Optical Isolation Can Occur In Linear And Passive Silicon
... involves multiple channels of signal, however, all output signals are reversed and input back into the grating itself by the mirror. It is worth saying a few more words here for better drawing a clear picture about the physics discussed in the above. In nature, as time always flows forward and canno ...
... involves multiple channels of signal, however, all output signals are reversed and input back into the grating itself by the mirror. It is worth saying a few more words here for better drawing a clear picture about the physics discussed in the above. In nature, as time always flows forward and canno ...
Birefringency: Calculation of Refracted Ray Paths in - Giga
... The phenomena of birefringency may be observed when light arrives at an anisotropic crystal surface and refracts through it. Using the ray model for light propagation, birefringency causes two main effects: first, the incident light ray splits into two rays that go through the crystal at two differe ...
... The phenomena of birefringency may be observed when light arrives at an anisotropic crystal surface and refracts through it. Using the ray model for light propagation, birefringency causes two main effects: first, the incident light ray splits into two rays that go through the crystal at two differe ...
Passive Light and Viewpoint Sensitive Display of 3D Content
... marked by“ ·” indicates that this dimension is assumed uniform or that the output is invariant to it. An entry with superscript o implies that its value is fixed and known when content is designed. The “?” mark indicates that to our best knowledge, this configuration was not yet demonstrated. BRDF d ...
... marked by“ ·” indicates that this dimension is assumed uniform or that the output is invariant to it. An entry with superscript o implies that its value is fixed and known when content is designed. The “?” mark indicates that to our best knowledge, this configuration was not yet demonstrated. BRDF d ...
Controlling the Phase and Amplitude of Plasmon Sources at a Subwavelength Scale
... plasmonic antenna similar to the one that was studied very recently by López-Tejeira et al.16 In our unidirectional antenna, however, the lateral size can be reduced to half a plasmon wavelength (compared to a minimum size of several wavelengths in ref 16). Additionally, the top surface of our ante ...
... plasmonic antenna similar to the one that was studied very recently by López-Tejeira et al.16 In our unidirectional antenna, however, the lateral size can be reduced to half a plasmon wavelength (compared to a minimum size of several wavelengths in ref 16). Additionally, the top surface of our ante ...
Electromagnetic field intensity distribution along focal region of a
... fields is important in the current arena of advanced technologies for microwave, millimeter-wave, and optical device applications. The analysis of focal region filed is useful for optical spectroscopy, medical treatment and hyperthermia. The image field may be also useful to generate images of the h ...
... fields is important in the current arena of advanced technologies for microwave, millimeter-wave, and optical device applications. The analysis of focal region filed is useful for optical spectroscopy, medical treatment and hyperthermia. The image field may be also useful to generate images of the h ...
Transformational Plasmon Optics Yongmin Liu, Thomas Zentgraf, Guy Bartal,
... that SPPs can be molded more effectively and efficiently than ever, with only isotropic, nonmagnetic, and nondispersive dielectric materials introduced by the transformation. SPPs are bound surface waves at metal-dielectric interfaces, which implies that both the metal and dielectric materials need ...
... that SPPs can be molded more effectively and efficiently than ever, with only isotropic, nonmagnetic, and nondispersive dielectric materials introduced by the transformation. SPPs are bound surface waves at metal-dielectric interfaces, which implies that both the metal and dielectric materials need ...
Holografie – lasery
... Pulsed lasers, quite the opposite of continuous wave lasers, emit extremely quick bursts of very powerful laser light. Exposures can be made in ‘nanoseconds' (billionths of a second). No vibration table is needed and holograms can be made of people, animals, or even splashing water because no signif ...
... Pulsed lasers, quite the opposite of continuous wave lasers, emit extremely quick bursts of very powerful laser light. Exposures can be made in ‘nanoseconds' (billionths of a second). No vibration table is needed and holograms can be made of people, animals, or even splashing water because no signif ...
Transformational Plasmon Optics Yongmin Liu, Thomas Zentgraf, Guy Bartal,
... that SPPs can be molded more effectively and efficiently than ever, with only isotropic, nonmagnetic, and nondispersive dielectric materials introduced by the transformation. SPPs are bound surface waves at metal-dielectric interfaces, which implies that both the metal and dielectric materials need ...
... that SPPs can be molded more effectively and efficiently than ever, with only isotropic, nonmagnetic, and nondispersive dielectric materials introduced by the transformation. SPPs are bound surface waves at metal-dielectric interfaces, which implies that both the metal and dielectric materials need ...
Phase space of partially coherent light with discontinuous surfaces
... through a refractive material with a height of Δz accumulates the phase term exp(i2πnΔz/λ), where n is the refractive index of the material. Meanwhile another ray of light next to the material traveling through air of the same thickness Δz carries another phase term exp(i2πΔz/λ). We define the norma ...
... through a refractive material with a height of Δz accumulates the phase term exp(i2πnΔz/λ), where n is the refractive index of the material. Meanwhile another ray of light next to the material traveling through air of the same thickness Δz carries another phase term exp(i2πΔz/λ). We define the norma ...
Étendue and spectral resolution
... spectral line profiles for determining the details of the Doppler broadened line profile. For weak light sources or fast plasma processes the optical system must have a high étendue1 (optical throughput), and in a case of fast varying plasma such as pulsed magnetron or cathodic arc plasma, it is ess ...
... spectral line profiles for determining the details of the Doppler broadened line profile. For weak light sources or fast plasma processes the optical system must have a high étendue1 (optical throughput), and in a case of fast varying plasma such as pulsed magnetron or cathodic arc plasma, it is ess ...
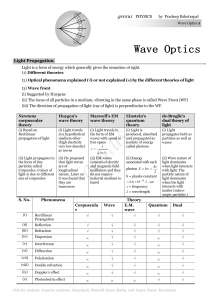
genius PHYSICS by Pradeep Kshetrapal Newtons corpuscular
... Shift is independent of the order of fringe (i.e. shift of zero order maxima = shift of nth order maxima. Shift is independent of wavelength. ...
... Shift is independent of the order of fringe (i.e. shift of zero order maxima = shift of nth order maxima. Shift is independent of wavelength. ...
Superposed Strokes Analysis by Conoscopic Holography as aid for
... In Conoscopic holography, the object and reference beams of coherent holography are replaced by the ordinary and the extraordinary components of a single beam propagating in birefringent media. Therefore, the signal and reference beams have the same geometrical paths but different optical path-lengt ...
... In Conoscopic holography, the object and reference beams of coherent holography are replaced by the ordinary and the extraordinary components of a single beam propagating in birefringent media. Therefore, the signal and reference beams have the same geometrical paths but different optical path-lengt ...
A Survivable Protection and Restoration Scheme using Wavelength
... solution to meet the ever increasing bandwidth demand with high quality of services (QoS) for the next-generation broadband access systems [1]. The WDM-PON incorporated with centrally managed colorless optical network units (ONUs) is the most desirable one as it can provide cost-effective and operat ...
... solution to meet the ever increasing bandwidth demand with high quality of services (QoS) for the next-generation broadband access systems [1]. The WDM-PON incorporated with centrally managed colorless optical network units (ONUs) is the most desirable one as it can provide cost-effective and operat ...
Phase contrast and DIC - Nikon Imaging Center at UCSF
... Sensitive to phase gradients Contrast best along the direction of shear Objects appear shaded or in pseudo 3D relief ...
... Sensitive to phase gradients Contrast best along the direction of shear Objects appear shaded or in pseudo 3D relief ...
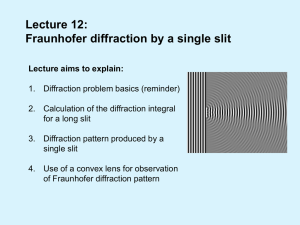
Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... History of discovery of diffraction The effects of diffraction of light were first observed and characterized by Francesco Maria Grimaldi in the 17th century. James Gregory (1638–1675) observed the diffraction patterns caused by a bird feather. Thomas Young performed a celebrated experiment in 1803 ...
... History of discovery of diffraction The effects of diffraction of light were first observed and characterized by Francesco Maria Grimaldi in the 17th century. James Gregory (1638–1675) observed the diffraction patterns caused by a bird feather. Thomas Young performed a celebrated experiment in 1803 ...
2 Pulsed Optics
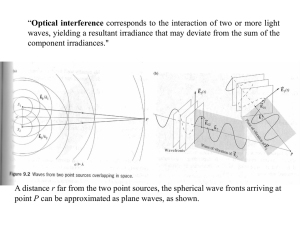
... allows the introduction of the wave vector k of the light. Figure 2.1 shows the geometry of the propagation of a plane wave. Let us consider the plane P orthogonal to the propagation vector k , at distance x from the origin O. For any point in this plane, at distance r from the origin O, the scalar ...
... allows the introduction of the wave vector k of the light. Figure 2.1 shows the geometry of the propagation of a plane wave. Let us consider the plane P orthogonal to the propagation vector k , at distance x from the origin O. For any point in this plane, at distance r from the origin O, the scalar ...
Lab 8: Polarization of Light
... retarder; linear polarization is thus converted to elliptical polarization due to the arbitrary phase shift. The phase difference depends on the incident wavelength, the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of ...
... retarder; linear polarization is thus converted to elliptical polarization due to the arbitrary phase shift. The phase difference depends on the incident wavelength, the refractive indices (along the two different directhey don’t reduce the intensity of the incident light tions) and the thickness of ...
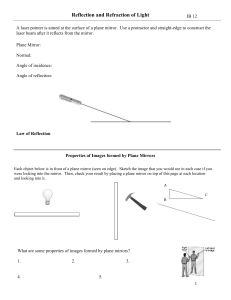
Physics for Scientists & Geometric Optics
... ! However, unlike the plane mirror, the surface of a curved mirror is not flat ! Thus light rays that are parallel before they strike the mirror are reflected in different directions depending on the part of the mirror that they strike ! Depending of the shape of the mirror, the light rays can be fo ...
... ! However, unlike the plane mirror, the surface of a curved mirror is not flat ! Thus light rays that are parallel before they strike the mirror are reflected in different directions depending on the part of the mirror that they strike ! Depending of the shape of the mirror, the light rays can be fo ...
Combining Photonic Crystal and Optical Monte
... The agreement between UMeas and USimu was analyzed using a two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test [15]. In this procedure, a p-value is calculated based on the differences of two continuous distributions. The null hypothesis H0 , which states that the two functions stem from the same distribution, ...
... The agreement between UMeas and USimu was analyzed using a two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test [15]. In this procedure, a p-value is calculated based on the differences of two continuous distributions. The null hypothesis H0 , which states that the two functions stem from the same distribution, ...
CHAPTER 1 Wave Nature of Light
... Dispersive medium • In general, for many materials the refractive index n and the group index Ng depend on the wavelength of light by virtue of r being frequency dependent. Both the phase velocity v and the group velocity vg depend on the wavelength. • The medium is called dispersive medium. ...
... Dispersive medium • In general, for many materials the refractive index n and the group index Ng depend on the wavelength of light by virtue of r being frequency dependent. Both the phase velocity v and the group velocity vg depend on the wavelength. • The medium is called dispersive medium. ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.