INTRODUCTION The HSAB concept is an acronym for `hard and soft
... 'hard' or 'soft', and 'acid' or 'base' to chemical species. 'Hard' applies to species which are small, have high charge states (the charge criterion applies mainly to acids, to a lesser extent to bases), and are weakly polarizable. 'Soft' applies to species which are big, have low charge states and ...
... 'hard' or 'soft', and 'acid' or 'base' to chemical species. 'Hard' applies to species which are small, have high charge states (the charge criterion applies mainly to acids, to a lesser extent to bases), and are weakly polarizable. 'Soft' applies to species which are big, have low charge states and ...
Basic chemistry - Ross University
... on the vacuum side, to limit heat transfer by radiation. You may have used such vessels to keep your coffee hot. Standard conditions: Some thermodynamic properties of a system depend on the conditions that system is in. Chemists have agreed to reference their measurement to a pressure of 1014 hPa (s ...
... on the vacuum side, to limit heat transfer by radiation. You may have used such vessels to keep your coffee hot. Standard conditions: Some thermodynamic properties of a system depend on the conditions that system is in. Chemists have agreed to reference their measurement to a pressure of 1014 hPa (s ...
CHEM 102 FINAL EXAM WINTER 07-08
... 7. Polyamides can be produced from a. two monomers, one containing two amino groups, the other containing two carboxylic acid groups. b. one monomer, containing one amino and one carboxylic acid group. c. one monomer, containing two amide groups. d. either a or b above. ANSWER: d 8. Which statement ...
... 7. Polyamides can be produced from a. two monomers, one containing two amino groups, the other containing two carboxylic acid groups. b. one monomer, containing one amino and one carboxylic acid group. c. one monomer, containing two amide groups. d. either a or b above. ANSWER: d 8. Which statement ...
Experiment 1
... excess of zinc powder to a measured amount of CuSO4 (aq) and measuring the temperature change over a period of time. This quantity of heat is measured experimentally by allowing the reaction to take place in a thermally insulated vessel called calorimeter. The heat liberated in the reaction will cau ...
... excess of zinc powder to a measured amount of CuSO4 (aq) and measuring the temperature change over a period of time. This quantity of heat is measured experimentally by allowing the reaction to take place in a thermally insulated vessel called calorimeter. The heat liberated in the reaction will cau ...
Chemistry 30 - SharpSchool
... this led to the empirical generalization known as the ______________ ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
... this led to the empirical generalization known as the ______________ ___________________________________________ which says that there is a ________________________________ between the concentrations of the products and the concentrations of the reactants at equilibrium ...
Press here to hemy 102 lab manual
... excess of zinc powder to a measured amount of CuSO4 (aq) and measuring the temperature change over a period of time. This quantity of heat is measured experimentally by allowing the reaction to take place in a thermally insulated vessel called calorimeter. The heat liberated in the reaction will cau ...
... excess of zinc powder to a measured amount of CuSO4 (aq) and measuring the temperature change over a period of time. This quantity of heat is measured experimentally by allowing the reaction to take place in a thermally insulated vessel called calorimeter. The heat liberated in the reaction will cau ...
A.P. Chemistry Writing Chemical Reactions Generally students do
... Note that net-ionic versions of these reactions really don't exist since liquid water is generally not present. The most significant hurdle with these reactions is likely to be the organic compound names. If you don’t know what propanal is then it doesn’t matter that it is easy to write the combusti ...
... Note that net-ionic versions of these reactions really don't exist since liquid water is generally not present. The most significant hurdle with these reactions is likely to be the organic compound names. If you don’t know what propanal is then it doesn’t matter that it is easy to write the combusti ...
Chemistry1100 Practice Exam 4 Choose the best answer for
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
... 11. A compound has an empirical formula CH2- An independent analysis gave a value of 70 for its molar mass. What is the correct molecular formula? a. C2H4 b. C3H6 c. C4O8 d. C5H10 e. C5H11 12. Given the balanced chemical equation, C4H4 + 5 O2 → 4 CO2 + 2 H2O. If 0.3618 moles of C4H4 are allowed to ...
Writing Chemical Reactions
... Note that net-ionic versions of these reactions really don't exist since liquid water is generally not present. The most significant hurdle with these reactions is likely to be the organic compound names. If you don’t know what propanal is then it doesn’t matter that it is easy to write the combusti ...
... Note that net-ionic versions of these reactions really don't exist since liquid water is generally not present. The most significant hurdle with these reactions is likely to be the organic compound names. If you don’t know what propanal is then it doesn’t matter that it is easy to write the combusti ...
Solution
... We see that HBr is a strong acid and H2SO4 is a strong acid for the first step ionization and a weak acid for the second step ...
... We see that HBr is a strong acid and H2SO4 is a strong acid for the first step ionization and a weak acid for the second step ...
Name:__Grading key
... Question 6 (6 points) deals with your analysis of a reaction where you add the metal Pd to a yellowgreen solution of 0.10 M FeCl2(aq) and observe no apparent reaction. Circle every observation (1and/or 2 and/or 3) that can help confirm that NO reaction took place. ...
... Question 6 (6 points) deals with your analysis of a reaction where you add the metal Pd to a yellowgreen solution of 0.10 M FeCl2(aq) and observe no apparent reaction. Circle every observation (1and/or 2 and/or 3) that can help confirm that NO reaction took place. ...
Chemistry II Aqueous Reactions and Solution Chemistry Chapter 4
... Can you determine if a solute is a strong or weak electrolyte by how well it dissolves? No, for example acetic acid (vinegar) is very soluble in water, but only partially dissociates into ions. ...
... Can you determine if a solute is a strong or weak electrolyte by how well it dissolves? No, for example acetic acid (vinegar) is very soluble in water, but only partially dissociates into ions. ...
Document
... Element B : . does not conduct electricity; . has 7 electrons in its outermost shell; . is found in very small quantities in nature; Element C : . does not form compounds with other elements; . is in a gaseous state; . is a poor conductor of heat; Element D : . in non-ductile and non-malleable; . co ...
... Element B : . does not conduct electricity; . has 7 electrons in its outermost shell; . is found in very small quantities in nature; Element C : . does not form compounds with other elements; . is in a gaseous state; . is a poor conductor of heat; Element D : . in non-ductile and non-malleable; . co ...
Assistant Professor Chemistry, Class-2, Advt No. 84/2016
... A light source that is commonly used in a Visible spectrometer is (A) Tungsten lamp ...
... A light source that is commonly used in a Visible spectrometer is (A) Tungsten lamp ...
Gas Laws
... 14. Using the following Ka values, place the following acids in order of increasing acid strength. HClO4 (ka = 1 x 107), HCN (Ka = 4.93 x 10-10), CH3OOH (ka = 1.76 x 10-5 ), HF (Ka = 3.53 x 10-4) 15. Using the Ka values from above, calculate the Kb values and place the following bases in order of in ...
... 14. Using the following Ka values, place the following acids in order of increasing acid strength. HClO4 (ka = 1 x 107), HCN (Ka = 4.93 x 10-10), CH3OOH (ka = 1.76 x 10-5 ), HF (Ka = 3.53 x 10-4) 15. Using the Ka values from above, calculate the Kb values and place the following bases in order of in ...
Example 1-2
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
Gas Laws
... 14. Using the following Ka values, place the following acids in order of increasing acid strength. HClO4 (ka = 1 x 107), HCN (Ka = 4.93 x 10-10), CH3OOH (ka = 1.76 x 10-5 ), HF (Ka = 3.53 x 10-4) 15. Using the Ka values from above, calculate the Kb values and place the following bases in order of in ...
... 14. Using the following Ka values, place the following acids in order of increasing acid strength. HClO4 (ka = 1 x 107), HCN (Ka = 4.93 x 10-10), CH3OOH (ka = 1.76 x 10-5 ), HF (Ka = 3.53 x 10-4) 15. Using the Ka values from above, calculate the Kb values and place the following bases in order of in ...
Hein and Arena - faculty at Chemeketa
... The solubility of AgCl in water is 1.3 x 10-5 mol/L. AgCl(s) → Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Because each formula unit of AgCl that dissolves yields one Ag+ and one Cl- , the concentrations of the two ions are equal. ...
... The solubility of AgCl in water is 1.3 x 10-5 mol/L. AgCl(s) → Ag+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Because each formula unit of AgCl that dissolves yields one Ag+ and one Cl- , the concentrations of the two ions are equal. ...
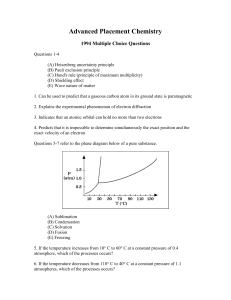
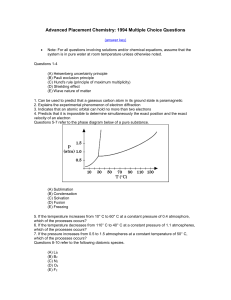
Advanced Placement Chemistry
... 49. The isomerization of cyclopropane to propylene is a first-order process with a halflife of 19 minutes at 500 °C. The time it takes for the partial pressure of cyclopropane to decrease from 1.0 atmosphere to 0.125 atmosphere at 500 °C is closest to (A) 38 minutes (B) 57 minutes (C) 76 minutes (D) ...
... 49. The isomerization of cyclopropane to propylene is a first-order process with a halflife of 19 minutes at 500 °C. The time it takes for the partial pressure of cyclopropane to decrease from 1.0 atmosphere to 0.125 atmosphere at 500 °C is closest to (A) 38 minutes (B) 57 minutes (C) 76 minutes (D) ...
MC94 - Southchemistry.com
... 72. The nuclide 245Cm is radioactive and decays by the loss of one beta ([beta]¯) particle. The product nuclide is (A) 245Pu (B) 95Am (C) 248Cm (D) 250Cm (E) 97Bk 73. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) <===> 2 SO3(g) When 0.40 mole of SO2 and 0.60 mole of O2 are placed in an evacuated 1.00-liter flask, the reaction ...
... 72. The nuclide 245Cm is radioactive and decays by the loss of one beta ([beta]¯) particle. The product nuclide is (A) 245Pu (B) 95Am (C) 248Cm (D) 250Cm (E) 97Bk 73. 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) <===> 2 SO3(g) When 0.40 mole of SO2 and 0.60 mole of O2 are placed in an evacuated 1.00-liter flask, the reaction ...
Fe(H2O)63+ + H2O → ← H3O+ + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+
... 12. The addition of a small amount of acid or base will have very little effect on the pH value of a solution containing equal molar concentrations of (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... 12. The addition of a small amount of acid or base will have very little effect on the pH value of a solution containing equal molar concentrations of (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
2nd Semester final review
... 37. What is the difference between a solute, a solvent, and a solution? Solute is the substance being dissolved (often solid) Solvent is the substance doing dissolving (usually liquid) Solution is the mixture of the two 38. Why do equations have to be balanced in the first place? Atoms can’t be crea ...
... 37. What is the difference between a solute, a solvent, and a solution? Solute is the substance being dissolved (often solid) Solvent is the substance doing dissolving (usually liquid) Solution is the mixture of the two 38. Why do equations have to be balanced in the first place? Atoms can’t be crea ...
PS_CHEM7_ch4 - WordPress.com
... (a) Write balanced total and net ionic equations for its reaction with aqueous NaOH. (b) What mass of precipitate forms when185.5 mL of 0.533 M NaOH is added to 627 mL of a solution that contains 15.8 g of aluminum sulfate per liter? ...
... (a) Write balanced total and net ionic equations for its reaction with aqueous NaOH. (b) What mass of precipitate forms when185.5 mL of 0.533 M NaOH is added to 627 mL of a solution that contains 15.8 g of aluminum sulfate per liter? ...
Chapter 4 2013
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
... 3. Break the compounds into their ions and write the ionic equation for the reaction. 3. Refer to the table of solubility rules and decide whether any of the ion combinations is insoluble. 4. If a candidate is insoluble, that reaction will occur. 5. Remove the spectator ions and write the net ionic ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO3, HClO4 and H2SO4 are all strong acids. All other acids are assumed to be weak acids. • A weak acid or weak base only partially ionizes (dissociates) in aqueous solution. • Amphiprotic substances can behave as either a proton acceptor or a proton donor. Water is an example ...
... • HCl, HBr, HI, HNO3, HClO3, HClO4 and H2SO4 are all strong acids. All other acids are assumed to be weak acids. • A weak acid or weak base only partially ionizes (dissociates) in aqueous solution. • Amphiprotic substances can behave as either a proton acceptor or a proton donor. Water is an example ...