Review on N acylation reaction
... base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acylation was also found to depend on steric effect such as in acylation of mixt ...
... base R1NH2. So the acylation of an equimolar mixture of two amines usually observed the conversion of weaker amine to amide and hydrochloride of the stronger amine in number of solvents. In some cases the selectivity of acylation was also found to depend on steric effect such as in acylation of mixt ...
Predicting Equations Reference #2
... follows are a few suggestions on how to successfully predict the products to a chemical reaction. The College Board requests that the reaction equations not be balanced, nor are physical states necessary. For purposes of clarity the article will include physical states. For brevity purposes this boo ...
... follows are a few suggestions on how to successfully predict the products to a chemical reaction. The College Board requests that the reaction equations not be balanced, nor are physical states necessary. For purposes of clarity the article will include physical states. For brevity purposes this boo ...
Experiment 15: Reduction and Oxidation of Organic Compounds
... weighing paper and obtain the mass. Measure the melting point of the purified material. Review Chapter 21 in LTOC, which discusses Infrared Spectroscopy, pp 311-344. Click on Fig. 2, Expt. 15 to find the infrared spectrum of isoborneol. Place a spatula-tip amount of your product in a small test tube ...
... weighing paper and obtain the mass. Measure the melting point of the purified material. Review Chapter 21 in LTOC, which discusses Infrared Spectroscopy, pp 311-344. Click on Fig. 2, Expt. 15 to find the infrared spectrum of isoborneol. Place a spatula-tip amount of your product in a small test tube ...
Document
... determine when the reaction has proceeded to the extent that the cheese (curds) are ready for consumption or storage. The concentration of lactic acid present in the whey can be determined at any time during the cheese making process via a simple titration. This usually involves taking a 10 mL sampl ...
... determine when the reaction has proceeded to the extent that the cheese (curds) are ready for consumption or storage. The concentration of lactic acid present in the whey can be determined at any time during the cheese making process via a simple titration. This usually involves taking a 10 mL sampl ...
Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... The acidity of the hydrides of elements in Group 16 of the Periodic table increases as the group is descended due to the bond energy of the covalent bond (in the undissolved, molecular, form of the acid) becoming weaker as it gets longer. Thus if we compare aqueous solutions of equal concentrations ...
... The acidity of the hydrides of elements in Group 16 of the Periodic table increases as the group is descended due to the bond energy of the covalent bond (in the undissolved, molecular, form of the acid) becoming weaker as it gets longer. Thus if we compare aqueous solutions of equal concentrations ...
More Reaction Information
... • Acid: Substance that produces H+ HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl–(aq) – Some acids—called polyprotic acids • These acids contain more than one ionizable proton and release them sequentially. • For example, sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is a diprotic acid. • It is strong in its first ionizable proton, but weak in its s ...
... • Acid: Substance that produces H+ HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl–(aq) – Some acids—called polyprotic acids • These acids contain more than one ionizable proton and release them sequentially. • For example, sulfuric acid, H2SO4 is a diprotic acid. • It is strong in its first ionizable proton, but weak in its s ...
File
... - so in looking at a bottle of HCl(aq) that has a molar concentration 1.0 mol/L , we would assume that the bottle contained 1.0mol/L of H+(aq) and 1.0 mol/L of Cl-(aq) - there are only a few strong acids e.g. HCl(aq), HBr(aq), H2SO4(aq), HNO3(aq) and H3PO4(aq) to name some familiar ones - __________ ...
... - so in looking at a bottle of HCl(aq) that has a molar concentration 1.0 mol/L , we would assume that the bottle contained 1.0mol/L of H+(aq) and 1.0 mol/L of Cl-(aq) - there are only a few strong acids e.g. HCl(aq), HBr(aq), H2SO4(aq), HNO3(aq) and H3PO4(aq) to name some familiar ones - __________ ...
Structural Studies on Sulfated Glycopeptides from the Carbohydrate
... 20 and 30 h. Following incubation the sample was lyophilized, mixed with 1 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid, and centrifuged in a Beckman microcentrifuge for 10 min. The precipitate was washed with 0.3 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid three times and thecombined supernatant fluid was chromatographed on Se ...
... 20 and 30 h. Following incubation the sample was lyophilized, mixed with 1 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid, and centrifuged in a Beckman microcentrifuge for 10 min. The precipitate was washed with 0.3 ml of 5% trichloroacetic acid three times and thecombined supernatant fluid was chromatographed on Se ...
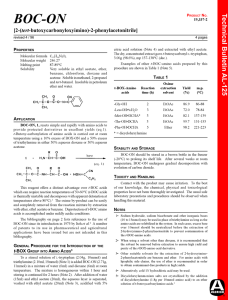
BOC-ON - Sigma
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
... Active Analog of the C-Terminal Heptapeptide with ,-Hydroxynorleucine Sulfate Replacing Tyrosine Sulfate. J. Med. Chem. 1978, 21, 1030. 13 Cachia, P.J.; Sykes, B.D.; Hodges, R.S. Calcium-dependant Inhibitory Region of Troponin: A protein Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study of the Interaction between T ...
File
... Most acids are weak; only a few common strong acids: HCl(aq), HBr(aq), (Not HF(aq), HNO3(aq), H2SO4(aq) – 1st H+ only, HClO4(aq), NOT HClO3(aq) Strong base is completely ionized in water, while weak base is only partially dissociated: NaOH(s) completely ionizes; NH3 partially dissociates Common stro ...
... Most acids are weak; only a few common strong acids: HCl(aq), HBr(aq), (Not HF(aq), HNO3(aq), H2SO4(aq) – 1st H+ only, HClO4(aq), NOT HClO3(aq) Strong base is completely ionized in water, while weak base is only partially dissociated: NaOH(s) completely ionizes; NH3 partially dissociates Common stro ...
Equation Writing Information
... ELEMENTS - both metals and non-metals ACIDS - both dilute and concentrated BASES - soluble metal hydroxides (NaOH and KOH being the most common, by far) - soluble carbonates (Na 2CO3 and K2CO3 being the most common) - an aqueous solution of ammonia, NH3(aq) SALTS ionic compounds that are neither aci ...
... ELEMENTS - both metals and non-metals ACIDS - both dilute and concentrated BASES - soluble metal hydroxides (NaOH and KOH being the most common, by far) - soluble carbonates (Na 2CO3 and K2CO3 being the most common) - an aqueous solution of ammonia, NH3(aq) SALTS ionic compounds that are neither aci ...
practical identification of organic compounds.docx
... dilute alkali: like wise, the salt of a water-soluble, weak acid is decomposed by dilute hydrochloric acid or by concentrated sulphuric acid. The water soluble salt of a water- insoluble acid or base will give a precipitate of either the free acid or the base when treated with dilute acid or diluted ...
... dilute alkali: like wise, the salt of a water-soluble, weak acid is decomposed by dilute hydrochloric acid or by concentrated sulphuric acid. The water soluble salt of a water- insoluble acid or base will give a precipitate of either the free acid or the base when treated with dilute acid or diluted ...
KEY
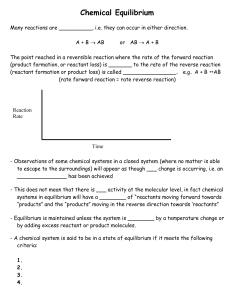
... 4. the temperature is decreased. 5. more oxygen is added. Explanation: 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇀ ↽ 2 SO2 (g) + heat According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the amount of reactant SO2 (g) is increased when the equilibrium shifts to the left. This will happen when another reactant (O2 ) is removed. For an e ...
... 4. the temperature is decreased. 5. more oxygen is added. Explanation: 2 SO2 (g) + O2 (g) ⇀ ↽ 2 SO2 (g) + heat According to Le Chatelier’s principle, the amount of reactant SO2 (g) is increased when the equilibrium shifts to the left. This will happen when another reactant (O2 ) is removed. For an e ...
Net ionic equation
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
chapter4-bur.2917051..
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
... The forces holding an ionic compound together are the strong electrical attraction that exists between cations and anions. It is therefore somewhat surprising that ionic compounds will dissolve in water. The reason some ionic compounds will dissolve in water is because the water molecules have a par ...
Chemistry 12 - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
... 40. What effect does a catalyst have? A. increases the reaction rate by decreasing the heat of reaction B. increases the reaction rate by increasing the activation energy of the reverse reaction C. increases the reaction rate by lowering the activation energy of the forward reaction only D. increase ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... the HCl and the H and Cl ions is 1:1, a 0.250 M solution on dissociation will produce 0.250 M solution of H+ and 0.250 M solution of Cl-. Thus the sum of thee two will be equal to 0.500 M 2. A strong electrolyte is one that __________ completely in solution. (a). reacts (b). decomposes (c). disappea ...
... the HCl and the H and Cl ions is 1:1, a 0.250 M solution on dissociation will produce 0.250 M solution of H+ and 0.250 M solution of Cl-. Thus the sum of thee two will be equal to 0.500 M 2. A strong electrolyte is one that __________ completely in solution. (a). reacts (b). decomposes (c). disappea ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry in Action
... 1) Calculate the mass of 4mol of lithium 2) Calculate the mass of 2mol of sodium 3) Calculate the number of moles in 36g of carbon ...
... 1) Calculate the mass of 4mol of lithium 2) Calculate the mass of 2mol of sodium 3) Calculate the number of moles in 36g of carbon ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry In Action
... 1) Calculate the mass of 4mol of lithium 2) Calculate the mass of 2mol of sodium 3) Calculate the number of moles in 36g of carbon ...
... 1) Calculate the mass of 4mol of lithium 2) Calculate the mass of 2mol of sodium 3) Calculate the number of moles in 36g of carbon ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... (a) An acidified solution of hydrogen peroxide is added to a solution of sodium iodide. (b) Chlorine gas is passed over powdered aluminum. (c) Solutons of mercury (I) nitrate and potassium sulfate are mixed. (d) A strip of magnesium metal is added to a solution of silver nitrate. (e) Solutions of le ...
... (a) An acidified solution of hydrogen peroxide is added to a solution of sodium iodide. (b) Chlorine gas is passed over powdered aluminum. (c) Solutons of mercury (I) nitrate and potassium sulfate are mixed. (d) A strip of magnesium metal is added to a solution of silver nitrate. (e) Solutions of le ...
CLASS X carbon and its compound
... called branched chain hydrocarbons. 13. Isomerism : The phenomenon due to which there can exist two or more organic compounds, with different physical and chemical properties, due to the difference in arrangement of carbon atoms in their structure, but have same chemical formula is called isomerism. ...
... called branched chain hydrocarbons. 13. Isomerism : The phenomenon due to which there can exist two or more organic compounds, with different physical and chemical properties, due to the difference in arrangement of carbon atoms in their structure, but have same chemical formula is called isomerism. ...
X012/12/02
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish ...
... 1 Check that the answer sheet provided is for Chemistry Higher (Section A). 2 For this section of the examination you must use an HB pencil and, where necessary, an eraser. 3 Check that the answer sheet you have been given has your name, date of birth, SCN (Scottish ...
- Vijay Education Academy
... 36. A compound consisting of the monovalent ions A , B crystallizes in the body centred cubic lattice. (i) What is the formula of the compound? (ii) If one of A+ ions from the corner is replaced by a monovalent ion C +, what would be the simplest formula of the resulting compound? 37. Maneesh, a stu ...
... 36. A compound consisting of the monovalent ions A , B crystallizes in the body centred cubic lattice. (i) What is the formula of the compound? (ii) If one of A+ ions from the corner is replaced by a monovalent ion C +, what would be the simplest formula of the resulting compound? 37. Maneesh, a stu ...
CHEM110P1_06_2015_Y_P1
... (CH2(COOH)2, molar mass = 104.1 g mol–1). The student weighed 1.08 g of the unknown acid and transferred it to a 250.0 mL volumetric flask and prepared a standard solution. The burette was filled with 0.09970 M NaOH solution and 20.00 mL aliquots of the acid solution were titrated. The titration dat ...
... (CH2(COOH)2, molar mass = 104.1 g mol–1). The student weighed 1.08 g of the unknown acid and transferred it to a 250.0 mL volumetric flask and prepared a standard solution. The burette was filled with 0.09970 M NaOH solution and 20.00 mL aliquots of the acid solution were titrated. The titration dat ...
Chapter 13: Water and the Lithosphere Preview
... The earth is believed to have formed some 4.5 billion years ago from the coalescence of meteorites that circled the early sun. Heating from gravitational forces and nuclear decay melted the interior of the evolving planet, allowing the minerals to separate according to their density. The result is a ...
... The earth is believed to have formed some 4.5 billion years ago from the coalescence of meteorites that circled the early sun. Heating from gravitational forces and nuclear decay melted the interior of the evolving planet, allowing the minerals to separate according to their density. The result is a ...