Smart Materials
... materials change in colour depending on their temperature, and photochromic materials, which change colour in response to light - for example, light sensitive sunglasses that darken when exposed to bright sunlight. ...
... materials change in colour depending on their temperature, and photochromic materials, which change colour in response to light - for example, light sensitive sunglasses that darken when exposed to bright sunlight. ...
Integrated Modeling of Physical System Dynamics © Neville Hogan 1994 page 1
... The primitive elements which have been defined so far are intended to describe aspects of energetic behavior and they can be used in the construction of detailed models of specific physical systems. We should also be able to use energetic considerations to draw some general conclusions about behavio ...
... The primitive elements which have been defined so far are intended to describe aspects of energetic behavior and they can be used in the construction of detailed models of specific physical systems. We should also be able to use energetic considerations to draw some general conclusions about behavio ...
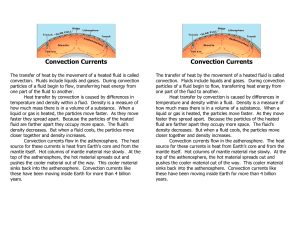
Convection Currents The transfer of heat by the movement of a
... top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. This cooler material sinks back into the asthenosphere. Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than 4 billion years. ...
... top of the asthenosphere, the hot material spreads out and pushes the cooler material out of the way. This cooler material sinks back into the asthenosphere. Convection currents like these have been moving inside Earth for more than 4 billion years. ...
Elasticity Theory Stress
... A large part of geophysics concerns understanding how material deforms when it is squeezed, stretched, or sheared. Elasticity theory is the mathematical framework which describes such deformation. By elastic, we mean that the material rebounds to its original shape after the forces on it are removed ...
... A large part of geophysics concerns understanding how material deforms when it is squeezed, stretched, or sheared. Elasticity theory is the mathematical framework which describes such deformation. By elastic, we mean that the material rebounds to its original shape after the forces on it are removed ...
Document
... pressure supplied by the pump (battery) or a water tower. • The symbol for voltage = V ...
... pressure supplied by the pump (battery) or a water tower. • The symbol for voltage = V ...
Electric Circuits - hss-1.us
... Just as the capacity of a water tower depends on the size and shape, so the capacitance of a capacitor depends on its size and shape. Just as a big water tower can contain more water per foot (or per unit pressure), so a big capacitor can store more charge per volt. ...
... Just as the capacity of a water tower depends on the size and shape, so the capacitance of a capacitor depends on its size and shape. Just as a big water tower can contain more water per foot (or per unit pressure), so a big capacitor can store more charge per volt. ...
The Momentum Equation
... for measuring discharge. A weir is a notch on a larger scale. It may be sharp crested but also may have a substantial width in the direction of flow - it is used as both a flow measuring device and a device to raise water levels. Weir Assumptions We will assume that the velocity of the fluid appro ...
... for measuring discharge. A weir is a notch on a larger scale. It may be sharp crested but also may have a substantial width in the direction of flow - it is used as both a flow measuring device and a device to raise water levels. Weir Assumptions We will assume that the velocity of the fluid appro ...
The Usability of Rock-Like Materials for Numerical Studies on Rocks
... modulus of elasticity and Poisson ratio. In some cases, it can be difficult or even impossible to acquire representative rock samples for laboratory experiments from heavily jointed rock masses and vuggy rocks. Considering this limitation, in this study, it was aimed to investigate the applicability ...
... modulus of elasticity and Poisson ratio. In some cases, it can be difficult or even impossible to acquire representative rock samples for laboratory experiments from heavily jointed rock masses and vuggy rocks. Considering this limitation, in this study, it was aimed to investigate the applicability ...
AT Physics II. Air Resistance The motion of
... where L is a characteristic length for the object moving through a fluid (say the radius or the diameter of a sphere), v its speed, ρ the density of the liquid and η its viscosity. Generally, high Reynolds number (anything much bigger than 1) means that viscosity is negligible; low Reynolds number ( ...
... where L is a characteristic length for the object moving through a fluid (say the radius or the diameter of a sphere), v its speed, ρ the density of the liquid and η its viscosity. Generally, high Reynolds number (anything much bigger than 1) means that viscosity is negligible; low Reynolds number ( ...
The Relation between the Coefficient of Friction and Pressure Drop
... After conducting tests and recording the required measurements, such as the amount of pressure inside the copper tube and knowing the system dimensions (length and diameter of the tube, air density) can extract the following amounts (Re, Cf, U and Δp). Figure 2 represents the relationship between pr ...
... After conducting tests and recording the required measurements, such as the amount of pressure inside the copper tube and knowing the system dimensions (length and diameter of the tube, air density) can extract the following amounts (Re, Cf, U and Δp). Figure 2 represents the relationship between pr ...
p = F /A - Derry Area School District
... 1)What is pressure? What is the SI unit of pressure? the perpendicular force per unit area or p = F┴/A; Pascal (Pa) 2)What is gauge pressure? the difference between the pressure you are measuring and atmospheric pressure 3) What is density? What is the density of water? the mass per unit volume or ρ ...
... 1)What is pressure? What is the SI unit of pressure? the perpendicular force per unit area or p = F┴/A; Pascal (Pa) 2)What is gauge pressure? the difference between the pressure you are measuring and atmospheric pressure 3) What is density? What is the density of water? the mass per unit volume or ρ ...
ALUMINUM AND ITS ALLOYS - redemat
... polyparaphenylene, polypyrrole, and polyaniline that have been doped with appropriate impurities. As is the case with semiconductors, these polymers may be made either n-type (i.e., free-electron charge carriers) or p-type (i.e., electron-hole charge carriers) depending on the dopant. However, unlik ...
... polyparaphenylene, polypyrrole, and polyaniline that have been doped with appropriate impurities. As is the case with semiconductors, these polymers may be made either n-type (i.e., free-electron charge carriers) or p-type (i.e., electron-hole charge carriers) depending on the dopant. However, unlik ...
mel715-20
... •The velocity potential must then satisfy the Laplace equation and it consequently is a harmonic function of space. •Solution of the Laplace equation, with an appropriate set of boundary conditions, leads then to the determination of the flow field. •Laplace equation has been widely studied in many ...
... •The velocity potential must then satisfy the Laplace equation and it consequently is a harmonic function of space. •Solution of the Laplace equation, with an appropriate set of boundary conditions, leads then to the determination of the flow field. •Laplace equation has been widely studied in many ...
Contextual Integrity in PORTIA
... Embedding Values in Design: Constitutive Activities • Discovery Discovering the values relevant to a project ...
... Embedding Values in Design: Constitutive Activities • Discovery Discovering the values relevant to a project ...
Continuous and Episodic Fluid Flow in Regional Metamorphism
... The overall pattern of fluid behaviour in regional metamorphism is controlled by large scale factors such as rate of heat input/loss, rock rheology and original lithological mix, and so cannot be considered to be independently variable, but locally anomalous behaviour can occur. Is it able to produc ...
... The overall pattern of fluid behaviour in regional metamorphism is controlled by large scale factors such as rate of heat input/loss, rock rheology and original lithological mix, and so cannot be considered to be independently variable, but locally anomalous behaviour can occur. Is it able to produc ...
Study Guide – Earthquake / Volcano
... e. After observing the ____________________ of seismic waves, scientists decided the core is made of a solid and liquid layer. f. ________and_________ waves cannot pass through liquids. g. A scale based on visual damage and personal accounts is called the ____________________ scale. h. The _________ ...
... e. After observing the ____________________ of seismic waves, scientists decided the core is made of a solid and liquid layer. f. ________and_________ waves cannot pass through liquids. g. A scale based on visual damage and personal accounts is called the ____________________ scale. h. The _________ ...
Effects of non-newtonian properties of blood flow on magnetic
... Objective(s): One applications of nanotechnology is in the area of medicine which is called nanomedicine. Primary instruments in nanomedicine can help us to detect diseases and used for drug delivery to inaccessible areas of human tissues. An important issue in simulating the motion of nanoparticles ...
... Objective(s): One applications of nanotechnology is in the area of medicine which is called nanomedicine. Primary instruments in nanomedicine can help us to detect diseases and used for drug delivery to inaccessible areas of human tissues. An important issue in simulating the motion of nanoparticles ...
The water cycle and energy transformations
... Flow rate depends on: • Potential difference • “resistance” (or “conductance”) ...
... Flow rate depends on: • Potential difference • “resistance” (or “conductance”) ...