Optical contrast and clarity of graphene on an
... The simplest substrate that gives graphene high contrast is thermal oxide on silicon. The trajectory of r on SiO2 / Si as a function of oxide thickness is a perfect circle as the SiO2 thickness increases. The r circle evolves evenly as the SiO2 thickness grows with a period of 183 nm at a wavelength ...
... The simplest substrate that gives graphene high contrast is thermal oxide on silicon. The trajectory of r on SiO2 / Si as a function of oxide thickness is a perfect circle as the SiO2 thickness increases. The r circle evolves evenly as the SiO2 thickness grows with a period of 183 nm at a wavelength ...
An optical fibre based evanescent wave sensor to
... are needed in this case. In the radiation absorption method, the absorption in discontinuous films is strongly influenced by the granular nature of films, but it may still be used for relative measurement of the average film thickness. The photometric method uses the oscillatory nature of the interf ...
... are needed in this case. In the radiation absorption method, the absorption in discontinuous films is strongly influenced by the granular nature of films, but it may still be used for relative measurement of the average film thickness. The photometric method uses the oscillatory nature of the interf ...
Evanescent-field optical microscopy: effects of polarization, tip
... generation, data-acquisition and 3D image visualization are controlled by a standard personal computer. ...
... generation, data-acquisition and 3D image visualization are controlled by a standard personal computer. ...
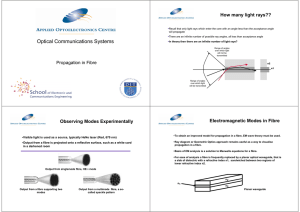
Unit 1.5 Propagation in Fibre
... For the most common value of α show that for fibres with similar relative refractive indices, core radii and operating wavelengths, the number of modes propagating in a step index fibre is twice that in a graded index fibre ...
... For the most common value of α show that for fibres with similar relative refractive indices, core radii and operating wavelengths, the number of modes propagating in a step index fibre is twice that in a graded index fibre ...
Optical Detection of Early Damage in Retinal Ganglion Cells in a
... in vivo. Areas of CO (red) and NO (blue) were labeled. I, inferior; N, nasal; S, superior; T, temporal. Scale bar: 0.4 mm. (B) Representative crosssectional OCT images of mouse retinas. ELM, external limiting membrane; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; IS/OS: inner segment/ outer ...
... in vivo. Areas of CO (red) and NO (blue) were labeled. I, inferior; N, nasal; S, superior; T, temporal. Scale bar: 0.4 mm. (B) Representative crosssectional OCT images of mouse retinas. ELM, external limiting membrane; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; IS/OS: inner segment/ outer ...
Near-perfect hologram reconstruction with a spatial light modulator
... the two-dimensional Fourier transform of the desired holographic image (optionally superposed with a parabolic phase term to control the imaging distance) onto an incoming wave. However, in practice the “imprinting process” is difficult. One reason for this is that the twodimensional Fourier transfo ...
... the two-dimensional Fourier transform of the desired holographic image (optionally superposed with a parabolic phase term to control the imaging distance) onto an incoming wave. However, in practice the “imprinting process” is difficult. One reason for this is that the twodimensional Fourier transfo ...
THz Materials
... in UV, visible, and THz ranges that for example allows using a HeNe laser beam for alignment. Index of refraction is ~1.46 and is relatively ...
... in UV, visible, and THz ranges that for example allows using a HeNe laser beam for alignment. Index of refraction is ~1.46 and is relatively ...
Dynamic lighting system for specular surface inspection
... lighting system. In our case, the geometrical optics is applicable because the wavelength of the incident light is weak compared to the dimensions of the surface imperfections. 6 So, inverse ray tracing is used to analyze the reflection of the lighting through the surface. To perform easy understand ...
... lighting system. In our case, the geometrical optics is applicable because the wavelength of the incident light is weak compared to the dimensions of the surface imperfections. 6 So, inverse ray tracing is used to analyze the reflection of the lighting through the surface. To perform easy understand ...
Controllable optical negative refraction and
... through a perturbative medium12 . Realization of phase conjugation is based on degenerate four-wave mixing, in which two counterpropagating beams are used to write a holographic grating into a nonlinear crystal, while a third beam is diffracted in a direction exactly opposite to the incident wave. T ...
... through a perturbative medium12 . Realization of phase conjugation is based on degenerate four-wave mixing, in which two counterpropagating beams are used to write a holographic grating into a nonlinear crystal, while a third beam is diffracted in a direction exactly opposite to the incident wave. T ...
Paper Title
... many advantages due to high tunability of the acousto-optical technique. Namely, exciting frequency (and therefore grating period) can be adjusted with ppm accuracy to any value in the kHz – GHz region, enabling therefore tuning (scaling) the given waveguide to many available lasers or other narrow- ...
... many advantages due to high tunability of the acousto-optical technique. Namely, exciting frequency (and therefore grating period) can be adjusted with ppm accuracy to any value in the kHz – GHz region, enabling therefore tuning (scaling) the given waveguide to many available lasers or other narrow- ...
No Slide Title
... – Shows amplitude and timing noise – Wide open eye is better than mostly closed one. – Standards often have exclusion zones in the center and above and below ...
... – Shows amplitude and timing noise – Wide open eye is better than mostly closed one. – Standards often have exclusion zones in the center and above and below ...
Through the Looking Glass
... interference pattern formed by an undistorted reference beam with a distorted beam reflected off the object. The result, after development of the film, is the hologram, a grain pattern in the emulsion. (b) A second undistorted reference beam, here pattern formed in the film emulsion. But this is a p ...
... interference pattern formed by an undistorted reference beam with a distorted beam reflected off the object. The result, after development of the film, is the hologram, a grain pattern in the emulsion. (b) A second undistorted reference beam, here pattern formed in the film emulsion. But this is a p ...
Multiplexing in high-density optical data storage using the orbital
... implying a phase increase over one full turn of l 2π where l is known as the topological charge, and k = 2π/λ. We assume a wave propagating in the z direction as exp[-i(ω t - k z)]. We have dropped the term exp(-iω t) since in the laboratory frame, the dynamics occur as the beam propagates through s ...
... implying a phase increase over one full turn of l 2π where l is known as the topological charge, and k = 2π/λ. We assume a wave propagating in the z direction as exp[-i(ω t - k z)]. We have dropped the term exp(-iω t) since in the laboratory frame, the dynamics occur as the beam propagates through s ...
(Lithium Fluoride-Poly-Vinyl Alcohol) Composites
... Figure (2) shows the relationship of the absorption coefficient with photon energy of different weight percentages of lithium fluoride. The figure shows that the absorption coefficient increases with increase weight percentages of lithium fluoride, this may be attributed to increase the absorbance w ...
... Figure (2) shows the relationship of the absorption coefficient with photon energy of different weight percentages of lithium fluoride. The figure shows that the absorption coefficient increases with increase weight percentages of lithium fluoride, this may be attributed to increase the absorbance w ...
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
... Abbe’s limit implies that even the best optical microscope will be unable to distinguish features less than about 200 nanometers apart. This would seem to bar optical microscopy from use in nanoscience. It also implies a limit to the use of optical lithography (the inverse of microscopy) in microele ...
... Abbe’s limit implies that even the best optical microscope will be unable to distinguish features less than about 200 nanometers apart. This would seem to bar optical microscopy from use in nanoscience. It also implies a limit to the use of optical lithography (the inverse of microscopy) in microele ...
The Theory of the Rainbow
... directions are equivalent and there is only one significant variable: the dis placement of the incident ray from an axis passing through the center of the droplet. That displacement is called the impact parameter. It ranges from zerO. when the ray coincides with the central axis. to the radius of t ...
... directions are equivalent and there is only one significant variable: the dis placement of the incident ray from an axis passing through the center of the droplet. That displacement is called the impact parameter. It ranges from zerO. when the ray coincides with the central axis. to the radius of t ...
Binocular Performance Index
... may exist, I have not seen any binoculars specified as diffraction limited. Therefore, it might be expected that most if not all binoculars would never be able to reach these limits. It is reasonable to expect that the scopes used for comparison would be able to achieve slightly better results, and ...
... may exist, I have not seen any binoculars specified as diffraction limited. Therefore, it might be expected that most if not all binoculars would never be able to reach these limits. It is reasonable to expect that the scopes used for comparison would be able to achieve slightly better results, and ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.