Yellow nanosecond sum-frequency generating optical
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
... copper vapour lasers at 578 nm and dye lasers operating at 585 nm and 595 nm. These lasers are both bulky and inefficient and it would be attractive to develop a solid-state alternative to these lasers. One path that has been followed for the generation of yellow light is second harmonic generation ...
Projecting Chromatic Aberrations
... bulbs, 12 a circular and colorful-flower like pattern appears, showing the filament reflected in the bulb's multiple mirrorreflector segments. Moving the third lens further (two or three times its focal length) from the projector once again creates a large white central spot, but this time the spot ...
... bulbs, 12 a circular and colorful-flower like pattern appears, showing the filament reflected in the bulb's multiple mirrorreflector segments. Moving the third lens further (two or three times its focal length) from the projector once again creates a large white central spot, but this time the spot ...
Fig. 1 - Computational Manufacturing and Materials Research Lab
... Thus, the rate of flow of energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the electric field. Furthermore, in isotropic media, which we consider for the duration of the work, the direction of energy is in the direction of S and in the same direction as k. Since I is the energy per unit area p ...
... Thus, the rate of flow of energy is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the electric field. Furthermore, in isotropic media, which we consider for the duration of the work, the direction of energy is in the direction of S and in the same direction as k. Since I is the energy per unit area p ...
Relation between nonlinear refractive index and
... tion coefficient) which could be potentially modulated by the amount of doping (i.e., by modifying its absorption). Obviously, the interplay between n 2 , k 2 , n 0 , k 0 , and ( 3 ) is much clearer in the case of strongly absorbing systems (k 0 /n 0 ⬎ 10⫺2 ) such as metals, or systems with resona ...
... tion coefficient) which could be potentially modulated by the amount of doping (i.e., by modifying its absorption). Obviously, the interplay between n 2 , k 2 , n 0 , k 0 , and ( 3 ) is much clearer in the case of strongly absorbing systems (k 0 /n 0 ⬎ 10⫺2 ) such as metals, or systems with resona ...
Student`s guide - National Centre for Biotechnology Education
... Neutral density filters are grey-coloured. They reduce the amount of light passing through them across the spectrum (in the 400–680 nm range). They can be used singly or combined with one another to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Using filters like this has ...
... Neutral density filters are grey-coloured. They reduce the amount of light passing through them across the spectrum (in the 400–680 nm range). They can be used singly or combined with one another to investigate the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis. Using filters like this has ...
EOSTAR: an electro-optical sensor performance
... As mentioned above, EOSTAR utilizes bulk models to calculate vertical meteorological profiles on the basis of simple standard observations. EOSTAR is provided with three different micrometeorological models2,3,4 and with two different sets of stability functions10,11. In addition, users can define t ...
... As mentioned above, EOSTAR utilizes bulk models to calculate vertical meteorological profiles on the basis of simple standard observations. EOSTAR is provided with three different micrometeorological models2,3,4 and with two different sets of stability functions10,11. In addition, users can define t ...
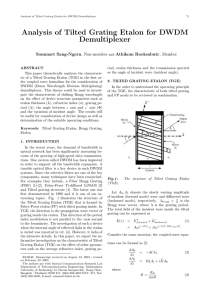
Development of a New Optical Wavelength Rejection Filter
... used to replace gratings as wavelength-selective elements. These filters appear to have significant advantages over the typical dielectric interference filter. For example, greater than 95 % of the light is Bragg diffracted, in contrast to the typical narrow-band interference filter, which typically ...
... used to replace gratings as wavelength-selective elements. These filters appear to have significant advantages over the typical dielectric interference filter. For example, greater than 95 % of the light is Bragg diffracted, in contrast to the typical narrow-band interference filter, which typically ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... Keywords: polystyrene/ fullerene/ plasma exposure/ optical constants/ optical band gap/ doping ...
... Keywords: polystyrene/ fullerene/ plasma exposure/ optical constants/ optical band gap/ doping ...
MieScatt09
... scattering is quite strong yields an indication of the scattering particle size. Reflection from clouds: We know from experience that clouds are in general very bright reflectors of sunlight. However, the figure above indicates that most of the sunlight striking a cloud droplet is forward scattered. ...
... scattering is quite strong yields an indication of the scattering particle size. Reflection from clouds: We know from experience that clouds are in general very bright reflectors of sunlight. However, the figure above indicates that most of the sunlight striking a cloud droplet is forward scattered. ...
Coherence scanning interferometry: linear theory of surface
... The theory that underpins this work is based on a linear theory of 3D imaging that was first published in the context of optical holography by Wolf [12], and Dandliker and Weiss [13]. Using this approach the performance of 3D imaging techniques including digital holography, confocal microscopy, CSI, ...
... The theory that underpins this work is based on a linear theory of 3D imaging that was first published in the context of optical holography by Wolf [12], and Dandliker and Weiss [13]. Using this approach the performance of 3D imaging techniques including digital holography, confocal microscopy, CSI, ...
CE-PHY II - OPTICS
... Which of the following statements concerning the properties of virtual images is/are correct ? ...
... Which of the following statements concerning the properties of virtual images is/are correct ? ...
Plasmonic orbital angular momentum manipulation through
... transferring the OAM to absorptive particles and inducing them to rotate circumferentially in the azimuthal direction in the focal region of PV with different topological charges. Gold particles were chosen here to strengthen the transfer of OAM from PV to the particles because of their highly absor ...
... transferring the OAM to absorptive particles and inducing them to rotate circumferentially in the azimuthal direction in the focal region of PV with different topological charges. Gold particles were chosen here to strengthen the transfer of OAM from PV to the particles because of their highly absor ...
Ophthalmic lens
... Thin layer of Dichronic crystals is sandwiched between two layers. Reflected light is polarized and absorbed by middle layer. Light transmission reduce by 50% improves vision and comfort. ...
... Thin layer of Dichronic crystals is sandwiched between two layers. Reflected light is polarized and absorbed by middle layer. Light transmission reduce by 50% improves vision and comfort. ...
Synopsis by Ping Zhou
... For transmissive optics, standard or high efficiency anti-reflective evaporative coatings can be applied in the same manner as conventionally polished optics. Residual reflections can be held to 0.2% to 0.3%. Total transmission can be specified as a minimum over a spectral band or as an average over ...
... For transmissive optics, standard or high efficiency anti-reflective evaporative coatings can be applied in the same manner as conventionally polished optics. Residual reflections can be held to 0.2% to 0.3%. Total transmission can be specified as a minimum over a spectral band or as an average over ...
holography - UCSB Physics
... The laser light passes through the substrate and then through the emulsion. In this trek a Bragg-plane (standing wave) is established by the incoming beam and the reflected light. As the light exits, it proceeds toward the objects that now scatter light back toward the emulsion where it interferes w ...
... The laser light passes through the substrate and then through the emulsion. In this trek a Bragg-plane (standing wave) is established by the incoming beam and the reflected light. As the light exits, it proceeds toward the objects that now scatter light back toward the emulsion where it interferes w ...
Advantages of Holographic Optical Tweezers
... Introducing a light modulator into the optical setup opens up the possibility to correct the setup for aberrations. This was done using a method described in? . The SLM displays two small apertures – similar to Young’s experiment– which move over the SLMs area probing the wavefront. A camera is posi ...
... Introducing a light modulator into the optical setup opens up the possibility to correct the setup for aberrations. This was done using a method described in? . The SLM displays two small apertures – similar to Young’s experiment– which move over the SLMs area probing the wavefront. A camera is posi ...
lecture plan
... L7: Detailed Theory of Plane Transmission Grating, Formation of Spectra, Concept of Absent Spectra, Dispersive Power of Diffraction Grating. L8: Resolving Power of an Optical Instrument, Rayleigh Criteria for Resolution, Resolving Power of Plane Transmission Grating and Resolving Power of a Glass Pr ...
... L7: Detailed Theory of Plane Transmission Grating, Formation of Spectra, Concept of Absent Spectra, Dispersive Power of Diffraction Grating. L8: Resolving Power of an Optical Instrument, Rayleigh Criteria for Resolution, Resolving Power of Plane Transmission Grating and Resolving Power of a Glass Pr ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.