lab11
... The speed of light and other wave properties in a coaxial cable Object: Time the speed of travel of a pulse along a coaxial cable to determine the speed of light in the material, and to investigate the nature of terminating the cable. Prior to Lab: Look up in an appropriate handbook the dielectric c ...
... The speed of light and other wave properties in a coaxial cable Object: Time the speed of travel of a pulse along a coaxial cable to determine the speed of light in the material, and to investigate the nature of terminating the cable. Prior to Lab: Look up in an appropriate handbook the dielectric c ...
Full Text PDF
... of the interparticle scattering of light. Their analysis employs a modified version of the Korringa—Kohn—Rostoker (KKR)` procedure used in the calculation of electron-energy-bands in solids. It yields an effective propagation wave vector in an infinite crystal and as such is related to a transmissio ...
... of the interparticle scattering of light. Their analysis employs a modified version of the Korringa—Kohn—Rostoker (KKR)` procedure used in the calculation of electron-energy-bands in solids. It yields an effective propagation wave vector in an infinite crystal and as such is related to a transmissio ...
Deliverable 9: Blueprints of ICT relevant demonstrators As pointed
... As pointed out in the original PHOME proposal, using chiral metamaterials can be used as thin-film optical isolators. In addition, we have proposed to use photonic metamaterials that can be used as tunable switches at THz frequencies, and finally we have proposed to use photonic metamaterials for el ...
... As pointed out in the original PHOME proposal, using chiral metamaterials can be used as thin-film optical isolators. In addition, we have proposed to use photonic metamaterials that can be used as tunable switches at THz frequencies, and finally we have proposed to use photonic metamaterials for el ...
SI - ECE@NUS
... them have been supported by some experiments [2, 3]. However, it is more reasonable in the current paper to use the Minkowski formula in the force calculation due to the following reasons. First, our target is not only to prove the suitability of a certain momentum formula, but also to find the obse ...
... them have been supported by some experiments [2, 3]. However, it is more reasonable in the current paper to use the Minkowski formula in the force calculation due to the following reasons. First, our target is not only to prove the suitability of a certain momentum formula, but also to find the obse ...
Optical Basicity and Polarizability of Nd3+
... where X Bi2 O3 , X Li2 O , X ZnO , X B2 O3 , X Nd 2 O3 are the molar fraction of the constituent oxides and Z Bi2O3 , Z Li2O , Z ZnO , Z B2 O3 , Z Nd 2 O3 are the molar weights of the constituent oxides. Refractive index measurement Refractive index is another important property to be considered wit ...
... where X Bi2 O3 , X Li2 O , X ZnO , X B2 O3 , X Nd 2 O3 are the molar fraction of the constituent oxides and Z Bi2O3 , Z Li2O , Z ZnO , Z B2 O3 , Z Nd 2 O3 are the molar weights of the constituent oxides. Refractive index measurement Refractive index is another important property to be considered wit ...
Optical Broadband Angular Selectivity Yichen Shen, Dexin Ye, Ivan Celanovic,
... An angularly selective material-system should ideally work over a broadband spectrum. Such a system could potentially play a crucial role in many applications, such as high efficiency solar energy conversion (9, 10), privacy protection (11), and detectors with high signal-to-noise ratios. Some progr ...
... An angularly selective material-system should ideally work over a broadband spectrum. Such a system could potentially play a crucial role in many applications, such as high efficiency solar energy conversion (9, 10), privacy protection (11), and detectors with high signal-to-noise ratios. Some progr ...
Lecture 13: Heisenberg and Uncertainty
... 0.5*10-6 m = 0.5 μm = 500 nm in size. This is because visible light, with a wavelength of ~500 nm cannot resolve objects whose size is smaller than it’s wavelength. ...
... 0.5*10-6 m = 0.5 μm = 500 nm in size. This is because visible light, with a wavelength of ~500 nm cannot resolve objects whose size is smaller than it’s wavelength. ...
Playing with Light
... Activity 3: Emission Spectroscopy of Sparklers and Candles 1. This activity should be performed entirely in a fume hood. Be careful with open flames. You should have the following: a set of colored candles, several colored sparklers, and ...
... Activity 3: Emission Spectroscopy of Sparklers and Candles 1. This activity should be performed entirely in a fume hood. Be careful with open flames. You should have the following: a set of colored candles, several colored sparklers, and ...
Efficient visible light detection using individual germanium nanowire
... sensitive optical response especially in the low intensity regime. We observe a high internal gain in PC in conjunction with strong saturation behavior, which is attributed to the filling of surface trapping states. This mechanism for high internal gain is consistent with spatially resolved scanning ...
... sensitive optical response especially in the low intensity regime. We observe a high internal gain in PC in conjunction with strong saturation behavior, which is attributed to the filling of surface trapping states. This mechanism for high internal gain is consistent with spatially resolved scanning ...
Mirror contamination in space I: mirror modelling
... Our hypothesis is that both scan mirrors and surface diffusers suffer from a thin absorbing layer of contaminant, which slowly builds up over time. Many previous studies of such contaminant layers that form on mirrors and/or diffusers in space have been performed. However, despite their good quality ...
... Our hypothesis is that both scan mirrors and surface diffusers suffer from a thin absorbing layer of contaminant, which slowly builds up over time. Many previous studies of such contaminant layers that form on mirrors and/or diffusers in space have been performed. However, despite their good quality ...
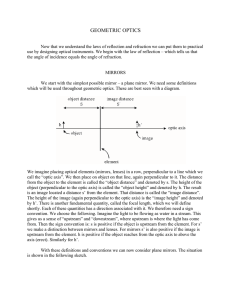
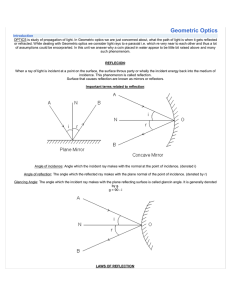
Geometric Optics - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
... OPTICS is study of propagation of light. In Geometric optics we are just concerned about, what the path of light is when it gets reflected or refracted. While dealing with Geometric optics we consider light rays to e paraxial i.e. which re very near to each other and thus a lot of assumptions could ...
The Double Etalon filter in Vernier configuration
... When using identical Etalons, this difference cannot be practically achieved by simple changes in the refractive index: if, for instance, temperature is used to modulate n, too large thermal control should be required to achieve the proper conditions. It follows the need to setup since the beginning ...
... When using identical Etalons, this difference cannot be practically achieved by simple changes in the refractive index: if, for instance, temperature is used to modulate n, too large thermal control should be required to achieve the proper conditions. It follows the need to setup since the beginning ...
Reduction of ocular chromatic aberration by a blue light filtering
... 1. Thibos LN, Bradley A, Zhang XX. Effect of ocular chromatic aberration on monocular visual performance. Optom Vis Sci. 1991;68:599-607. 2. Rieger G. Improvement of contrast sensitivity with yellow filter glasses. Can J Ophthalmol. 1992;27:137-138. 3. Manzanera S, Piers P, Weeber H, Artal P. Visual ...
... 1. Thibos LN, Bradley A, Zhang XX. Effect of ocular chromatic aberration on monocular visual performance. Optom Vis Sci. 1991;68:599-607. 2. Rieger G. Improvement of contrast sensitivity with yellow filter glasses. Can J Ophthalmol. 1992;27:137-138. 3. Manzanera S, Piers P, Weeber H, Artal P. Visual ...
Document
... the indices of refraction are plotted as radii that are parallel to the vibration direction of light. In isotropic minerals the indicatrix was a sphere, because the refractive index was the same in all directions. In uniaxial minerals, because n omega and n epsilon are not equal, the indicatrix ...
... the indices of refraction are plotted as radii that are parallel to the vibration direction of light. In isotropic minerals the indicatrix was a sphere, because the refractive index was the same in all directions. In uniaxial minerals, because n omega and n epsilon are not equal, the indicatrix ...
375_Lo.pdf
... phase retardation are correctly chosen. It should be noticed that the dynamic range in measuring the apparent phase retardation is restricted in the range of 0~90°. Thus, the measured apparent phase retardation is needed to be verified and modified by the above reason and the further discussion is i ...
... phase retardation are correctly chosen. It should be noticed that the dynamic range in measuring the apparent phase retardation is restricted in the range of 0~90°. Thus, the measured apparent phase retardation is needed to be verified and modified by the above reason and the further discussion is i ...
Red Tide Specifications
... and then reflects off the Collimating Mirror onto the Grating. Diffracts light from the Collimating Mirror and directs the diffracted light onto the Focusing Mirror. Only Ocean Optics technicians can change the Grating. ...
... and then reflects off the Collimating Mirror onto the Grating. Diffracts light from the Collimating Mirror and directs the diffracted light onto the Focusing Mirror. Only Ocean Optics technicians can change the Grating. ...
A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism
... therefore obtain the numerical value of some property of the medium, such as the velocity with which a disturbance is propagated through it, which can be calculated from electromagnetic experiments, and al ...
... therefore obtain the numerical value of some property of the medium, such as the velocity with which a disturbance is propagated through it, which can be calculated from electromagnetic experiments, and al ...
Analytical Expression for the Standing Wave Intensity in Photoresist
... paper presents an analytical expression for the standing wave intensity within a thin film. This film may be homogeneous or of a known inhomogeneity. The film may be on a substrate or between one or more other thin films. Finally, applications of this expression are given for photoresist exposure. ...
... paper presents an analytical expression for the standing wave intensity within a thin film. This film may be homogeneous or of a known inhomogeneity. The film may be on a substrate or between one or more other thin films. Finally, applications of this expression are given for photoresist exposure. ...
The Faraday Effect
... optical activity, occurring in sugar solutions. In a sugar solution, the optical rotation proceeds in the same direction, whichever way the light is directed. In particular, when a beam is reflected back through the solution it emerges with the same polarization as it entered before reflection. In t ...
... optical activity, occurring in sugar solutions. In a sugar solution, the optical rotation proceeds in the same direction, whichever way the light is directed. In particular, when a beam is reflected back through the solution it emerges with the same polarization as it entered before reflection. In t ...
PART 3_ir spectra_01
... An interferogram is generated because of the unique optics of an FT-IR instrument. The key components are a moveable mirror and beam splitter. The moveable mirror is responsible for the quality of the interferogram, and it is very important to move the mirror at constant speed. For this reason, the ...
... An interferogram is generated because of the unique optics of an FT-IR instrument. The key components are a moveable mirror and beam splitter. The moveable mirror is responsible for the quality of the interferogram, and it is very important to move the mirror at constant speed. For this reason, the ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.