HW2 Solutions
... first order with m=1 is R= 14800 since the total number of lines is N=3700*4=14800. Tipler 33.P.080 A radio telescope is situated at the edge of a lake. The telescope is looking at light from a radio galaxy that is just rising over the horizon. If the height of the antenna is 16 m above the surface ...
... first order with m=1 is R= 14800 since the total number of lines is N=3700*4=14800. Tipler 33.P.080 A radio telescope is situated at the edge of a lake. The telescope is looking at light from a radio galaxy that is just rising over the horizon. If the height of the antenna is 16 m above the surface ...
Supplementary Methods and References
... profile. Therefore, the drOPD quantifies the changing (increasing or decreasing) optical density within the gate, and its mean heterogeneity. Numerical simulation to illustrate depth-resolved drOPD imaging Figure S1 illustrates the concept of depth-resolved imaging with numerical simulation. To perf ...
... profile. Therefore, the drOPD quantifies the changing (increasing or decreasing) optical density within the gate, and its mean heterogeneity. Numerical simulation to illustrate depth-resolved drOPD imaging Figure S1 illustrates the concept of depth-resolved imaging with numerical simulation. To perf ...
HERCULES_Neutron_reflectivity
... usually possible to distinguish between the a/b and c/d pairs from knowledge of the properties of the bulk media involved, but determining which of each pair is in question is problematic for very thin films ( 50Å), when the experimentally accessible q-range does not allow the observation of inter ...
... usually possible to distinguish between the a/b and c/d pairs from knowledge of the properties of the bulk media involved, but determining which of each pair is in question is problematic for very thin films ( 50Å), when the experimentally accessible q-range does not allow the observation of inter ...
Introduction
... In the Czerny-Turner spectrograph the imaging optics use a pair of concave mirrors and the dispersive element is a plane grating. The first mirror collimates the light from the slit and directs it on the grating. The second mirror gathers the light from the grating and directs the multiple images of ...
... In the Czerny-Turner spectrograph the imaging optics use a pair of concave mirrors and the dispersive element is a plane grating. The first mirror collimates the light from the slit and directs it on the grating. The second mirror gathers the light from the grating and directs the multiple images of ...
INFRA-RED OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS*
... has been used to modulate light from a carbon dioxide laser at 10.6 p wavelength at frequencies of 20-300 MHz with good efficiency.cG) Other possible modulation techniques are free carrier absorption effects in semiconductors, absorption edge shift by electric fields and the Faraday magneto-optical ...
... has been used to modulate light from a carbon dioxide laser at 10.6 p wavelength at frequencies of 20-300 MHz with good efficiency.cG) Other possible modulation techniques are free carrier absorption effects in semiconductors, absorption edge shift by electric fields and the Faraday magneto-optical ...
Technical Information on Optics
... the strongest lines A through H. Fresnel equations They describe the intensity of reflected and refracted unpolarized light striking a non-absorbing optical medium having a refractive index of n' at an angle of incidence α. In the process, the reflected ray at the angle of reflection becomes partial ...
... the strongest lines A through H. Fresnel equations They describe the intensity of reflected and refracted unpolarized light striking a non-absorbing optical medium having a refractive index of n' at an angle of incidence α. In the process, the reflected ray at the angle of reflection becomes partial ...
National 5 Waves and Radiation Summary Notes
... count rate to fall from 35 counts per minute to 17.5 counts per minute is also approximately 120s. When enough examples have been taken from the graph we can state that the half-life for the Cs140 will be 120s. ...
... count rate to fall from 35 counts per minute to 17.5 counts per minute is also approximately 120s. When enough examples have been taken from the graph we can state that the half-life for the Cs140 will be 120s. ...
Sample Pages
... a statistical approach.199 The tissue components that contribute most to the local refractive index variations are the connective tissue fibers (either collagen or elastin forming, or reticulin forming) that form part of the noncellular tissue matrix around and among cells, and cell membrane; cytopl ...
... a statistical approach.199 The tissue components that contribute most to the local refractive index variations are the connective tissue fibers (either collagen or elastin forming, or reticulin forming) that form part of the noncellular tissue matrix around and among cells, and cell membrane; cytopl ...
TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion
... TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion The refractive index of glass is not only dependent on wavelength, but also on temperature. The relationship of refractive index change to temperature change is called the temperature coefficient of refractive index. This can be a positive or a negative value. ...
... TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion The refractive index of glass is not only dependent on wavelength, but also on temperature. The relationship of refractive index change to temperature change is called the temperature coefficient of refractive index. This can be a positive or a negative value. ...
Aalborg Universitet
... we have used cylindrical segments to represent the groove walls approaching each other down to a minimum gap of width δ at the groove bottom (rounded accordingly) and introduced the wall inclination angle α so that dw/dz ≅ 2α at the rounding point (Fig. 1b). We have found, that for realistic wedges ...
... we have used cylindrical segments to represent the groove walls approaching each other down to a minimum gap of width δ at the groove bottom (rounded accordingly) and introduced the wall inclination angle α so that dw/dz ≅ 2α at the rounding point (Fig. 1b). We have found, that for realistic wedges ...
TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion
... TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion The refractive index of glass is not only dependent on wavelength, but also on temperature. The relationship of refractive index change to temperature change is called the temperature coefficient of refractive index. This can be a positive or a negative value. ...
... TIE-29 Refractive Index and Dispersion The refractive index of glass is not only dependent on wavelength, but also on temperature. The relationship of refractive index change to temperature change is called the temperature coefficient of refractive index. This can be a positive or a negative value. ...
measuring wavelength discrimination threshold along the entire
... increased fatigue of the observer. The disadvantage of the second possibility is, that the instrument contains an element, which is designed for people with normal color vision, so it cannot function properly in the case of color deficient subjects. However, this inaccuracy is relatively low, so the ...
... increased fatigue of the observer. The disadvantage of the second possibility is, that the instrument contains an element, which is designed for people with normal color vision, so it cannot function properly in the case of color deficient subjects. However, this inaccuracy is relatively low, so the ...
5 - www2
... Home works. 1. With an incident laser wavelength of 514 nm, where would the water stretching band of 3500 cm-1 appear in the Raman spectrum? ...
... Home works. 1. With an incident laser wavelength of 514 nm, where would the water stretching band of 3500 cm-1 appear in the Raman spectrum? ...
Lab Writeup Michelson(New)
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
... The image of M1 appears in line with M2 and may be either in front of or behind M2 (see Fig. 2). The complete theory, which must take into account the fact that the source is an extended source, shows that when M2, and the image of M1 are parallel, then monochromatic light produces an interference p ...
Lecture 1
... Facebook has joined a consortium that will build by far the fastest intra-Asia submarine fiber optic network, the Asia Pacific Gateway (APG). Facebook is the only American company involved with the venture, which will see 10,000km (6,000 miles) of prime fiber laid between Malaysia and Japan (picture ...
... Facebook has joined a consortium that will build by far the fastest intra-Asia submarine fiber optic network, the Asia Pacific Gateway (APG). Facebook is the only American company involved with the venture, which will see 10,000km (6,000 miles) of prime fiber laid between Malaysia and Japan (picture ...
Anti-reflective coating

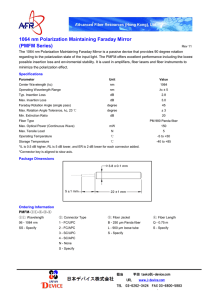
An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.