study guide and review for first semester final
... 17. Predict if metathesis occurs, explain why it occurs, and write ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. Ex. Predict if the following reaction occurs. If so, explain why and write ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. H2SO4 + 2 KOH K2SO4 + 2 H2O Yes because water is a product N ...
... 17. Predict if metathesis occurs, explain why it occurs, and write ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. Ex. Predict if the following reaction occurs. If so, explain why and write ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. H2SO4 + 2 KOH K2SO4 + 2 H2O Yes because water is a product N ...
Chemistry - Target Publications
... Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane. How is carbolic acid prepared from chlorobenzene? What is the action of bromine water on carbolic acid? Write chemical test to distinguish between carbolic acid and alcohol. ii. Explain cationic complexes and anionic complexes of coordina ...
... Discuss the mechanism of alkaline hydrolysis of bromomethane. How is carbolic acid prepared from chlorobenzene? What is the action of bromine water on carbolic acid? Write chemical test to distinguish between carbolic acid and alcohol. ii. Explain cationic complexes and anionic complexes of coordina ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... The chemical behaviour of a strong electrolyte behaviour of its constituent ions. Ionic equations can be written only for strong electrolytes which are soluble. ...
... The chemical behaviour of a strong electrolyte behaviour of its constituent ions. Ionic equations can be written only for strong electrolytes which are soluble. ...
Chemical laboratories Dipl.-Ing.(FH) Giovanna
... Sugar and lactic acid analysis by HPLC Ultimate 3000 from Dionex ...
... Sugar and lactic acid analysis by HPLC Ultimate 3000 from Dionex ...
Chapter 4 - Aqueous Reactions
... HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) unreactive - they do not tarnish ...
... HCl. They form very protective oxides. Cu reacts with nitric acid (HNO3) because that acid is a strong oxidizing agent in addition to being an acid. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are valuable because they are (a) rare and (b) unreactive - they do not tarnish ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
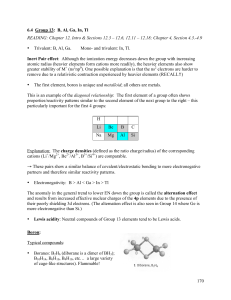
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
... • For an oxyacid (general formula HmXOn) it often happens that there are multiple possible values of n for each element X, and as such, within this series of compounds, – There is always an acid in the series that ends with “ic” • Adding another oxygen to the “ic” acid produces the “per….ic” acid • ...
6.5 Main Group
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
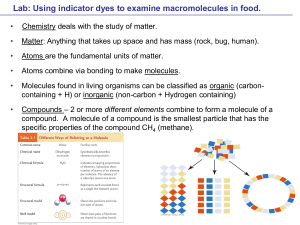
Solutions - Seattle Central
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
... Indicators are chemical compounds used to detect the presence of other compounds. They change shape in the presence of certain compounds as a result of chemical reactions. ...
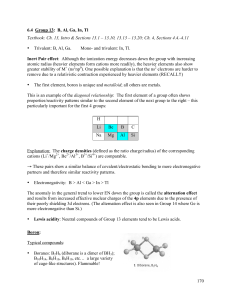
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
... Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and anions). NaCl, MgCl2, K2S, Na2SO4 Molecular (covalent)- Consists of non-metals only. HCl, N2O4, C3H6O, C6H12O6 Note- All compounds can be molecules; not all molecules can be compounds. Ions- Are chemical species th ...
name - cloudfront.net
... If the reaction of 150. g of ammonia with 150. g of oxygen gas yields 87. g of nitric oxide (NO), what is the percent yield of this reaction? (77%) 14.The Hall process for the production of aluminum involves the reaction of aluminum oxide with elemental carbon to give aluminum metal and carbon monox ...
... If the reaction of 150. g of ammonia with 150. g of oxygen gas yields 87. g of nitric oxide (NO), what is the percent yield of this reaction? (77%) 14.The Hall process for the production of aluminum involves the reaction of aluminum oxide with elemental carbon to give aluminum metal and carbon monox ...
Honors Chemistry II Review 1. Express the following in scientific
... monoxide to yield metallic iron and carbon dioxide. Write a balanced chemical equation and predict how many moles of CO will react with 0.5 moles of iron (III) oxide. 18. Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), a solvent used in the decaffeination of coffee beans, is prepared by the reaction of methane (CH4) with ...
... monoxide to yield metallic iron and carbon dioxide. Write a balanced chemical equation and predict how many moles of CO will react with 0.5 moles of iron (III) oxide. 18. Dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), a solvent used in the decaffeination of coffee beans, is prepared by the reaction of methane (CH4) with ...
Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation
... Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation with the appropriate interpretation. __ 1. 2CH4O(l) + O2(g) 2CH2O(l) + 2H2O(l) __ 2. NH2Cl(g) NH2Cl(aq) ...
... Chemical Equation Interpretations – Match the chemical equation with the appropriate interpretation. __ 1. 2CH4O(l) + O2(g) 2CH2O(l) + 2H2O(l) __ 2. NH2Cl(g) NH2Cl(aq) ...
Exam 2
... 6. In the reduction of 2-butanone to (2)-butanol using the (S)-CBS reagent (2-methyloxazaborolidine + BH3), what is transferred in the critical step in the reaction mechanism? a) a hydride ion, H- b) a hydrogen radical, H c) a proton, H+ d) both hydrogens simultaneously as molecular hydrogen, H2 e) ...
... 6. In the reduction of 2-butanone to (2)-butanol using the (S)-CBS reagent (2-methyloxazaborolidine + BH3), what is transferred in the critical step in the reaction mechanism? a) a hydride ion, H- b) a hydrogen radical, H c) a proton, H+ d) both hydrogens simultaneously as molecular hydrogen, H2 e) ...
CHEMISTRY 3
... Because esters are made by forcing the equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to the right, it should also be possible to split an ester back into its constituents by forcing the same equilibrium to shift itself in the reverse direction, ie to the left. (a) ...
... Because esters are made by forcing the equilibrium reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol to the right, it should also be possible to split an ester back into its constituents by forcing the same equilibrium to shift itself in the reverse direction, ie to the left. (a) ...
Mongar Higher Secondary School
... vi) Give reasons for the following. i) Table salt (NaCl) becomes moist and sticky during rainy season. ii) Alkalis should not be left exposed to air iii) Ionic compounds are bad conductors in solid state but are good conductiors in molten state or in their aqueous solutions. iv) The atomic size decr ...
... vi) Give reasons for the following. i) Table salt (NaCl) becomes moist and sticky during rainy season. ii) Alkalis should not be left exposed to air iii) Ionic compounds are bad conductors in solid state but are good conductiors in molten state or in their aqueous solutions. iv) The atomic size decr ...
Advanced Placement Chemistry: 1984 Free Response Questions
... For any given gas, the values of the constants a and b can be determined experimentally. Indicate which physical properties of a molecule determine the magnitudes of the constants a and b . Which of the two molecules, H2 or H2S has the higher value for a and which has the higher value for b ? Explai ...
... For any given gas, the values of the constants a and b can be determined experimentally. Indicate which physical properties of a molecule determine the magnitudes of the constants a and b . Which of the two molecules, H2 or H2S has the higher value for a and which has the higher value for b ? Explai ...
Chapter 2 – Chemical Composition of the Body
... • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molecules (especially water).. ...
... • These hydrogen bonds are very important because they alter the physical and chemical properties of many molecules (especially water).. ...
F324 summary - Macmillan Academy
... • Amines are bases since they can accept a proton by using the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. • Amines react with acids to form salts. • Aliphatic amines may be prepared by the substitution of halogenoalkanes with excess ammonia. • Aromatic amines can be prepared by reducing nitroarene ...
... • Amines are bases since they can accept a proton by using the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. • Amines react with acids to form salts. • Aliphatic amines may be prepared by the substitution of halogenoalkanes with excess ammonia. • Aromatic amines can be prepared by reducing nitroarene ...
Types of Weathering
... absorbs sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. Through a series of chemical reactions these pollutants are converted into acids that are a cause of acid precipitation. ...
... absorbs sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides. Through a series of chemical reactions these pollutants are converted into acids that are a cause of acid precipitation. ...