Hydrocarbons and Fuels - Deans Community High School
... 1. Before collecting the alcohol and carboxylic acid set up a water bath using the larger beaker and heat the water until it boils. Turn off the Bunsen. 2. Add the alcohol to a test tube to a depth of about 1 cm. To this add about the same volume of carboxylic acid. If the acid is a solid then use a ...
... 1. Before collecting the alcohol and carboxylic acid set up a water bath using the larger beaker and heat the water until it boils. Turn off the Bunsen. 2. Add the alcohol to a test tube to a depth of about 1 cm. To this add about the same volume of carboxylic acid. If the acid is a solid then use a ...
- Catalyst
... ion in solution. We can write the hydronium ion in solution as either H+(aq) or H3O+(aq) - they mean the same thing. The water (H2O) can be written as a reactant or above the arrow indicating that it is the solvent in which the HI was dissolved. ...
... ion in solution. We can write the hydronium ion in solution as either H+(aq) or H3O+(aq) - they mean the same thing. The water (H2O) can be written as a reactant or above the arrow indicating that it is the solvent in which the HI was dissolved. ...
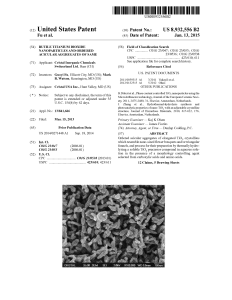
Rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles and ordered acicular
... Example 1 and shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 6 is an SEM image of the shaped rutile TiO2 nanopar ticles shown in FIG. 1 after calcining at 550° C. for 6 hours. FIG. 7 is an enlarged SEM image of the shaped rutile TiO2 nanoparticles shown in FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is anX-ray diffraction C(RD) pattern of the calcined ...
... Example 1 and shown in FIG. 1. FIG. 6 is an SEM image of the shaped rutile TiO2 nanopar ticles shown in FIG. 1 after calcining at 550° C. for 6 hours. FIG. 7 is an enlarged SEM image of the shaped rutile TiO2 nanoparticles shown in FIG. 6. FIG. 8 is anX-ray diffraction C(RD) pattern of the calcined ...
QUESTION BANK CHEMISTRY-XII THE SOLID STATE CHAPTER
... 38. Why the potential of the mercury cell remains constant throughout the life? 39. What is corrosion 40. How does molar conductivity varies with concentration for weak electrolyte? ...
... 38. Why the potential of the mercury cell remains constant throughout the life? 39. What is corrosion 40. How does molar conductivity varies with concentration for weak electrolyte? ...
Physical and Chemical equilibrium
... occurs at 1 atm pressure. Here, both the liquid and ice exist together. Also, at melting point of ice or freezing point of water, the rate of melting of ice equals with rate of freezing of water. With change in pressure the temperature at which this equilibrium onsets changes. (ii) Liquid-vapour equ ...
... occurs at 1 atm pressure. Here, both the liquid and ice exist together. Also, at melting point of ice or freezing point of water, the rate of melting of ice equals with rate of freezing of water. With change in pressure the temperature at which this equilibrium onsets changes. (ii) Liquid-vapour equ ...
Fragmentation pathway for glutamine identification: Loss of 73 da
... employing this method is used for about 4 million babies in the United States each year [12]. Typical amino acid analysis by MS/MS includes two steps: 1) the amino acids are esterified as butyl esters with butanol-hydrogen chloride, and 2) the amino acid butyl esters then are subjected to collision- ...
... employing this method is used for about 4 million babies in the United States each year [12]. Typical amino acid analysis by MS/MS includes two steps: 1) the amino acids are esterified as butyl esters with butanol-hydrogen chloride, and 2) the amino acid butyl esters then are subjected to collision- ...
2 - C7Chemistry
... Reaction 2 + 2H2 (g) Copper is below hydrogen in the activity series. Copper metal will only replace elements that are below it in the activity series. ...
... Reaction 2 + 2H2 (g) Copper is below hydrogen in the activity series. Copper metal will only replace elements that are below it in the activity series. ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... A. The rate of crystallization equals the rate of dissolving B. The rate of crystallization is greater than the rate of dissolving C. The rate of crystallization is less than the rate of dissolving D. The rate of crystallization will increase greatly with the addition of a salt crystal ...
... A. The rate of crystallization equals the rate of dissolving B. The rate of crystallization is greater than the rate of dissolving C. The rate of crystallization is less than the rate of dissolving D. The rate of crystallization will increase greatly with the addition of a salt crystal ...
1aUnit Two Handouts - Dunmore High School
... CaSO4 Fe(C2H3O2)2 K2SO4 HNO3 H2CO3 ZnS NOTE: When H2CO3, H2SO3 or NH4OH are formed as products, they do break down, though not into ions. They break down into H2O and a gaseous substance. ...
... CaSO4 Fe(C2H3O2)2 K2SO4 HNO3 H2CO3 ZnS NOTE: When H2CO3, H2SO3 or NH4OH are formed as products, they do break down, though not into ions. They break down into H2O and a gaseous substance. ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. Part II requires complete responses to questions involving problemsolving and explanations. One hour and forty-five minutes are allowed to complete this part. Be sure to print your name, the name of your school, and your identification number in the spac ...
... DO NOT TURN THE PAGE UNTIL DIRECTED TO DO SO. Part II requires complete responses to questions involving problemsolving and explanations. One hour and forty-five minutes are allowed to complete this part. Be sure to print your name, the name of your school, and your identification number in the spac ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
... If a beam of continuous radiation like white light is directed through a gaseous sample of an element, the radiation that emerges has certain wavelengths missing. This shows up as dark lines on a continuous spectrum and is called an atomic absorption spectrum, see Figure 1.4 (c). This also provides ...
... If a beam of continuous radiation like white light is directed through a gaseous sample of an element, the radiation that emerges has certain wavelengths missing. This shows up as dark lines on a continuous spectrum and is called an atomic absorption spectrum, see Figure 1.4 (c). This also provides ...
Default Normal Template
... E.x: Calculate the number of carbon atoms and the number of hydrogen atoms in 600g of propane, C3 H8 C = 12 , H = 1. MW = ( 3 x 12 ) + ( 8 x 1 ) = 44 amu Number of moles of propane = 600 g x 1 mol = 13.63 mol ...
... E.x: Calculate the number of carbon atoms and the number of hydrogen atoms in 600g of propane, C3 H8 C = 12 , H = 1. MW = ( 3 x 12 ) + ( 8 x 1 ) = 44 amu Number of moles of propane = 600 g x 1 mol = 13.63 mol ...
Prep UK-intro.p65
... problems. For the solutions of physical chemistry problems the units of the equilibrium constant, depending on the particular circumstances, have to be specified. If the constant appears in thermodynamic equations, the equilibrium constant (Ka) is dimensionless and its value depends on the choice of ...
... problems. For the solutions of physical chemistry problems the units of the equilibrium constant, depending on the particular circumstances, have to be specified. If the constant appears in thermodynamic equations, the equilibrium constant (Ka) is dimensionless and its value depends on the choice of ...
C. 3.5 g
... sulphuric acid at room conditions, the reaction stopped in 40 seconds. At the same time, 2400 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced. Which of the following statements about the reaction is INCORRECT? ...
... sulphuric acid at room conditions, the reaction stopped in 40 seconds. At the same time, 2400 cm3 of carbon dioxide was produced. Which of the following statements about the reaction is INCORRECT? ...
Amount of substance
... Q32.On heating, magnesium reacts vigorously with element X to produce compound Y. An aqueous solution of Y, when treated with aqueous silver nitrate, gives a white precipitate that is readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia. What is the minimum mass of X that is needed to react completely with 4.0 ...
... Q32.On heating, magnesium reacts vigorously with element X to produce compound Y. An aqueous solution of Y, when treated with aqueous silver nitrate, gives a white precipitate that is readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia. What is the minimum mass of X that is needed to react completely with 4.0 ...
379 - FTP
... A disproportion reaction occurs rapidly in water forming hypochlorous acid: Cl2 (aq) → H+ + Cl¯ + HOCl The equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction at 25°C is 4.2x10–4. The standard redox potentials for the following two reactions: H+ + HOCl + e¯ → ½Cl2 (g) + H2O 2H+ + 2Cl¯ + ½O2 → Cl2 + H2O are 1 ...
... A disproportion reaction occurs rapidly in water forming hypochlorous acid: Cl2 (aq) → H+ + Cl¯ + HOCl The equilibrium constant, K, for this reaction at 25°C is 4.2x10–4. The standard redox potentials for the following two reactions: H+ + HOCl + e¯ → ½Cl2 (g) + H2O 2H+ + 2Cl¯ + ½O2 → Cl2 + H2O are 1 ...
Use the following answers for questions 1
... 44. A rigid metal tank contains oxygen gas. Which of the following applies to the gas in the tank when additional oxygen is added at constant temperature? (A) The volume of the gas increase. (B) The pressure of the gas decreases. (C) The average speed of the gas molecules remains th same. (D) The to ...
... 44. A rigid metal tank contains oxygen gas. Which of the following applies to the gas in the tank when additional oxygen is added at constant temperature? (A) The volume of the gas increase. (B) The pressure of the gas decreases. (C) The average speed of the gas molecules remains th same. (D) The to ...
35 IChO Problems 1-13
... Problem 1: Proton – antiproton atom Experimental and theoretical work has shown that for each of the fundamental particles such as protons (p) and electrons (e) there exist antiparticles which differ from their counterparts usually in one property only, but have the same mass. Antielectrons (or posi ...
... Problem 1: Proton – antiproton atom Experimental and theoretical work has shown that for each of the fundamental particles such as protons (p) and electrons (e) there exist antiparticles which differ from their counterparts usually in one property only, but have the same mass. Antielectrons (or posi ...
vce chemistry trial exam 1
... 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. B is incorrect because thin-layer chromatography is not precise enough to reliably separate esters for collection. IR spectroscopy will enable the identification of func ...
... 13C and 1H spectra. A is incorrect because neither UV-visible spectroscopy nor NMR spectroscopy allow the separation of compounds. B is incorrect because thin-layer chromatography is not precise enough to reliably separate esters for collection. IR spectroscopy will enable the identification of func ...
Identification of Aspartic and Isoaspartic Acid Residues in Amyloid β
... and MS for the detection of IsoAsp.31 The 18O labeling coupled to MS can also be used for detection of Asn deamidation and Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological sa ...
... and MS for the detection of IsoAsp.31 The 18O labeling coupled to MS can also be used for detection of Asn deamidation and Asp isomerization;32,33 however, this can only be applied to detection of modification sites in the protein, but not to identify modifications already existing in biological sa ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... More electronegative element tends to pull the electron density towards it. H ------> F The arrow shows the shift of electron density towards fluorine (more electronegative) which leads to charge separation. Hydrogen will have a partial positive charge (positive end)and fluorine will have a partial ...
... More electronegative element tends to pull the electron density towards it. H ------> F The arrow shows the shift of electron density towards fluorine (more electronegative) which leads to charge separation. Hydrogen will have a partial positive charge (positive end)and fluorine will have a partial ...
getting started 3.1 hydrocarbons
... moved more slowly and were closer together, with stronger forces of attraction. The reverse is true for the warmed oils. (b) In cold winter temperatures, motor oils become more viscous. Therefore, a less viscous oil is needed in winter in order to have the same viscosity as the summer oils. ...
... moved more slowly and were closer together, with stronger forces of attraction. The reverse is true for the warmed oils. (b) In cold winter temperatures, motor oils become more viscous. Therefore, a less viscous oil is needed in winter in order to have the same viscosity as the summer oils. ...
C:\D\Books\Cambridge University Press\CUP Problems\Problems.wpd
... The water is led into a biological wastewater treatment plant which does not perform nitrification. The plant is assumed to oxidize 70 % of the organic contamination. b Calculate the amount and the mass of oxygen required per day. 100. A wastewater treatment plant produces biomass, C5H7O2N, and carb ...
... The water is led into a biological wastewater treatment plant which does not perform nitrification. The plant is assumed to oxidize 70 % of the organic contamination. b Calculate the amount and the mass of oxygen required per day. 100. A wastewater treatment plant produces biomass, C5H7O2N, and carb ...