An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption
... down to about 160 nm hence quartz windows must be used with these types of lamps since glass absorbs strongly at wavelengths less than about 350 nm. Tungsten Filament Lamps This lamp produces intense radiation by the passage of current through an atmosphere of xenon. The spectrum is continuous over ...
... down to about 160 nm hence quartz windows must be used with these types of lamps since glass absorbs strongly at wavelengths less than about 350 nm. Tungsten Filament Lamps This lamp produces intense radiation by the passage of current through an atmosphere of xenon. The spectrum is continuous over ...
N. Qureshi, H. Schmidt, A. Hawkins, “Near
... prepared using electron beam lithography on a silicon substrate followed by deposition of 150nm of nickel using electron beam deposition and lift-off. The structures were then coated with 70nm of silicon nitride using a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition system. This thickness provides an opt ...
... prepared using electron beam lithography on a silicon substrate followed by deposition of 150nm of nickel using electron beam deposition and lift-off. The structures were then coated with 70nm of silicon nitride using a plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition system. This thickness provides an opt ...
Plancks_Constant_Red_Tide
... holes—flow into the junction from electrodes with different voltages. When an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy level, and releases energy in the form of a photon. The wavelength of the light emitted, and therefore its color, depends on the band gap energy of the materials forming ...
... holes—flow into the junction from electrodes with different voltages. When an electron meets a hole, it falls into a lower energy level, and releases energy in the form of a photon. The wavelength of the light emitted, and therefore its color, depends on the band gap energy of the materials forming ...
Chapter 12. Wave Optics Optics can be divided into two categories: I
... Optics can be divided into two categories: I. Geometrical optics: describes processes that can be understood by ray tracing. This applies when the size of objects and lenses is much greater than the wavelength of light. Applies to: Optical instruments using mirrors and lenses. II. Wave optics: takes ...
... Optics can be divided into two categories: I. Geometrical optics: describes processes that can be understood by ray tracing. This applies when the size of objects and lenses is much greater than the wavelength of light. Applies to: Optical instruments using mirrors and lenses. II. Wave optics: takes ...
Thick Lenses and the ABCD Formalism
... focal length. An effective focal length is also often used… Principle Planes are the plane approximations to the locust of points where parallel incident rays would intersect converging exiting rays. There is a primary (on the front side) and a secondary (on the back side) principle plane. These are ...
... focal length. An effective focal length is also often used… Principle Planes are the plane approximations to the locust of points where parallel incident rays would intersect converging exiting rays. There is a primary (on the front side) and a secondary (on the back side) principle plane. These are ...
Generation of radially and azimuthally polarized light by optical
... subwavelength circular nanoslits, the total optical transmission could reach 80% in the visible wavelength range [27]. When its diameter is larger than the incident wavelengths, an individual circular nanoslit can be utilized to generate and focus surface plasmon waves, and thus was denoted as plasm ...
... subwavelength circular nanoslits, the total optical transmission could reach 80% in the visible wavelength range [27]. When its diameter is larger than the incident wavelengths, an individual circular nanoslit can be utilized to generate and focus surface plasmon waves, and thus was denoted as plasm ...
Wavefront shaping of infrared light through a subwavelength hole
... Light passing through a subwavelength hole in an opaque plate is a fundamental concern in both optical science and applications. Using both simulations and experiments, we show that, when a subwavelength hole in a silver thin film is surrounded by well-designed patterns of grooves, the wavefront of ...
... Light passing through a subwavelength hole in an opaque plate is a fundamental concern in both optical science and applications. Using both simulations and experiments, we show that, when a subwavelength hole in a silver thin film is surrounded by well-designed patterns of grooves, the wavefront of ...
September 20, 2000 - University of South Florida
... each other, respectively. Lr and La can be derived using single-scattering approximations, i.e., each photon, if scattered (assuming a non-absorbing atmosphere), will be scattered only once. Figure 1 describes the three processes that contribute to the sensor signal. Lr and La are each composed of t ...
... each other, respectively. Lr and La can be derived using single-scattering approximations, i.e., each photon, if scattered (assuming a non-absorbing atmosphere), will be scattered only once. Figure 1 describes the three processes that contribute to the sensor signal. Lr and La are each composed of t ...
class06
... • Light rays taking different paths will travel different distances and be reflected a different number of times • Both distance and reflection affect the how rays combine • Rays will combine in different ways, sometimes adding ...
... • Light rays taking different paths will travel different distances and be reflected a different number of times • Both distance and reflection affect the how rays combine • Rays will combine in different ways, sometimes adding ...
Polarization
... of light of wavelength 589 nm (the d line of a sodium lamp) passing through 10 cm of a 1 g ml-1 solution of a sample. ...
... of light of wavelength 589 nm (the d line of a sodium lamp) passing through 10 cm of a 1 g ml-1 solution of a sample. ...
Question 1 (a) ICSE X | PHYSICS Board Paper – 2016 ICSE Board
... This time is to be spent in reading the question paper. The time given at the head of paper is the time allotted for writing the answers. Section I is compulsory. Attend any four questions from Section II. The intended marks of questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ]. ...
... This time is to be spent in reading the question paper. The time given at the head of paper is the time allotted for writing the answers. Section I is compulsory. Attend any four questions from Section II. The intended marks of questions or parts of questions are given in brackets [ ]. ...
Ray Tracing
... Each ray interacts at the center of the lens. This approximation is why the lens is described as “thin”. With a thick lens one would have to apply Snell’s law in order to determine how that ray bends through the glass. However, in this case that is not a problem since the lens is thin and the light ...
... Each ray interacts at the center of the lens. This approximation is why the lens is described as “thin”. With a thick lens one would have to apply Snell’s law in order to determine how that ray bends through the glass. However, in this case that is not a problem since the lens is thin and the light ...
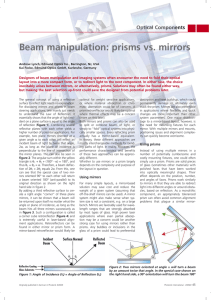
Beam manipulation: prisms vs. mirrors
... layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. ...
... layout into a more compact form, or to redirect light to the next component. In either case, the choice inevitably arises between mirrors, or alternatively, prisms. Solutions may often be found either way, but making the best selection up-front could save the designer from potential problems later. ...
Optical Properties of Plasmonic Ag/Ni Square Nanostructures
... values of k, which explains their high reflectivity of optical light and gives them their shiny appearance [4]. Knowing the optical properties of a material, one can easily extract valuable information about the reflection and transmission. Using the Fresnel Equations one can calculate how much of t ...
... values of k, which explains their high reflectivity of optical light and gives them their shiny appearance [4]. Knowing the optical properties of a material, one can easily extract valuable information about the reflection and transmission. Using the Fresnel Equations one can calculate how much of t ...
Supplementary information (docx 376K)
... coordinate perpendicular to the Si slab (see Fig. 1a). (The coordinate axis perpendicular to z and u is ignored as the system is translation-invariant along this direction.) Furthermore, 2 is a frequency from the pump pulse spectrum, and A(ku) is the amplitude of each Fourier component with wave ...
... coordinate perpendicular to the Si slab (see Fig. 1a). (The coordinate axis perpendicular to z and u is ignored as the system is translation-invariant along this direction.) Furthermore, 2 is a frequency from the pump pulse spectrum, and A(ku) is the amplitude of each Fourier component with wave ...
Laboratory 2 Thomas Young and the Wave
... Young’s card with the human hair established what would become known as the doubleslit experiment. Rather than making 2 slits, he allowed the light to pass around both edges of the hair. In Fig. 3, imagine a taut length of hair passing perpendicular through the page at d (the diameter of the hair); ...
... Young’s card with the human hair established what would become known as the doubleslit experiment. Rather than making 2 slits, he allowed the light to pass around both edges of the hair. In Fig. 3, imagine a taut length of hair passing perpendicular through the page at d (the diameter of the hair); ...
Experimental Competition
... frequency ranges over which the properties of the “image” are drastically different. To describe these observations complete the table on the answer form by adding a row to this table for each such frequency range and fill it in by using the appropriate notations explained on that page. ...
... frequency ranges over which the properties of the “image” are drastically different. To describe these observations complete the table on the answer form by adding a row to this table for each such frequency range and fill it in by using the appropriate notations explained on that page. ...
FIB – an easy tool for fabrication of high quality plasmonic structures
... promising solution in subwavelength optics and lithography beyond the diffraction limit. They also find their applications in photonic data storage, light generation, and bio-photonics. SPPs cannot be excited directly by incident electromagnetic radiation. One of the possible ways for their excitati ...
... promising solution in subwavelength optics and lithography beyond the diffraction limit. They also find their applications in photonic data storage, light generation, and bio-photonics. SPPs cannot be excited directly by incident electromagnetic radiation. One of the possible ways for their excitati ...
61
... media transforms itself into a kind of a GRIN structure, whose refractive index in the central is higher than that of the edges. In other word media is transformed to a positivegradient index lens, and hence the focusing effect. If this focusing effect keeps converging a beam, the beam intensity per ...
... media transforms itself into a kind of a GRIN structure, whose refractive index in the central is higher than that of the edges. In other word media is transformed to a positivegradient index lens, and hence the focusing effect. If this focusing effect keeps converging a beam, the beam intensity per ...
Transmisi Optik Pertemuan 10
... • There are five causes of this attenuation and loss of optical power within the fiber: optical fiber loss, micro bending loss, connector loss, splice loss, and coupling loss. ...
... • There are five causes of this attenuation and loss of optical power within the fiber: optical fiber loss, micro bending loss, connector loss, splice loss, and coupling loss. ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.