
Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE) - KCPE-KCSE
... spot. State what is observed on the screen if a low frequency a.c source is connected across the yinput of the C.R.O (1mk) ...
... spot. State what is observed on the screen if a low frequency a.c source is connected across the yinput of the C.R.O (1mk) ...
Organic Nonlinear Optic Devices
... • Fluorine content controls the refractive index of polyimide • Core and cladding layer can be made from the same polymer---polyimide. ...
... • Fluorine content controls the refractive index of polyimide • Core and cladding layer can be made from the same polymer---polyimide. ...
Strategies for the compensation of specimen
... quality diffraction limited images deep within a real specimen. This requirement is at odds with many standard microscope objective lenses that are designed, for example, to image thin objects located directly under a glass cover slip of specified thickness. Spherical aberration may be introduced du ...
... quality diffraction limited images deep within a real specimen. This requirement is at odds with many standard microscope objective lenses that are designed, for example, to image thin objects located directly under a glass cover slip of specified thickness. Spherical aberration may be introduced du ...
Surface Texture Effect on Luster of Anodized Aluminum
... Machining, Coatings, Pharmaceutical, Biomedical, Environmental and many others. Learn more about the Nanovea Profilometer or Lab Services ...
... Machining, Coatings, Pharmaceutical, Biomedical, Environmental and many others. Learn more about the Nanovea Profilometer or Lab Services ...
ap physics b
... • Rays that go through the center of the lens do not bend, but travel in straight lines. Rules for mirrors: Remember light reflects off the mirror. (concave mirrors cause light to converge while a convex mirror causes light to diverge) • Rays travelling parallel to the principal axis, either converg ...
... • Rays that go through the center of the lens do not bend, but travel in straight lines. Rules for mirrors: Remember light reflects off the mirror. (concave mirrors cause light to converge while a convex mirror causes light to diverge) • Rays travelling parallel to the principal axis, either converg ...
Opto-Mechanical Image Quality Degradation of Single Point
... n is the refractive index of the transparent or reflective material under test. i is the angle of incidence on sample is the total effective rms surface roughness, in microns, over frequencies from 0 to 1/. s, r is the scattered and reflectance power. S2(f) is the 2 Dimensional surface pow ...
... n is the refractive index of the transparent or reflective material under test. i is the angle of incidence on sample is the total effective rms surface roughness, in microns, over frequencies from 0 to 1/. s, r is the scattered and reflectance power. S2(f) is the 2 Dimensional surface pow ...
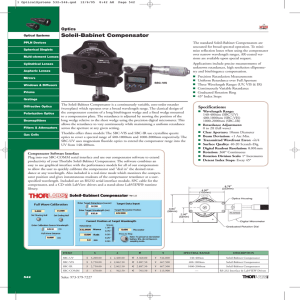
Soleil-Babinet Compensator
... uncoated for broad spectral operation. To minimize reflection losses when using the compensator over narrow wavelength ranges, AR-coated versions are available upon special request. ...
... uncoated for broad spectral operation. To minimize reflection losses when using the compensator over narrow wavelength ranges, AR-coated versions are available upon special request. ...
optical trap
... step in modern science, most notably to the fields of Cell Biology and Biophysics. In Biophysics it is important to be able to manipulate particles in the micron-size regime without damaging them. Optical tweezers prove very useful for this because, not only can they manipulate small particles very ...
... step in modern science, most notably to the fields of Cell Biology and Biophysics. In Biophysics it is important to be able to manipulate particles in the micron-size regime without damaging them. Optical tweezers prove very useful for this because, not only can they manipulate small particles very ...
Examples of convex lens
... heat carried bydifferent colors of the sunlight. William used a glass prism to create a visible spectrum. He placed blackened bulbs in each color region to absorb heat and he found that the temperature of the bulbs increased from violet to red. William decided to measure the heat of the region beyon ...
... heat carried bydifferent colors of the sunlight. William used a glass prism to create a visible spectrum. He placed blackened bulbs in each color region to absorb heat and he found that the temperature of the bulbs increased from violet to red. William decided to measure the heat of the region beyon ...
Zeeman Effect - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... Place all the elements (condenser, collimator, etc.) one at a time, so that their optical axis is at the same height as the interferometer. Start with the condensing lens. The focal length of lens 1 in the condensing unit is 12.5cm, so the discharge lamp should be positioned so that it is 12.5cm fro ...
... Place all the elements (condenser, collimator, etc.) one at a time, so that their optical axis is at the same height as the interferometer. Start with the condensing lens. The focal length of lens 1 in the condensing unit is 12.5cm, so the discharge lamp should be positioned so that it is 12.5cm fro ...
PLIs Classification
... Optical signals traverse the optical fibre links, passive and/or active optical components Signals encounter many impairments that affect their intensity level, as well as their temporal, spectral and polarization properties If the received signal quality is not within the receiver sensitivity thres ...
... Optical signals traverse the optical fibre links, passive and/or active optical components Signals encounter many impairments that affect their intensity level, as well as their temporal, spectral and polarization properties If the received signal quality is not within the receiver sensitivity thres ...
Direct Patterning of Three-Dimensional Periodic
... layers) is dependent upon several factors, among which the thickness of the photoresist and the number of grating apertures are the most important. In our experiments, a maximum of 8 layers was generated with 30 apertures and a 3-micrometer-thick photoresist. If a thicker photoresist was used, then ...
... layers) is dependent upon several factors, among which the thickness of the photoresist and the number of grating apertures are the most important. In our experiments, a maximum of 8 layers was generated with 30 apertures and a 3-micrometer-thick photoresist. If a thicker photoresist was used, then ...
CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... At θ1 = θc, θ2 = 90º sin(θc) = n2/n1 ...
... At θ1 = θc, θ2 = 90º sin(θc) = n2/n1 ...
PPT Lecture Notes
... • Light is “bouncy”. Unlike longer-wave energy, which passes through many opaque objects, light can be reflected (‘bounced’) off of objects, making them visible. Light’s a better messenger. • On our planet, light is plentiful. By contrast, shorter-wave energy tends to be absorbed by our atmosphere ( ...
... • Light is “bouncy”. Unlike longer-wave energy, which passes through many opaque objects, light can be reflected (‘bounced’) off of objects, making them visible. Light’s a better messenger. • On our planet, light is plentiful. By contrast, shorter-wave energy tends to be absorbed by our atmosphere ( ...
1. dia - Budapest University of Technology and Economics
... opaque to shorter wavelengths while Silica or quartz glass, depending on quality, can be transparent even to vacuum UV wavelengths. Ordinary window glass passes about 90% of the light above 350 nm, but blocks over 90% of the light below 300 nm[1][2][3]. The onset of vacuum UV, 200 nm, is defined by ...
... opaque to shorter wavelengths while Silica or quartz glass, depending on quality, can be transparent even to vacuum UV wavelengths. Ordinary window glass passes about 90% of the light above 350 nm, but blocks over 90% of the light below 300 nm[1][2][3]. The onset of vacuum UV, 200 nm, is defined by ...
CHAPTER 10
... 10.4 Red light, =600nm, enters a glass block whereupon its velocity is two-thirds that of its velocity in vacuum. Find the refractive index of the glass for this wavelength and the wavelength in the glass. 10.5 A ray of monochromatic light is incident at 40 on a plane air/glass boundary. If the r ...
... 10.4 Red light, =600nm, enters a glass block whereupon its velocity is two-thirds that of its velocity in vacuum. Find the refractive index of the glass for this wavelength and the wavelength in the glass. 10.5 A ray of monochromatic light is incident at 40 on a plane air/glass boundary. If the r ...
[pdf]
... Generally, DWS experiments have been analyzed by the use of a plane-wave input-point output geometry without diffuse reflection. In fact, the index of refraction of the cell walls is rarely matched to the solvent and, even worse, after moving from the sample to the cell wall, all photons traveling a ...
... Generally, DWS experiments have been analyzed by the use of a plane-wave input-point output geometry without diffuse reflection. In fact, the index of refraction of the cell walls is rarely matched to the solvent and, even worse, after moving from the sample to the cell wall, all photons traveling a ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.





















![[pdf]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008852311_1-a80c01e7dd06bde7495e825ae8833165-300x300.png)
