Photodetecting Fiber Webs—Y. Fink, J. Joannopoulos
... (MRSEC) program of the NSF with use of their Shared Experimental Facilities. Modal decomposition in multimode optical waveguides plays an important role in the study of multimode wave propagation by providing insight to the nature of mode interactions due to structural perturbation. Nevertheless, to ...
... (MRSEC) program of the NSF with use of their Shared Experimental Facilities. Modal decomposition in multimode optical waveguides plays an important role in the study of multimode wave propagation by providing insight to the nature of mode interactions due to structural perturbation. Nevertheless, to ...
Michelson Interferometry and Measurement of the Sodium Doublet Splitting
... where m is the “order” of the interference. Note that the beam in one arm undergoes an additional external reflection, and thus incurs one additional π phase shift, relative to the beam in the other arm, which is why the above condition produces a dark, rather than a bright, fringe. If the two mirro ...
... where m is the “order” of the interference. Note that the beam in one arm undergoes an additional external reflection, and thus incurs one additional π phase shift, relative to the beam in the other arm, which is why the above condition produces a dark, rather than a bright, fringe. If the two mirro ...
Investigating the Wavelength Dependency of Dot Gain in Color Print
... Characterizing the halftone print properties, is useful for system calibration and quality control of the color reproduction. There are numerous physical phenomena which influence color perception such as the light source, surface reflection, light absorption, light scattering, multiple internal ref ...
... Characterizing the halftone print properties, is useful for system calibration and quality control of the color reproduction. There are numerous physical phenomena which influence color perception such as the light source, surface reflection, light absorption, light scattering, multiple internal ref ...
An analogy strategy for transformation optics Yao Chen Liu
... Transformation optics has aroused interest from a wide spectrum of scientific communities [1–10]. The term was coined based on the fact that Maxwell’s equations are form-invariant under coordinate transformations [2], meaning electromagnetic waves in one coordinate system can be mapped into another o ...
... Transformation optics has aroused interest from a wide spectrum of scientific communities [1–10]. The term was coined based on the fact that Maxwell’s equations are form-invariant under coordinate transformations [2], meaning electromagnetic waves in one coordinate system can be mapped into another o ...
Advances In Processing of Compound Semiconductor Substrates
... Once the thinning process is complete (at which point, the device substrate is typically <100 µm thick), it is necessary to pattern the backside vias. Although the primary reason for wafer thinning is due to the heat management issue, another, and very important, reason for thinning is related to th ...
... Once the thinning process is complete (at which point, the device substrate is typically <100 µm thick), it is necessary to pattern the backside vias. Although the primary reason for wafer thinning is due to the heat management issue, another, and very important, reason for thinning is related to th ...
Slide 1
... • The evanescent field penetrates only ~10’s nm into the resist. Substrate • A two-layer resist process may be utilized to make this work. Evanescent near field region • I.e. top thin layer for exposure, then transfer the pattern into a thick bottom layer. ...
... • The evanescent field penetrates only ~10’s nm into the resist. Substrate • A two-layer resist process may be utilized to make this work. Evanescent near field region • I.e. top thin layer for exposure, then transfer the pattern into a thick bottom layer. ...
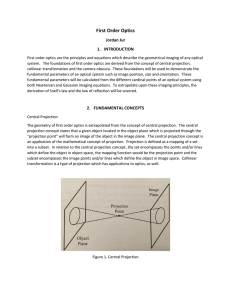
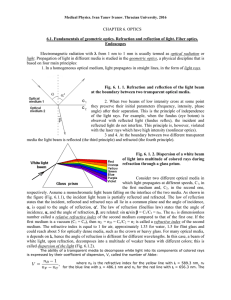
chapter 6
... medium. The refractive index is equal to 1 for air, approximately 1.33 for water, 1.5 for flint glass and could reach about 5 for optically dense media, such as the crown or heavy glass. For many optical media, n depends on , hence the angle of refraction is different for different wavelengths. In ...
... medium. The refractive index is equal to 1 for air, approximately 1.33 for water, 1.5 for flint glass and could reach about 5 for optically dense media, such as the crown or heavy glass. For many optical media, n depends on , hence the angle of refraction is different for different wavelengths. In ...
Model for estimating the penetration depth limit of
... optical focus even tens of centimeters deep in the human body. However, there are two important constraints that fundamentally limit the penetration depth of TRUE focusing technique for living tissue applications. First, the incident light fluence per pulse at the tissue surface has to be smaller th ...
... optical focus even tens of centimeters deep in the human body. However, there are two important constraints that fundamentally limit the penetration depth of TRUE focusing technique for living tissue applications. First, the incident light fluence per pulse at the tissue surface has to be smaller th ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... The Photoelectric Effect Mystery Another dilemma was how to properly explain the photoelectric effect. Around the same time, physicists knew that if one were to shine an ultraviolet light onto a charged metal plate in a vacuum, the metal plate would lose its charge, or discharge. The brighter the UV ...
... The Photoelectric Effect Mystery Another dilemma was how to properly explain the photoelectric effect. Around the same time, physicists knew that if one were to shine an ultraviolet light onto a charged metal plate in a vacuum, the metal plate would lose its charge, or discharge. The brighter the UV ...
Low-grazing angles scattering of electromagnetic waves from one
... understand that designing an accurate model for this quantity is challenging. The domain of validity of the most classical approximate models [2] has already been studied and more or less precisely defined (see for example [3–6]): height very small compared to the electromagnetic wavelength for the S ...
... understand that designing an accurate model for this quantity is challenging. The domain of validity of the most classical approximate models [2] has already been studied and more or less precisely defined (see for example [3–6]): height very small compared to the electromagnetic wavelength for the S ...
ChromatiC dispersion
... dispersion also has an effect in many other circumstances: for example, it causes pulses to spread in optical fibers, degrading signals over long distances; also, a cancellation between dispersion and nonlinear effects leads to soliton waves. Dispersion is most often described for light waves, but i ...
... dispersion also has an effect in many other circumstances: for example, it causes pulses to spread in optical fibers, degrading signals over long distances; also, a cancellation between dispersion and nonlinear effects leads to soliton waves. Dispersion is most often described for light waves, but i ...
Surface Watch - YMS Magazine
... and unprecedented bare substrate microroughness characterization are now possible, as well as excursion monitoring and process control based on surface topography. Previously, surface scattering was viewed mainly as a noise source for optical wafer inspection, a limiting factor in particle detection ...
... and unprecedented bare substrate microroughness characterization are now possible, as well as excursion monitoring and process control based on surface topography. Previously, surface scattering was viewed mainly as a noise source for optical wafer inspection, a limiting factor in particle detection ...
Temporal coherence characteristics of a superluminescent
... various optical feedback ratios. The one by one wave packets of interference patterns are caused by the Fabry-Perot modulation of the SLD device, and the schematic diagram of the optical paths due to multiple reflections in the SLD active layer is shown in Fig. 6(a). We assume that the output light ...
... various optical feedback ratios. The one by one wave packets of interference patterns are caused by the Fabry-Perot modulation of the SLD device, and the schematic diagram of the optical paths due to multiple reflections in the SLD active layer is shown in Fig. 6(a). We assume that the output light ...
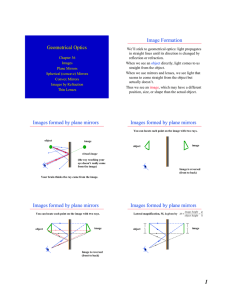
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... But, image forming instruments commonly have more than one lens! For example, a telescope. “Objective” f f “Eyepiece” o ...
... But, image forming instruments commonly have more than one lens! For example, a telescope. “Objective” f f “Eyepiece” o ...
Variable Incidence Angle Fluorescence Interference Contrast
... is quoted as ,0.1 nm; however, repeated measurements of the same SiO2 step on the same chip yielded variations in thickness of as much as 1 nm, possibly indicative of some variation in thickness arising from the etch process. The SiO2 thickness determined by ellipsometry is therefore reported to 1 n ...
... is quoted as ,0.1 nm; however, repeated measurements of the same SiO2 step on the same chip yielded variations in thickness of as much as 1 nm, possibly indicative of some variation in thickness arising from the etch process. The SiO2 thickness determined by ellipsometry is therefore reported to 1 n ...
Optical Elements
... worth mentioning that small-scale roughness of a typical mirror surface, measured on distances of a micrometer scale, is about 0.01 nm (standard float glass— 0.02 nm), while large-scale roughness measured on a millimeter scale may vary from 0.1 to 1 nm. Reflecting layer may be either wide-band or na ...
... worth mentioning that small-scale roughness of a typical mirror surface, measured on distances of a micrometer scale, is about 0.01 nm (standard float glass— 0.02 nm), while large-scale roughness measured on a millimeter scale may vary from 0.1 to 1 nm. Reflecting layer may be either wide-band or na ...
An ultrasmall wavelength-selective channel drop switch
... photonic bandgap changes because of the existence of the slotted mode. Also this waveguide is no longer single-mode. The band structure is also altered by a change in the gap, so we need to consider carefully the slotted mode in the design. At a large gap, the light wave propagates in the PC wavegui ...
... photonic bandgap changes because of the existence of the slotted mode. Also this waveguide is no longer single-mode. The band structure is also altered by a change in the gap, so we need to consider carefully the slotted mode in the design. At a large gap, the light wave propagates in the PC wavegui ...
Wavelength Converters in Optical Communication Systems
... wavelength to another without entering the electrical domain. A simple technique for the realization of this function is the use of cross gain modulation (XGM) in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA’s). The principle is depicted in Fig. 3.4.1(a)[9] [11] showing an intensity modulated input signal ...
... wavelength to another without entering the electrical domain. A simple technique for the realization of this function is the use of cross gain modulation (XGM) in semiconductor optical amplifiers (SOA’s). The principle is depicted in Fig. 3.4.1(a)[9] [11] showing an intensity modulated input signal ...
Anti-reflective coating

An antireflective or anti-reflection (AR) coating is a type of optical coating applied to the surface of lenses and other optical elements to reduce reflection. In typical imaging systems, this improves the efficiency since less light is lost. In complex systems such as a telescope, the reduction in reflections also improves the contrast of the image by elimination of stray light. This is especially important in planetary astronomy. In other applications, the primary benefit is the elimination of the reflection itself, such as a coating on eyeglass lenses that makes the eyes of the wearer more visible to others, or a coating to reduce the glint from a covert viewer's binoculars or telescopic sight.Many coatings consist of transparent thin film structures with alternating layers of contrasting refractive index. Layer thicknesses are chosen to produce destructive interference in the beams reflected from the interfaces, and constructive interference in the corresponding transmitted beams. This makes the structure's performance change with wavelength and incident angle, so that color effects often appear at oblique angles. A wavelength range must be specified when designing or ordering such coatings, but good performance can often be achieved for a relatively wide range of frequencies: usually a choice of IR, visible, or UV is offered.