni ...
Phys405-Chapter1
... spectrum, u v cn , where cn = c/n and n is the index of refraction of the medium.. In certain cases either u or v or both may be greater than cn; however when ucn, it can no longer be interpreted as the velocity with which energy propagates, i.e., the simple analysis given above no longer holds ...
... spectrum, u v cn , where cn = c/n and n is the index of refraction of the medium.. In certain cases either u or v or both may be greater than cn; however when ucn, it can no longer be interpreted as the velocity with which energy propagates, i.e., the simple analysis given above no longer holds ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.