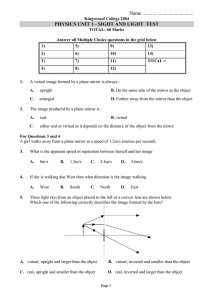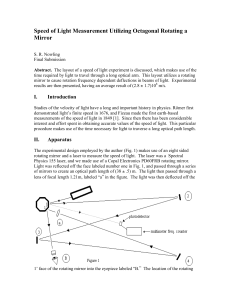
Speed of Light Measurement Utilizing Octagonal
... frequency. The main obstacle in these measurements will be to have a beam intense enough to view. Because our optical path length, lensÕ focal length, and rotational frequencies were low intensity was not a problem. However, increasing any of these will result in energy losses, which may effect visi ...
... frequency. The main obstacle in these measurements will be to have a beam intense enough to view. Because our optical path length, lensÕ focal length, and rotational frequencies were low intensity was not a problem. However, increasing any of these will result in energy losses, which may effect visi ...
The Compound Microscope
... • The stereoscopic microscope is actually two monocular compound microscopes properly spaced and aligned to present a three-dimensional image of a specimen to the viewer, who looks through both eyepiece lenses. • It is particularly useful for evidence not requiring very high magnification (10x–125x) ...
... • The stereoscopic microscope is actually two monocular compound microscopes properly spaced and aligned to present a three-dimensional image of a specimen to the viewer, who looks through both eyepiece lenses. • It is particularly useful for evidence not requiring very high magnification (10x–125x) ...
TEM - UiO
... Many beams are allowed to pass through the objective aperture (as opposed to bright and dark field where only one beam pases at the time). To obtain lattice images, a large objective aperture has to be selected that allows many beams to pass including the direct beam. The image is formed by the inte ...
... Many beams are allowed to pass through the objective aperture (as opposed to bright and dark field where only one beam pases at the time). To obtain lattice images, a large objective aperture has to be selected that allows many beams to pass including the direct beam. The image is formed by the inte ...
Total intensity and quasi-elastic light
... obscure this interpretation. Nonetheless, light-scattering methods can provide a powerful probe into the structure and dynamics of microbial systems, a probe which unlike electron microscopy, is nondestructive [ 13. For smaller microbes like many spherical plant viruses, the simpler Rayleigh-Gans-De ...
... obscure this interpretation. Nonetheless, light-scattering methods can provide a powerful probe into the structure and dynamics of microbial systems, a probe which unlike electron microscopy, is nondestructive [ 13. For smaller microbes like many spherical plant viruses, the simpler Rayleigh-Gans-De ...
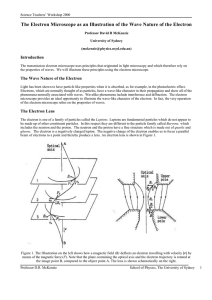
The Electron Microscope as an Illustration of the Wave Nature of the
... In the electron microscope, the source of electrons is a heated filament of tungsten, from which the electrons are emitted or “boiled off”. In advanced forms of the electron microscope the source is very bright and is made from a sharp metal tip from which electrons are drawn out by an electric fiel ...
... In the electron microscope, the source of electrons is a heated filament of tungsten, from which the electrons are emitted or “boiled off”. In advanced forms of the electron microscope the source is very bright and is made from a sharp metal tip from which electrons are drawn out by an electric fiel ...
Image formation with broad bundles of rays
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
... The change in phase along different rays between points of intersection with two given wave surfaces is the same. The total change in phase between the points O and O’ is the same for the different rays. The optical path length y is the same for all these rays. ...
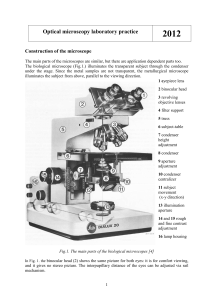
Optical microscopy laboratory practice 2012
... 5. Objective: The lens closest to the object being viewed which creates a magnified image in an area called the "primary image plane". This is the other half of the microscope magnification equation (eyepiece power times objective power equals magnification). Objective lenses have many designs and q ...
... 5. Objective: The lens closest to the object being viewed which creates a magnified image in an area called the "primary image plane". This is the other half of the microscope magnification equation (eyepiece power times objective power equals magnification). Objective lenses have many designs and q ...
FIB – an easy tool for fabrication of high quality plasmonic structures
... TESCAN LYRA3. This device integrates a high resolution Shottky FEG-SEM column and a high performance FIB with ultra-high resolution. This equipment enables fast and accurate production of excitation slits and other plasmonic structures, crucial for experimental detection using SNOM. ...
... TESCAN LYRA3. This device integrates a high resolution Shottky FEG-SEM column and a high performance FIB with ultra-high resolution. This equipment enables fast and accurate production of excitation slits and other plasmonic structures, crucial for experimental detection using SNOM. ...
Young`s Double Slits
... The two laser sources you will be using emit green and red visible light. Both are categorised as class 2 sources and thus defined to be eye safe (i.e. the human blink reflex will be sufficient to prevent damaging exposure), having a power output < 1mW. However, you must never look directly into the ...
... The two laser sources you will be using emit green and red visible light. Both are categorised as class 2 sources and thus defined to be eye safe (i.e. the human blink reflex will be sufficient to prevent damaging exposure), having a power output < 1mW. However, you must never look directly into the ...
Total 3D imaging of phase objects using defocusing microscopy
... defocusing the microscope, since the act of defocusing introduces a phase difference between the diffracted orders and the non-diffracted transmitted order (zero order). From contrast intensity measurements of images in two focal positions, one can obtain information about the phase of the optical e ...
... defocusing the microscope, since the act of defocusing introduces a phase difference between the diffracted orders and the non-diffracted transmitted order (zero order). From contrast intensity measurements of images in two focal positions, one can obtain information about the phase of the optical e ...
Click To
... replaces a single focal plane array detector with two focal plane array detectors orientated with respect to each other such that a power splitter divides an incoming light source equally between each detector. ...
... replaces a single focal plane array detector with two focal plane array detectors orientated with respect to each other such that a power splitter divides an incoming light source equally between each detector. ...
Chapter 9. Computer vision
... frequency, then the sinusoid will continue to be a sinusoid and the contras will continue to be one. The ideal mathematical model ignores the effect of noise in the signal. Noise will be an important factor in coherent imaging. The presence of foreign particulates in the optical system will cause li ...
... frequency, then the sinusoid will continue to be a sinusoid and the contras will continue to be one. The ideal mathematical model ignores the effect of noise in the signal. Noise will be an important factor in coherent imaging. The presence of foreign particulates in the optical system will cause li ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... Carry out experiments in sequence with square mesh object as shown in Table 2. Place the square mesh in vertical orientation. Mark the locations of the Fourier image dots which are on the x- and y-axis with a white paper pasted on an index card. These locations will be useful to make various spatial ...
... Carry out experiments in sequence with square mesh object as shown in Table 2. Place the square mesh in vertical orientation. Mark the locations of the Fourier image dots which are on the x- and y-axis with a white paper pasted on an index card. These locations will be useful to make various spatial ...
1. Modern Optics: Introduction - University of Toronto Physics
... Prisms disperse white light into its various colors. ...
... Prisms disperse white light into its various colors. ...
Micro Chapter 3 ppt 11th edition
... The refractive index is a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium The light may bend in air so much that it misses the small high-magnification lens Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending ...
... The refractive index is a measure of the light-bending ability of a medium The light may bend in air so much that it misses the small high-magnification lens Immersion oil is used to keep light from bending ...
Physics 300 - WordPress.com
... B • If the angle of incidence (for light on a plane boundary) is increased beyond the critical angle… a. the angle of refraction will decrease c. the light will not reflect at all b. total internal reflection will occur d. the frequency of the light will shift B • When the an opening (through which ...
... B • If the angle of incidence (for light on a plane boundary) is increased beyond the critical angle… a. the angle of refraction will decrease c. the light will not reflect at all b. total internal reflection will occur d. the frequency of the light will shift B • When the an opening (through which ...
Class07
... Optical Waveguides Summary • Dispersion means spreading • Signals in a fiber will have several sources of dispersion: – Chromatic: • Material: index of refraction depends on wavelength (prism) • Waveguide: some of wave travels through cladding with different index of refraction (primarily single-mo ...
... Optical Waveguides Summary • Dispersion means spreading • Signals in a fiber will have several sources of dispersion: – Chromatic: • Material: index of refraction depends on wavelength (prism) • Waveguide: some of wave travels through cladding with different index of refraction (primarily single-mo ...
11. Electro
... If the photon encounters another atom that has an electron in the same excited state, it can induce the electron to lose its energy in turn (called stimulated emission) The first photon can stimulate atomic emission such that the photon from the second atom has the same frequency and direction a ...
... If the photon encounters another atom that has an electron in the same excited state, it can induce the electron to lose its energy in turn (called stimulated emission) The first photon can stimulate atomic emission such that the photon from the second atom has the same frequency and direction a ...
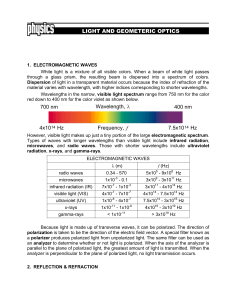
700 nm 400 nm Wavelength, λ Frequency, f 4x1014 Hz
... This relationship is known as Snell’s Law. If light rays traveling in a medium with a high index of refraction strike a second medium with a lower index of refraction at an angle that is large enough, the rays cannot ...
... This relationship is known as Snell’s Law. If light rays traveling in a medium with a high index of refraction strike a second medium with a lower index of refraction at an angle that is large enough, the rays cannot ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy
... criterion (δ ~ 0.61⋅λ), which limits the spatial resolution to the wavelength. The use of highenergy electrons on TEM, i.e. smaller wavelengths, enhances the achievable spatial resolution up to the 10-10 m scale. - Simultaneous acquisition of different signals: As mentioned before, TEM instrumentati ...
... criterion (δ ~ 0.61⋅λ), which limits the spatial resolution to the wavelength. The use of highenergy electrons on TEM, i.e. smaller wavelengths, enhances the achievable spatial resolution up to the 10-10 m scale. - Simultaneous acquisition of different signals: As mentioned before, TEM instrumentati ...
doc - The Crowned Anarchist Literature
... however, which led not only to the demise of the ether theory, but to the development of the Special Theory of Relativity by Albert Einstein 18 years later. Historically, the best-known interferometer is the one devised about 1887 by the American physicist Albert Michelson for an experiment he cond ...
... however, which led not only to the demise of the ether theory, but to the development of the Special Theory of Relativity by Albert Einstein 18 years later. Historically, the best-known interferometer is the one devised about 1887 by the American physicist Albert Michelson for an experiment he cond ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
Lecture 5. Confocal microscopy and instrumentation I
... Dye lasers are tunable and covers broad spectrum, but very difficult to operate. None appropriate for 2-p absorption, wrong colors, low power ...
... Dye lasers are tunable and covers broad spectrum, but very difficult to operate. None appropriate for 2-p absorption, wrong colors, low power ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.