Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
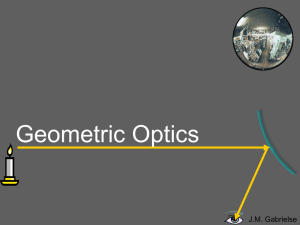
... When light rays go straight into our eyes, we see an image in the same spot as the object. ...
... When light rays go straight into our eyes, we see an image in the same spot as the object. ...
Exam 4-WWP
... screen is positioned 1.6 m from the double slits and the spacing between the two slits is 0.040 mm. What is the distance between the central and 1st bright fringes on the screen if the light source has a wavelength of 630 nm? ...
... screen is positioned 1.6 m from the double slits and the spacing between the two slits is 0.040 mm. What is the distance between the central and 1st bright fringes on the screen if the light source has a wavelength of 630 nm? ...
laser optical disk set
... Measure the focal lengths of the inner and outer rays. Now turn the lens around so that the curved surface is facing left, with the straight edge on the center of the ruler scale as before. Note that now both surfaces contribute to the refraction, and the focal points of the inner and outer ra ...
... Measure the focal lengths of the inner and outer rays. Now turn the lens around so that the curved surface is facing left, with the straight edge on the center of the ruler scale as before. Note that now both surfaces contribute to the refraction, and the focal points of the inner and outer ra ...
Document
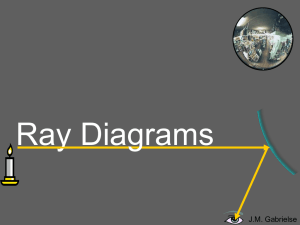
... The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Ray Diagrams Powerpoint
... The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The eye perceives light rays as if they came through the mirror. Imaginary light rays extended behind mirrors are called sight lines. The image is virtual since it is formed by imaginary sight lines, not real light rays. J.M. Gabrielse ...
A Fast Optical Propagation Technique for Modeling
... In our model, light reflecting from the down ribbons is multiplied by a phase term. The phase term is similar to a propagation term through a medium: Udown_ribbon = Uexp(j2kd), where, d is the distance that the ribbon is moved towards the substrate, typically λ/4 for the GLV. Far-field diffraction t ...
... In our model, light reflecting from the down ribbons is multiplied by a phase term. The phase term is similar to a propagation term through a medium: Udown_ribbon = Uexp(j2kd), where, d is the distance that the ribbon is moved towards the substrate, typically λ/4 for the GLV. Far-field diffraction t ...
Experimental demonstration of a narrowband, angular tolerant
... structures have been designed to have a low sideband reflectance, a spectral linewidth of 0.1 nm, and a 100% filtering efficiency [11] when they are illuminated by a plane wave. Yet, when they are illuminated by a Gaussian beam, the filtering efficiency of the single groove grating falls dramaticall ...
... structures have been designed to have a low sideband reflectance, a spectral linewidth of 0.1 nm, and a 100% filtering efficiency [11] when they are illuminated by a plane wave. Yet, when they are illuminated by a Gaussian beam, the filtering efficiency of the single groove grating falls dramaticall ...
View/Open - Dora.dmu.ac.uk
... Holography is a branch of optics and it is mostly unknown to a lay man as it contains complicated scientific terms in its definition such as diffraction and interference. The main focus of this paper is to briefly explain these terms using analogies and discuss the construction details of the CυBE. ...
... Holography is a branch of optics and it is mostly unknown to a lay man as it contains complicated scientific terms in its definition such as diffraction and interference. The main focus of this paper is to briefly explain these terms using analogies and discuss the construction details of the CυBE. ...
PC 481 Fiber Optics Lab Manual
... coupler allows two or more optical signals to be combined into one signal. The coupler can also be used to split the signals apart again. The fused coupler is the most common of the fibre couplers and the principle behind the fused couplers is that when two or more fibre cores are brought to within ...
... coupler allows two or more optical signals to be combined into one signal. The coupler can also be used to split the signals apart again. The fused coupler is the most common of the fibre couplers and the principle behind the fused couplers is that when two or more fibre cores are brought to within ...
Geometrical-optics code for computing the optical
... is the ray-optics approximation.10,22 The geometricaloptics method 共GOM兲 has been extensively used in scattering of radiation not only from spherical particles10 but also by nonspherical particles.23 Results from a Monte Carlo code based on the GOM show that differences in the simulated radiances be ...
... is the ray-optics approximation.10,22 The geometricaloptics method 共GOM兲 has been extensively used in scattering of radiation not only from spherical particles10 but also by nonspherical particles.23 Results from a Monte Carlo code based on the GOM show that differences in the simulated radiances be ...
Full-angle Negative Reflection with An Ultrathin Acoustic
... metasurface sample is sandwiched between two pieces of tempered glass(1.9 m length, 1.8 m width, 7 mm thick) and the gap is chosen as 5 cm, of which the cutoff frequency is higher than the operating frequency. Here, the incident acoustic wave is generated by 20 tightly arrayed loudspeakers, and the ...
... metasurface sample is sandwiched between two pieces of tempered glass(1.9 m length, 1.8 m width, 7 mm thick) and the gap is chosen as 5 cm, of which the cutoff frequency is higher than the operating frequency. Here, the incident acoustic wave is generated by 20 tightly arrayed loudspeakers, and the ...
R.J.Kasumova, Second harmonic generation in
... Following told above, we can see that refractive index for one and the same medium may be positive in one spectral field and negative in the other one. Therefore, features of negative refraction may become apparent at interaction of wave packages, bearing frequencies of which lie in the different sp ...
... Following told above, we can see that refractive index for one and the same medium may be positive in one spectral field and negative in the other one. Therefore, features of negative refraction may become apparent at interaction of wave packages, bearing frequencies of which lie in the different sp ...
Michelson Interferometer
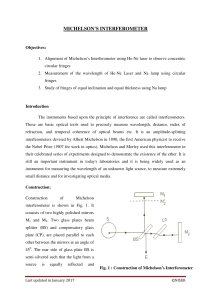
... monochromatic light of wavelength λ fall on BS. Half of light falling on BS is reflected towards the mirror M1 and the other half is transmitted towards mirror M2. Hence BS is known as a beam splitter. In case of sources which are not monochromatic, the glass plate CP is inserted between BS and M2. ...
... monochromatic light of wavelength λ fall on BS. Half of light falling on BS is reflected towards the mirror M1 and the other half is transmitted towards mirror M2. Hence BS is known as a beam splitter. In case of sources which are not monochromatic, the glass plate CP is inserted between BS and M2. ...
Plasmonic Nearfield Scanning Probe with High Transmission
... lens, the photoresist can never be exposed with such low input power (Figure 4c). Keeping the same scanning speed, a similar exposure result was obtained by using 10× higher input power (0.08 mW) through the tip without the plasmonic lens (Figure 4d). By comparing the depth and width of the fabricat ...
... lens, the photoresist can never be exposed with such low input power (Figure 4c). Keeping the same scanning speed, a similar exposure result was obtained by using 10× higher input power (0.08 mW) through the tip without the plasmonic lens (Figure 4d). By comparing the depth and width of the fabricat ...
Chapter 4
... From this derivation we learn that: - the conversion efficiency is proportional to the power density, so the total amount of generated light at the second harmonic is proportional to [P()] 2. Thus second harmonic generation is a process that is non-linear in the power dependence. - the efficiency i ...
... From this derivation we learn that: - the conversion efficiency is proportional to the power density, so the total amount of generated light at the second harmonic is proportional to [P()] 2. Thus second harmonic generation is a process that is non-linear in the power dependence. - the efficiency i ...
How can the reflections of light on the surface of
... In 1816, André-Marie Ampère finally released the wave theory from its deadlocked position by saying that polarization can be explained if it is assumed that light is a transverse wave instead of a longitudinal wave. It was a little weird to propose this at the time. Then, it was believed that light ...
... In 1816, André-Marie Ampère finally released the wave theory from its deadlocked position by saying that polarization can be explained if it is assumed that light is a transverse wave instead of a longitudinal wave. It was a little weird to propose this at the time. Then, it was believed that light ...
Experimental realization of three-color entanglement at optical fiber
... (1) are simultaneously violated the three optical modes a2 , a3 and a4 are in a CV entangled state [33]. In the experiments we should select the optimal gain factors (gjopt ) to obtain the minimal correlation variance combinations, which can be accomplished by adjusting the electronic gains of the d ...
... (1) are simultaneously violated the three optical modes a2 , a3 and a4 are in a CV entangled state [33]. In the experiments we should select the optimal gain factors (gjopt ) to obtain the minimal correlation variance combinations, which can be accomplished by adjusting the electronic gains of the d ...
Manuscript2 - Open Research Exeter
... accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Jeffrey M. Gordon et.al [4–6]. When comparing the types of solar concentrator photovoltai ...
... accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Jeffrey M. Gordon et.al [4–6]. When comparing the types of solar concentrator photovoltai ...
Breakup and Fusion of Self-Guided Femtosecond Light Pulses in Air
... through the atmosphere, in view of potential LIDAR applications [1]. Laser beams with high peak power are, indeed, known to form robust light guides over very long distances [2–4]. Various attempts in modeling this phenomenon have been proposed, by solving nonlinear Schrödingerlike systems [5–9]. Ba ...
... through the atmosphere, in view of potential LIDAR applications [1]. Laser beams with high peak power are, indeed, known to form robust light guides over very long distances [2–4]. Various attempts in modeling this phenomenon have been proposed, by solving nonlinear Schrödingerlike systems [5–9]. Ba ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.