Microscope Power Point File
... hair strand, or pond scum. Unfortunately, they do not have excellent resolution, so the image may be blurry. On the other hand, stereoscopic microscopes, as the name implies, provide a 3-D picture of bisected items, like muscle tissue or an organ. In this case, magnification is poor, so you can't ma ...
... hair strand, or pond scum. Unfortunately, they do not have excellent resolution, so the image may be blurry. On the other hand, stereoscopic microscopes, as the name implies, provide a 3-D picture of bisected items, like muscle tissue or an organ. In this case, magnification is poor, so you can't ma ...
50 GHz Velocity-matched, Broad Wavelength LiNbO3
... M-Z modulators were fabricated in both x and z cut LiNb0 3 as well as straight guides and y-junctions (one-half of an interferometer). It was verified that the 6 p.m straight guides supported at least two modes at 1.3 p.m wavelength. When y-junctions were excited at the 4 p.m end, however, only the ...
... M-Z modulators were fabricated in both x and z cut LiNb0 3 as well as straight guides and y-junctions (one-half of an interferometer). It was verified that the 6 p.m straight guides supported at least two modes at 1.3 p.m wavelength. When y-junctions were excited at the 4 p.m end, however, only the ...
852_1.pdf
... characteristic inversion of the profile when the surface acoustic wave reaches the second probe beam. The time delay required for the SAW to travel 4.5 mm (beam separation distance) gives a straightforward method to estimate SAW phase velocity. In an agarose gel specimen, SAW velocity is 40.9 cm/s. ...
... characteristic inversion of the profile when the surface acoustic wave reaches the second probe beam. The time delay required for the SAW to travel 4.5 mm (beam separation distance) gives a straightforward method to estimate SAW phase velocity. In an agarose gel specimen, SAW velocity is 40.9 cm/s. ...
Department of Physics, Technical University Ostrava 17. listopadu
... not compensated for dispersion [17]. In this paper, a spectral-domain white-light interferometric technique of measuring the effective thickness of optical elements of known dispersion is presented when a Michelson interferometer with a cube beam splitter is not compensated for dispersion and when t ...
... not compensated for dispersion [17]. In this paper, a spectral-domain white-light interferometric technique of measuring the effective thickness of optical elements of known dispersion is presented when a Michelson interferometer with a cube beam splitter is not compensated for dispersion and when t ...
21. Specific rotation of sugar solution
... (see the left or the right part of the Figure 21.2). In case of the focused image, the bright and the dark side are clearly separated. 3. Scroll to the zero position of the polarimeter. For that purpose turn the analyzer to a position where the entire field of view of the telescope is illuminated un ...
... (see the left or the right part of the Figure 21.2). In case of the focused image, the bright and the dark side are clearly separated. 3. Scroll to the zero position of the polarimeter. For that purpose turn the analyzer to a position where the entire field of view of the telescope is illuminated un ...
Was there a measurable power received when
... yards per microsecond. In more common units, they travel nearly 186; 000 miles per second or 3x108 m/s. In almost any other medium the velocity of the waves differ from their velocity in a vacuum, and signals of different frequencies travel with different velocities. Visible light, for example, trav ...
... yards per microsecond. In more common units, they travel nearly 186; 000 miles per second or 3x108 m/s. In almost any other medium the velocity of the waves differ from their velocity in a vacuum, and signals of different frequencies travel with different velocities. Visible light, for example, trav ...
How can I tell what the polarization axis is for a linear polarizer? The
... T|| = maximum transmittance of two polarizers parallel in unpolarized beam T⊥ = minimum transmittance of two polarizers perpendicular in unpolarized beam Note: all "T" values are for monochromatic light. Example : If using an unpolarized light source, a direct reading of the extinction ratio is not ...
... T|| = maximum transmittance of two polarizers parallel in unpolarized beam T⊥ = minimum transmittance of two polarizers perpendicular in unpolarized beam Note: all "T" values are for monochromatic light. Example : If using an unpolarized light source, a direct reading of the extinction ratio is not ...
Bragg waveguides with low-index liquid cores
... This effect was also demonstrated in the regime of low refractive index contrast by Qu and Skorobogatiy [27] where an application to bulk refractive index sensing was demonstrated: a sensitivity of ≈ 1400 nm/RIU was achieved for aqueous solutions of salt (indices from ≈ 1.33 to 1.38). As discussed ...
... This effect was also demonstrated in the regime of low refractive index contrast by Qu and Skorobogatiy [27] where an application to bulk refractive index sensing was demonstrated: a sensitivity of ≈ 1400 nm/RIU was achieved for aqueous solutions of salt (indices from ≈ 1.33 to 1.38). As discussed ...
Three-dimensional digitization of highly reflective and transparent
... points of a light beam from the light source to a surface point. Kutulakos et al. [7,15] developed an algorithm in which they assume that one reflection event exactly occurs along the ray. Measuring the reflected and the observed ray, a surface position and its associated normal direction are recove ...
... points of a light beam from the light source to a surface point. Kutulakos et al. [7,15] developed an algorithm in which they assume that one reflection event exactly occurs along the ray. Measuring the reflected and the observed ray, a surface position and its associated normal direction are recove ...
1 Janaky Narayanan PC 5213 AY 2004
... atoms that are obtained when parts of the molecule are rotated about one of the bonds. A change in the conformation necessarily does not involve any breaking of covalent bonds. Groups that are connected by a single bond can undergo rotation leading to different relative orientations with respect to ...
... atoms that are obtained when parts of the molecule are rotated about one of the bonds. A change in the conformation necessarily does not involve any breaking of covalent bonds. Groups that are connected by a single bond can undergo rotation leading to different relative orientations with respect to ...
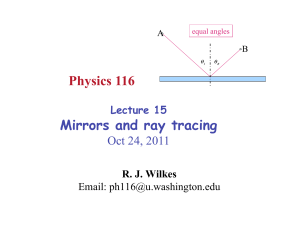
Physics 116 Mirrors and ray tracing
... –! Rays of light appear to come from image plane when viewed, but never actually converge in space •! You can view a virtual image, but cannot capture it on a screen (or film or video camera) –! Of course, a camera (lens system) can view it, and record it that way ...
... –! Rays of light appear to come from image plane when viewed, but never actually converge in space •! You can view a virtual image, but cannot capture it on a screen (or film or video camera) –! Of course, a camera (lens system) can view it, and record it that way ...
Writing a superlattice with light forces
... standing light waves. For the λ/ 2 lattice, an interference pattern with four laser beams that were polarized perpendicular to the substrate plane was used. Another way of switching between these two lattice periods is to change the relative phase between the two standing light waves. In the situati ...
... standing light waves. For the λ/ 2 lattice, an interference pattern with four laser beams that were polarized perpendicular to the substrate plane was used. Another way of switching between these two lattice periods is to change the relative phase between the two standing light waves. In the situati ...
Interference of Light waves Wave Optics
... different media, one of lower index than the film and one of higher index, the conditions for constructive and destructive interference are reversed With different materials on either side of the film, you may have a situation in which there is a 180o phase change at both surfaces or at neither surf ...
... different media, one of lower index than the film and one of higher index, the conditions for constructive and destructive interference are reversed With different materials on either side of the film, you may have a situation in which there is a 180o phase change at both surfaces or at neither surf ...
Enhanced transmission in near-field imaging of layered plasmonic
... excitation. Such resonance in the gap can be thought of an an optical LC circuit, where the gap provides the effect of optical capacitance and the metal particles provide optical inductance [7]. For coupling between the two particles, the local illumination induces a z-direction resonance in the sy ...
... excitation. Such resonance in the gap can be thought of an an optical LC circuit, where the gap provides the effect of optical capacitance and the metal particles provide optical inductance [7]. For coupling between the two particles, the local illumination induces a z-direction resonance in the sy ...
Wavefront control of UV narrow bandpass filters prepared
... As a coating process sensitive property, mechanical stress of metal oxide films has been an interesting research topic for UV optics.13 In general, metal oxide films prepared by electron-beam reactive evaporation with substrate temperatures in the range 20oC to 300oC, may exhibit tensile or compress ...
... As a coating process sensitive property, mechanical stress of metal oxide films has been an interesting research topic for UV optics.13 In general, metal oxide films prepared by electron-beam reactive evaporation with substrate temperatures in the range 20oC to 300oC, may exhibit tensile or compress ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.