chapter 4 types of chemical reactions and solution
... a. Imprecise and inaccurate data: 12.32 cm, 9.63 cm, 11.98 cm, 13.34 cm b. Precise but inaccurate data: 8.76 cm, 8.79 cm, 8.72 cm, 8.75 cm c. Precise and accurate data: 10.60 cm, 10.65 cm, 10.63 cm, 10.64 cm Data can be imprecise if the measuring device is imprecise as well as if the user of the mea ...
... a. Imprecise and inaccurate data: 12.32 cm, 9.63 cm, 11.98 cm, 13.34 cm b. Precise but inaccurate data: 8.76 cm, 8.79 cm, 8.72 cm, 8.75 cm c. Precise and accurate data: 10.60 cm, 10.65 cm, 10.63 cm, 10.64 cm Data can be imprecise if the measuring device is imprecise as well as if the user of the mea ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
COMPETITION PTOBLEMS 1
... Consequently, it was necessary to make some corrections in order to unify the form of the problems. However, they did not concern the contents and language of the problems. Many of the first problems were published separately in various national journals, in different languages and they were hard to ...
... Consequently, it was necessary to make some corrections in order to unify the form of the problems. However, they did not concern the contents and language of the problems. Many of the first problems were published separately in various national journals, in different languages and they were hard to ...
SCH3U: Final Exam Review Note: These questions a
... 43. 65 mL of a 2.5 mol/L solution of silver nitrate is added to an excess of calcium chloride. Identify the precipitate, and calculate the mass of this precipitate that is formed. 44. An excess of sodium carbonate solution is added to 75.0 mL of calcium chloride solution. 7.50 g of precipitate is fo ...
... 43. 65 mL of a 2.5 mol/L solution of silver nitrate is added to an excess of calcium chloride. Identify the precipitate, and calculate the mass of this precipitate that is formed. 44. An excess of sodium carbonate solution is added to 75.0 mL of calcium chloride solution. 7.50 g of precipitate is fo ...
CHAPTER 4 REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
CO2 Capture from Flue gas using Amino acid salt
... from coal-fired power plants, so that it is almost completely free of this greenhouse gas. The most advanced techniques towards practical application are based on chemical absorption, where CO2 in the flue gas is chemically bond by a solvent, usually an aqueous solution of amines, resulting in a cle ...
... from coal-fired power plants, so that it is almost completely free of this greenhouse gas. The most advanced techniques towards practical application are based on chemical absorption, where CO2 in the flue gas is chemically bond by a solvent, usually an aqueous solution of amines, resulting in a cle ...
Chapter 4 - Chemistry
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
SCH3U: Final Exam Review
... 24. Iron reacts with antimony trisulphide in a single replacement reaction. Antimony and iron (II) sulphide are produced. Calculate the mass of iron that is needed to react with 15.6 g of antimony trisulphide. 25. The theoretical yield of a reaction is 62.9 g, but the actual yield is 47.8 g. Calcula ...
... 24. Iron reacts with antimony trisulphide in a single replacement reaction. Antimony and iron (II) sulphide are produced. Calculate the mass of iron that is needed to react with 15.6 g of antimony trisulphide. 25. The theoretical yield of a reaction is 62.9 g, but the actual yield is 47.8 g. Calcula ...
questions based on high order thinking skill
... 0.01 M aqueous soln ? (Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol) Ans. Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol ...
... 0.01 M aqueous soln ? (Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol) Ans. Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol ...
questions based on high order thinking skill - Entrance
... 0.01 M aqueous soln ? (Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol) Ans. Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol ...
... 0.01 M aqueous soln ? (Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol) Ans. Kb = 0.51 k kg/mol ...
Derivatization - Sigma
... properties. These compounds are either silylated, acylated, or alkylated in order to render them more volatile. Organic acids, amides, hydroxy compounds, amino acids are examples of polar compounds that need to be derivatized. The functional group (e.g., O-H, COOH, N-H, and S-H) on these polar compo ...
... properties. These compounds are either silylated, acylated, or alkylated in order to render them more volatile. Organic acids, amides, hydroxy compounds, amino acids are examples of polar compounds that need to be derivatized. The functional group (e.g., O-H, COOH, N-H, and S-H) on these polar compo ...
Laboratory Works and Home Tasks in General Chemistry
... For bases with a single hydroxyl group — monoacidic bases (NaOH, KOH and others) the equivalent factor is equal to one (feq = 1); for bases with two hydroxyl groups — diacidic bases (Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 and others) equivalent factor may take the values 1 or 1/2 (feq = 1 or 1/2); for bases with three hy ...
... For bases with a single hydroxyl group — monoacidic bases (NaOH, KOH and others) the equivalent factor is equal to one (feq = 1); for bases with two hydroxyl groups — diacidic bases (Ca(OH)2, Ba(OH)2 and others) equivalent factor may take the values 1 or 1/2 (feq = 1 or 1/2); for bases with three hy ...
1 – Introduction
... 3 - Labeling of fertilizers: 3 – 1 - Macro nutrient fertilizers; Macronutrient fertilizers are labeled with an NPK analysis and also "N-P-K-S" in Australia . An example of labeling for the fertilizer potash is composed of 1:1 potassium to chloride or 52 % potassium and 48% chlorine by weight (owing ...
... 3 - Labeling of fertilizers: 3 – 1 - Macro nutrient fertilizers; Macronutrient fertilizers are labeled with an NPK analysis and also "N-P-K-S" in Australia . An example of labeling for the fertilizer potash is composed of 1:1 potassium to chloride or 52 % potassium and 48% chlorine by weight (owing ...
COMPARATIVE EVALUATION OF TCF BLEACHED
... levels for Standard viscose and acetate grades were achieved by choosing the appropriate alkali charges in the E-Stage. The (EO) pretreated pulps were subjected to medium consistency ozone (Z) bleaching. The amount of ozone Charge necessary to adjust the viscosity was determined in a set of pre-tria ...
... levels for Standard viscose and acetate grades were achieved by choosing the appropriate alkali charges in the E-Stage. The (EO) pretreated pulps were subjected to medium consistency ozone (Z) bleaching. The amount of ozone Charge necessary to adjust the viscosity was determined in a set of pre-tria ...
Section 1.3 - The Student Room
... most stable states at 1 atmosphere pressure and at a stated temperature, often 298 K). b Standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements, with both the compound and its elements being in their standard states (ie their most stable st ...
... most stable states at 1 atmosphere pressure and at a stated temperature, often 298 K). b Standard enthalpy change of formation is the enthalpy change when 1 mole of a compound is formed from its elements, with both the compound and its elements being in their standard states (ie their most stable st ...
Part 1-ICHO-21-25
... 3.3 Assuming that the sulphur dioxide is not being removed and equally spread in an ...
... 3.3 Assuming that the sulphur dioxide is not being removed and equally spread in an ...
CHAPTER 4 REACTIONS IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
... In general, an acid-base neutralization reaction produces salt and water. At the neutralization point, the correct amount of base has been added to completely react with the acid. The resulting solution only contains salt and water. ...
... In general, an acid-base neutralization reaction produces salt and water. At the neutralization point, the correct amount of base has been added to completely react with the acid. The resulting solution only contains salt and water. ...
chapter 5 gases
... In general, an acid-base neutralization reaction produces salt and water. At the neutralization point, the correct amount of base has been added to completely react with the acid. The resulting solution only contains salt and water. ...
... In general, an acid-base neutralization reaction produces salt and water. At the neutralization point, the correct amount of base has been added to completely react with the acid. The resulting solution only contains salt and water. ...
Chapter 4
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
... Strategy: Recall that strong acids and strong bases are strong electrolytes. They are completely ionized in solution. An ionic equation will show strong acids and strong bases in terms of their free ions. Weak acids and weak bases are weak electrolytes. They only ionize to a small extent in solution ...
Chemistry Appendixes
... questions by applying consistent, logical reasoning to describe, explain, and predict observations, and by doing experiments to test hypotheses or predictions from these hypotheses. In this way science progresses using a general model for solving problems and employing specific processes as part of ...
... questions by applying consistent, logical reasoning to describe, explain, and predict observations, and by doing experiments to test hypotheses or predictions from these hypotheses. In this way science progresses using a general model for solving problems and employing specific processes as part of ...
Chapter 4 - AP Chemistry with dr hart
... defined them as proton donors. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
... defined them as proton donors. Aqueous Reactions © 2009, Prentice-Hall, Inc. ...
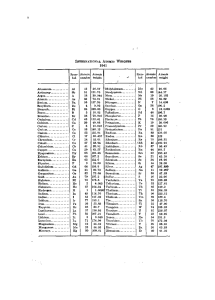
INTEKNATIONAL ATOMIC WEIGHTS Aluminum... Antimony..., Argon
... particularly for more advanced work. It is designed not only to encourage students to undertake special work but to aid them in later years in the solution of practical problems. No claim whatsoever is made for completeness. In their selection of material the authors have been guided simply by their ...
... particularly for more advanced work. It is designed not only to encourage students to undertake special work but to aid them in later years in the solution of practical problems. No claim whatsoever is made for completeness. In their selection of material the authors have been guided simply by their ...
BRIEF ANSWERS TO SELECTED PROBLEMS APPENDIX G
... is the volume of the container. Solids and liquids have a definite volume. The volume of the container does not affect the volume of a solid or liquid. (a) gas (b) liquid (c) liquid 1.4 Physical property: a characteristic shown by a substance itself, without any interaction with or change into other ...
... is the volume of the container. Solids and liquids have a definite volume. The volume of the container does not affect the volume of a solid or liquid. (a) gas (b) liquid (c) liquid 1.4 Physical property: a characteristic shown by a substance itself, without any interaction with or change into other ...
Cliffs Notes
... Acquisitions Editor: Sherry Gomoll Technical Editor: Christopher Bushee Production Proofreader: Joel K. Draper Hungry Minds Indianapolis Production Services ...
... Acquisitions Editor: Sherry Gomoll Technical Editor: Christopher Bushee Production Proofreader: Joel K. Draper Hungry Minds Indianapolis Production Services ...