Document
... excited state to create a population inversion. Then, an input photon with a particular wavelength strikes an excited atom of the medium and pushes it back to a lower energy state to emit a photon with the same wavelength and in phase and in the same direction as the input photon. The process is cal ...
... excited state to create a population inversion. Then, an input photon with a particular wavelength strikes an excited atom of the medium and pushes it back to a lower energy state to emit a photon with the same wavelength and in phase and in the same direction as the input photon. The process is cal ...
Critical angle - Kelso High School
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... Cells from the human dermis after lysis form a protective coating. Butterfly epidermal cells also form a coating upon cell death. According to H. Ghiradella “…scales are highly structures, scale formation is a virtuoso exercise in biological pattern formation at the cellular level”. The scales chang ...
... Cells from the human dermis after lysis form a protective coating. Butterfly epidermal cells also form a coating upon cell death. According to H. Ghiradella “…scales are highly structures, scale formation is a virtuoso exercise in biological pattern formation at the cellular level”. The scales chang ...
n - LSU Physics
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). • How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg ...
Slide
... The two parallel beams leaving the film at A and C can be brought together by a converging lens The wavelength of light n in a medium of refractive index n is given by n = 0 /n, where 0 is the wavelength in air The optical path difference (OPD) for normal incidence is (AB+BC) times the refractiv ...
... The two parallel beams leaving the film at A and C can be brought together by a converging lens The wavelength of light n in a medium of refractive index n is given by n = 0 /n, where 0 is the wavelength in air The optical path difference (OPD) for normal incidence is (AB+BC) times the refractiv ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
Physics 234 Exam # 2 Review
... (d) What are the electric and magnetic field amplitudes (rms) near the earth’s surface (due to the solar radiation)? ...
... (d) What are the electric and magnetic field amplitudes (rms) near the earth’s surface (due to the solar radiation)? ...
Sample Problems for Final
... Problem 3 Two narrow slits are separated by 10 microns. Light that passes through the slits illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central ...
... Problem 3 Two narrow slits are separated by 10 microns. Light that passes through the slits illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central ...
No Slide Title
... •What is the phase difference in the beams when they come out? The difference in wavelengths is Ns-Ng=496.41. Each wavelength is 360o, so DN=496.41 means Df=DNx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) DN=D/ ...
... •What is the phase difference in the beams when they come out? The difference in wavelengths is Ns-Ng=496.41. Each wavelength is 360o, so DN=496.41 means Df=DNx360o=0.41x360o=148o •How thick should the glass be so that the beams are exactly out of phase at the exit (destructive interference!) DN=D/ ...
Lecture 28 - LSU Physics
... distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). •How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg=0.625µm/1.46= 0.428 µm and Ng=D/ λg=2336.45 In sapphire, λs=0.625µm/1.77= 0.3 ...
... distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). •How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? In glass, λg=0.625µm/1.46= 0.428 µm and Ng=D/ λg=2336.45 In sapphire, λs=0.625µm/1.77= 0.3 ...
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Document
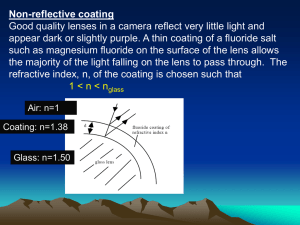
... of a glass surface is to coat it with an antireflection (AR) coating (giving an ARC). A good ARC can cut the percentage of light reflected from >5% to <0.2%. One example is the purple colored ARC on binocular and camera lens. Catalogs for optical equipment will often indicate whether the lens has an ...
... of a glass surface is to coat it with an antireflection (AR) coating (giving an ARC). A good ARC can cut the percentage of light reflected from >5% to <0.2%. One example is the purple colored ARC on binocular and camera lens. Catalogs for optical equipment will often indicate whether the lens has an ...
Double Layer Anti Reflection Coatings
... Solar cell design involves specifying the parameters of a solar cell structure in order to maximize efficiency, given a certain set of constraints. working environment in which solar cells are produced power. commercial environment: a competitively priced solar cell the cost of solar cell struct ...
... Solar cell design involves specifying the parameters of a solar cell structure in order to maximize efficiency, given a certain set of constraints. working environment in which solar cells are produced power. commercial environment: a competitively priced solar cell the cost of solar cell struct ...
Chapter 35 Light: Reflection and Refraction
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
... At some critical angle of incidence, θc, the light is totally reflected back into the medium of higher refractive index. This is called the total internal reflection and was first noted by Kepler in 1604. ...
Lecture_Feb18_2015
... as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is the square root of the dielectric constant for non-magnetic materials. ...
... as the fraction of light transmitted versus reflected (Fresnel Equations). • By conservation of energy, R + T = 1 • The index of refraction has a real and imaginary part, and is the square root of the dielectric constant for non-magnetic materials. ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.