Chapter 2 - Viscosity of Fluids
... fluids require the development of a significant level of shear stress before flow will begin, as illustrated in Fig. 2.2. Once flow starts, there is an essentially linear slope to the curve indicating a constant apparent viscosity. Eg. Chocolate, mayonnaise, toothpaste ...
... fluids require the development of a significant level of shear stress before flow will begin, as illustrated in Fig. 2.2. Once flow starts, there is an essentially linear slope to the curve indicating a constant apparent viscosity. Eg. Chocolate, mayonnaise, toothpaste ...
Document
... Elasticity can be seen by a reduction, at least partial, of the deformation when the load applied on a body is released. From ambient temperature (or below) and up to relatively high temperatures (T < 1,000°C), ceramics are elastic materials par excellence: their behavior under load is most often li ...
... Elasticity can be seen by a reduction, at least partial, of the deformation when the load applied on a body is released. From ambient temperature (or below) and up to relatively high temperatures (T < 1,000°C), ceramics are elastic materials par excellence: their behavior under load is most often li ...
Boundary Layers - The Colorful Fluid Mixing Gallery
... • The objective is to take the effects of the boundary layer correctly into account without having to use a mesh that is so fine that the flow pattern in the layer can be calculated explicitly. • Using the no-slip boundary condition at wall, velocities at the nodes at the wall equal those of the wal ...
... • The objective is to take the effects of the boundary layer correctly into account without having to use a mesh that is so fine that the flow pattern in the layer can be calculated explicitly. • Using the no-slip boundary condition at wall, velocities at the nodes at the wall equal those of the wal ...
1.Electromagnetic Blood Flow Meters
... • The electromagnetic flow-transducer is a tube of nonmagnetic material to ensure that the magnetic flux does not bypass the flowing liquid and go into the walls of the tube. • The tube is made of a conducting material and generally has an insulating lining to prevent short circuiting of ...
... • The electromagnetic flow-transducer is a tube of nonmagnetic material to ensure that the magnetic flux does not bypass the flowing liquid and go into the walls of the tube. • The tube is made of a conducting material and generally has an insulating lining to prevent short circuiting of ...
The Problems of Using USMs at Low Reynolds Numbers (High
... • “Reynolds found that the transition occurred between Re = 2000 and 13000, depending on the smoothness of the entry conditions. When extreme care is taken, the transition can even happen with Re as high as 40000. On the other hand, Re = 2000 appears to be about the lowest value obtained at a rough ...
... • “Reynolds found that the transition occurred between Re = 2000 and 13000, depending on the smoothness of the entry conditions. When extreme care is taken, the transition can even happen with Re as high as 40000. On the other hand, Re = 2000 appears to be about the lowest value obtained at a rough ...
P - WordPress.com
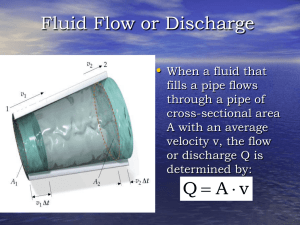
... General Characteristics of Fluid Flow • Fluid flow can be viscous or nonviscous. Viscosity in fluid motion is the analogue of friction in the motion of solids We shall confine our discussion of fluid dynamics to steady, irrotational, incompressible, nonviscous flow. In steady flow, the velocity v a ...
... General Characteristics of Fluid Flow • Fluid flow can be viscous or nonviscous. Viscosity in fluid motion is the analogue of friction in the motion of solids We shall confine our discussion of fluid dynamics to steady, irrotational, incompressible, nonviscous flow. In steady flow, the velocity v a ...
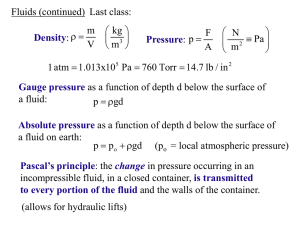
Gauge pressure as a function of depth d below the surface of a fluid
... same over time. For turbulent flow this is not true. For the situation above two photographs taken at different times would show that the streamlines on the left and upper right would be unchanged, while the smoke pattern on the lower right would be quite different. ...
... same over time. For turbulent flow this is not true. For the situation above two photographs taken at different times would show that the streamlines on the left and upper right would be unchanged, while the smoke pattern on the lower right would be quite different. ...
Regular and Singular Points
... Consider the differential equation ẋ = f (x) and its associated dynamical system ϕ(t, x) on a phase space Ω. Definition We say that a point x ∈ Ω is an equilibrium point or a singular point or a critical point if f (x) = 0. For such a point, ϕ(t, x) = x for all t ∈ R. Definition A point x ∈ Ω that ...
... Consider the differential equation ẋ = f (x) and its associated dynamical system ϕ(t, x) on a phase space Ω. Definition We say that a point x ∈ Ω is an equilibrium point or a singular point or a critical point if f (x) = 0. For such a point, ϕ(t, x) = x for all t ∈ R. Definition A point x ∈ Ω that ...
Surficial Processes Take Home Problems
... foothills. Summarize 4 different processes by which that particle can move downslope. Include qualitative descriptions of the driving forces and resisting forces for each process. Problem 4. List 4 physical variables (landscape properties or forces) that promote or inhibit slope failure and explain ...
... foothills. Summarize 4 different processes by which that particle can move downslope. Include qualitative descriptions of the driving forces and resisting forces for each process. Problem 4. List 4 physical variables (landscape properties or forces) that promote or inhibit slope failure and explain ...
On fluid flow induced by a rotating magnetic field
... particular case of a circular cylindrical container in a transverse magnetic field is studied in detail. Under certain reasonable assumptions, the resulting flow is shown to have only the steady component, and the distribution of this component is determined. Some conjectures are offered about the s ...
... particular case of a circular cylindrical container in a transverse magnetic field is studied in detail. Under certain reasonable assumptions, the resulting flow is shown to have only the steady component, and the distribution of this component is determined. Some conjectures are offered about the s ...
Technical Article Using fans in series and parallel - ebm
... Fans operating in free air generate the maximum possible flow rates, but when fitted within an enclosure the fan is required to overcome the inherent airflow resistance. In order to achieve this the fan needs to produce a pressure increase which will in turn decrease the flow rate. A characteristic ...
... Fans operating in free air generate the maximum possible flow rates, but when fitted within an enclosure the fan is required to overcome the inherent airflow resistance. In order to achieve this the fan needs to produce a pressure increase which will in turn decrease the flow rate. A characteristic ...
Blood flow modeling in a synthetic cylindrical vessel for validating
... Image segmentation techniques are used to divide data into regions with common characteristics. In case of MRA images the purpose is to separate blood vessels from other tissues. As mentioned earlier, it allows to portray arteries and veins as a 3D model. Data in that form is much easier to be analy ...
... Image segmentation techniques are used to divide data into regions with common characteristics. In case of MRA images the purpose is to separate blood vessels from other tissues. As mentioned earlier, it allows to portray arteries and veins as a 3D model. Data in that form is much easier to be analy ...
umax
... The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and 24 psia, respectively. Calculate the horizontal (x and y) components of the anc ...
... The flow cross-sectional area is constant at a value of 0.1 ft2 through the bend. The flow velocity everywhere in the bend is axial and 50 ft/s. The absolute pressures at the entrance and exit of the bend are 30 psia and 24 psia, respectively. Calculate the horizontal (x and y) components of the anc ...
MOVING BUBBLES, DROPS, AND OTHER FLUID BLOBS
... might expect that such fluid fields could be explained quantitatively with a very few characteristic non-dimensional numbers; attempts to do this, however, have only provided qualitative information. It appears that not only the usual bulk fluid properties of viscosity and density, but the detailed ...
... might expect that such fluid fields could be explained quantitatively with a very few characteristic non-dimensional numbers; attempts to do this, however, have only provided qualitative information. It appears that not only the usual bulk fluid properties of viscosity and density, but the detailed ...
Compression The mechanical properties of a ductile metal are
... methods have been attempted to overcome the effects of barreling, none of which is completely successful. The most satisfactory appears to be the technique of using several cylinders of the same metal having different diameter – to – length ratios. Incremental compression tests are conducted on the ...
... methods have been attempted to overcome the effects of barreling, none of which is completely successful. The most satisfactory appears to be the technique of using several cylinders of the same metal having different diameter – to – length ratios. Incremental compression tests are conducted on the ...
Fluid Dynamics
... How does it work? Think of the water in terms of distinct “packets". Since the dry end of the hose is lower than the wet end, there are more water "packets" towards the dry end. As such, the column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the t ...
... How does it work? Think of the water in terms of distinct “packets". Since the dry end of the hose is lower than the wet end, there are more water "packets" towards the dry end. As such, the column of water being pulled downward by gravity is heavier than the column of water at the wet end of the t ...
Materials Science & Engineering “Because without materials, there
... • It can also be a problem, e.g. Ga is a fast diffuser at Al grain boundaries and make Al catastrophically brittle (no plastic behavior vs. strain). • Need to know T vs. c phase diagrams for what alloying does. • Need to know T-T-T (temp - time - transition) diagrams to know treatment. ...
... • It can also be a problem, e.g. Ga is a fast diffuser at Al grain boundaries and make Al catastrophically brittle (no plastic behavior vs. strain). • Need to know T vs. c phase diagrams for what alloying does. • Need to know T-T-T (temp - time - transition) diagrams to know treatment. ...