PPT Version
... Exporting flow sampling Info • It is Metering/exporting process Info, not single flows Info – As for packet sampling, use Option records: flow records contain an options record ID where this info is contained. “Scope” can be the interface, the cache, etc. ...
... Exporting flow sampling Info • It is Metering/exporting process Info, not single flows Info – As for packet sampling, use Option records: flow records contain an options record ID where this info is contained. “Scope” can be the interface, the cache, etc. ...
A Derivation of the Navier
... it is impossible to ever pack more fluid into it or take fluid out without changing the volume. This is equivalent to saying that ∇·u = 0; using the mass continuity equation, if density is constant then we have ∇ · (ρu) = ρ∇ · u = 0; ρ > 0, so ∇ · u = 0. Stress and body forces are the two other impo ...
... it is impossible to ever pack more fluid into it or take fluid out without changing the volume. This is equivalent to saying that ∇·u = 0; using the mass continuity equation, if density is constant then we have ∇ · (ρu) = ρ∇ · u = 0; ρ > 0, so ∇ · u = 0. Stress and body forces are the two other impo ...
Compact ultrasonic fluid flow sensors for automotive engine testing
... The FlowSonic line of sensors from Sentronics is a breakthrough in fluid flow testing technology for automotive engines of every type. The FlowSonic LF has been designed for the ultra-low fuel flow conditions found in today’s high-efficiency road car engines, while the FlowSonic HF has been develope ...
... The FlowSonic line of sensors from Sentronics is a breakthrough in fluid flow testing technology for automotive engines of every type. The FlowSonic LF has been designed for the ultra-low fuel flow conditions found in today’s high-efficiency road car engines, while the FlowSonic HF has been develope ...
Fluid Mechanics
... • Fluid Mechanics: the study of forces that develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
... • Fluid Mechanics: the study of forces that develop when an object moves through a fluid medium. • Two fluids of interest – Water – Air ...
Lecture01 - University of Utah Engineering Department
... Turbulence mixes quantities with the result that gradients are reduced (e.g. pollutants, chemicals, velocity components, etc.). This lowers the concentration of harmful scalars but increases drag. 5. A continuous spectrum (range) of scales: Range of eddy scales ...
... Turbulence mixes quantities with the result that gradients are reduced (e.g. pollutants, chemicals, velocity components, etc.). This lowers the concentration of harmful scalars but increases drag. 5. A continuous spectrum (range) of scales: Range of eddy scales ...
This can be better explained by demonstrating a steady flow
... by having a change in static head in one direction contributed by the centrifugal effect and an equal change in the other direction contributed by the change in relative velocity. However, this has not been established in practice. Thus for as axial flow impulse machine U1 U 2 , Vr1 Vr2 . For an ...
... by having a change in static head in one direction contributed by the centrifugal effect and an equal change in the other direction contributed by the change in relative velocity. However, this has not been established in practice. Thus for as axial flow impulse machine U1 U 2 , Vr1 Vr2 . For an ...
Wing / boom Control for Anhydrous Applicators
... 1. A pump to boost the pressure of anhydrous ammonia coming from the nurse tank. This pump maintains constant pressure of ammonia distributed to knives. Anhydrous ammonia can be applied consistently over a wide variation in tank pressure, even on a very cold day. 2. Orifices are used at the manifo ...
... 1. A pump to boost the pressure of anhydrous ammonia coming from the nurse tank. This pump maintains constant pressure of ammonia distributed to knives. Anhydrous ammonia can be applied consistently over a wide variation in tank pressure, even on a very cold day. 2. Orifices are used at the manifo ...
Control volume analysis (Part 2) Linear Momentum Equations
... 5. If the CS is selected so that it is perpendicular to the flow where fluid enters or leaves the CV, the surface force exerted at these locations by fluid outside the CV on fluid inside will be due to pressure. Furthermore, when subsonic flow exits from a control volume into the atmosphere, atmosph ...
... 5. If the CS is selected so that it is perpendicular to the flow where fluid enters or leaves the CV, the surface force exerted at these locations by fluid outside the CV on fluid inside will be due to pressure. Furthermore, when subsonic flow exits from a control volume into the atmosphere, atmosph ...
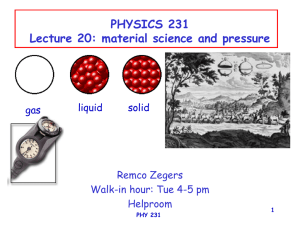
1 PHYSICS 231 Lecture 20: material science and pressure
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
... Stress: Tells something about the force causing the deformation Strain: Measure of the degree of deformation For small stress, strain and stress are linearly correlated. Strain = Constant*Stress Constant: elastic modulus The elastic modulus depends on: • Material that is deformed • Type of deformati ...
V - ME304
... The second law of thermodynamics: The entropy of the universe must increase or, in the ideal case, remain constant in all natural processes. The state of postulate (law of property relations): The various properties of a fluid are related. If a certain minimum number (usually two) of fluid’s propert ...
... The second law of thermodynamics: The entropy of the universe must increase or, in the ideal case, remain constant in all natural processes. The state of postulate (law of property relations): The various properties of a fluid are related. If a certain minimum number (usually two) of fluid’s propert ...
Chapter 14
... When a body is fully or partially submerged in a fluid, a buoyant force from the surrounding fluid acts on the body. The force is directed upward and has a magnitude equal to the weight of the fluid that has been displaced by the body. ...
... When a body is fully or partially submerged in a fluid, a buoyant force from the surrounding fluid acts on the body. The force is directed upward and has a magnitude equal to the weight of the fluid that has been displaced by the body. ...
Current Electricity
... • A large amount of potential energy at a place where large amounts of charge are present results in a large electric potential • A small amount of energy for a given amount of charge results in a small electric potential • The difference between two such points (one high potential and the other low ...
... • A large amount of potential energy at a place where large amounts of charge are present results in a large electric potential • A small amount of energy for a given amount of charge results in a small electric potential • The difference between two such points (one high potential and the other low ...
PowerPoint - UMD Physics
... Equation of Continuity, cont • The equation is a consequence of conservation of mass and a steady flow • A v = constant – This is equivalent to the fact that the volume of fluid that enters one end of the tube in a given time interval equals the volume of fluid leaving the tube in the same interval ...
... Equation of Continuity, cont • The equation is a consequence of conservation of mass and a steady flow • A v = constant – This is equivalent to the fact that the volume of fluid that enters one end of the tube in a given time interval equals the volume of fluid leaving the tube in the same interval ...
Slides from the lecture
... Dimples cause the air-flow above the ball to travel faster and thus the pressure on the ball from the top to be lower than the air pressure below the ball. This pressure difference (i.e. more relative pressure from below than on top) causes the ball to lift (Magnus effect) and stay in the air for a ...
... Dimples cause the air-flow above the ball to travel faster and thus the pressure on the ball from the top to be lower than the air pressure below the ball. This pressure difference (i.e. more relative pressure from below than on top) causes the ball to lift (Magnus effect) and stay in the air for a ...
semiconductors
... The PN Junction Diode Up to now we have examined p-type and n-type material separately. However, the properties of these extrinsic semiconductor materials become useful only when the two types are combined in some way. The area where the two types meet is called a pn junction, and the resulting pro ...
... The PN Junction Diode Up to now we have examined p-type and n-type material separately. However, the properties of these extrinsic semiconductor materials become useful only when the two types are combined in some way. The area where the two types meet is called a pn junction, and the resulting pro ...