Project_FEA.doc
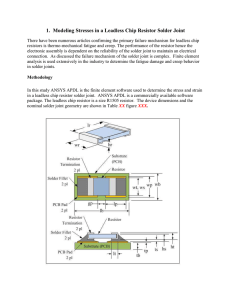
... -40OC to 125OC (-40OF to 257OF). The transition rate from the minimum to maximum temperature is 10OC per minute and a 20 minute dwell at the temperature extremes. The thermal cycle profile is shown in Figure XXX. The purpose of thermal cycle load is to induce plastic work due to the mismatch in the ...
... -40OC to 125OC (-40OF to 257OF). The transition rate from the minimum to maximum temperature is 10OC per minute and a 20 minute dwell at the temperature extremes. The thermal cycle profile is shown in Figure XXX. The purpose of thermal cycle load is to induce plastic work due to the mismatch in the ...
article: force feedback-based microinstrument for measuring tissue
... Another is that, since the time the article was written, further developments in the haptic feedback system has been made. Though the paper focuses on the importance of differentiating between skin tissues, I believe more research should be done in fine-tuning it to obtain quantitative numbers. Thou ...
... Another is that, since the time the article was written, further developments in the haptic feedback system has been made. Though the paper focuses on the importance of differentiating between skin tissues, I believe more research should be done in fine-tuning it to obtain quantitative numbers. Thou ...
Provedení, principy činnosti a základy výpočtu pro výměníky tepla
... applied to the tube causing it to vibrate, the fluid flowing through the tube will induce a rotation or twist to the tube because of the Coriolis acceleration acting in opposite directions on either side of the applied force. This twist results in a phase difference (time lag) between the inlet side ...
... applied to the tube causing it to vibrate, the fluid flowing through the tube will induce a rotation or twist to the tube because of the Coriolis acceleration acting in opposite directions on either side of the applied force. This twist results in a phase difference (time lag) between the inlet side ...
Preparation of Papers in Two-Column Format
... considering the complete boundary condition of no tangential velocity of the fluid along the sphere surface. For 5 < Re < 130, the wake forms a steady recirculating eddy of axisymmetric ring shape. In this flow regime occurs a flow detachment and the detachment angle (θ) can be accuracy measured in ...
... considering the complete boundary condition of no tangential velocity of the fluid along the sphere surface. For 5 < Re < 130, the wake forms a steady recirculating eddy of axisymmetric ring shape. In this flow regime occurs a flow detachment and the detachment angle (θ) can be accuracy measured in ...
Ore-forming magmatic-hydrothermal systems
... processes underlying hydrothermal heat and mass transfer in the Earth’s crust, including the formation of economic mineral deposits. The practical aim is to advance our ability of predicting the location and composition of still undiscovered resources, with an emphasis on the long-term development o ...
... processes underlying hydrothermal heat and mass transfer in the Earth’s crust, including the formation of economic mineral deposits. The practical aim is to advance our ability of predicting the location and composition of still undiscovered resources, with an emphasis on the long-term development o ...
Current Electricity
... What is the difference between static electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or vol ...
... What is the difference between static electricity and current electricity? Static electricity is stationary or collects on the surface of an object, whereas current electricity is flowing very rapidly through a conductor. The flow of electricity in current electricity has electrical pressure or vol ...
Chapter 6 Scaling Laws in Miniaturization
... - Examples: Gravitational forces dominate on an astronomical scale (e.g., the earth ...
... - Examples: Gravitational forces dominate on an astronomical scale (e.g., the earth ...
Fluid Flow Concepts and Basic Control Volume Equations
... pressure drag. The only practical way of reducing pressure drag is to design the ball so that the point of separation moves back further on the ball. The golf ball's dimples increase the turbulence in the inertia of the boundary layer, increase the _______ boundary layer, and delay the onset of sepa ...
... pressure drag. The only practical way of reducing pressure drag is to design the ball so that the point of separation moves back further on the ball. The golf ball's dimples increase the turbulence in the inertia of the boundary layer, increase the _______ boundary layer, and delay the onset of sepa ...
Final Exam - iMechanica
... 5 problems, 5 points each. 3 hours. No books or notes. Calculator is allowed. 1. Residual stress around an inclusion Consider a composite consisting of a small spherical particle of one material embedded in a large matrix of another material. The radius of the particle is a. The composite is solidif ...
... 5 problems, 5 points each. 3 hours. No books or notes. Calculator is allowed. 1. Residual stress around an inclusion Consider a composite consisting of a small spherical particle of one material embedded in a large matrix of another material. The radius of the particle is a. The composite is solidif ...
Mass Flow Theory
... Difference in air density is the primary reason user’s can observe slightly different results when temperature and gauge pressures are identical. For this reason, it is important to establish all test parameters at the same altitude and under the same conditions at which the tester will be used. Com ...
... Difference in air density is the primary reason user’s can observe slightly different results when temperature and gauge pressures are identical. For this reason, it is important to establish all test parameters at the same altitude and under the same conditions at which the tester will be used. Com ...
Chapter 9
... Indeterminate structures • Indeterminate systems cannot be solved by a simple application of the equilibrium conditions • In reality, physical objects are not absolutely rigid bodies ...
... Indeterminate structures • Indeterminate systems cannot be solved by a simple application of the equilibrium conditions • In reality, physical objects are not absolutely rigid bodies ...
Current Electricity - Super Teacher Worksheets
... A ____________________________ circuit is a circuit in which electrical current has more than one path to follow. ...
... A ____________________________ circuit is a circuit in which electrical current has more than one path to follow. ...
Macro Traffic Flow Model Based on the Hydromechanics Theory WANG Fu
... hydromechanics, are not closely ranged one by one, but hold interspaces between each other. From the view of microcosmic, liquid is not a matter of consistency distribution. However, on engineering application, hydromechanics merely discusses the law of motion, dynamic property of liquid and the int ...
... hydromechanics, are not closely ranged one by one, but hold interspaces between each other. From the view of microcosmic, liquid is not a matter of consistency distribution. However, on engineering application, hydromechanics merely discusses the law of motion, dynamic property of liquid and the int ...
Section_1_Intro_01
... Short reviews of some of these topics will be provided at the appropriate times during the presentation. The validity of MHD as a mathematical model for magnetized plasmas has been discussed in great detail elsewhere, particularly in the book by Freidberg. It cannot be said better, so it will not be ...
... Short reviews of some of these topics will be provided at the appropriate times during the presentation. The validity of MHD as a mathematical model for magnetized plasmas has been discussed in great detail elsewhere, particularly in the book by Freidberg. It cannot be said better, so it will not be ...
Zahn, M., Ferrohydrodynamic Torque-Driven Flows, Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, U85U, 181-186, 1990
... exerted on each magnetic domain which is balanced by the fluid viscous drag. Conservation of linear and angular momentum equations are solved in the steady state for a ferrofluid layer stressed by a traveling wave magnetic field. This configuration can be easily set up as an experiment, allows close ...
... exerted on each magnetic domain which is balanced by the fluid viscous drag. Conservation of linear and angular momentum equations are solved in the steady state for a ferrofluid layer stressed by a traveling wave magnetic field. This configuration can be easily set up as an experiment, allows close ...
Stress and Deformation, Part 1
... What is it? Tensile fracture filled with vein during dilation s1 is parallel to the structure. What does this suggest about very low the magnitude of effective stress? What mechanism may help produce this structure within the deeper crust? high fluid pressure to counteract lithostatic stress ...
... What is it? Tensile fracture filled with vein during dilation s1 is parallel to the structure. What does this suggest about very low the magnitude of effective stress? What mechanism may help produce this structure within the deeper crust? high fluid pressure to counteract lithostatic stress ...
Chapter 11 – Potential Vorticity – Lee and Rossby Waves
... changes sign somewhere within the fluid column. This result is called the Rayleigh’s inflection point criterion for instability. Recall that one major assumption for the above analysis is that the flow is barotropic. For atmospheric flows, this result is applicable for the tropic regions as well as ...
... changes sign somewhere within the fluid column. This result is called the Rayleigh’s inflection point criterion for instability. Recall that one major assumption for the above analysis is that the flow is barotropic. For atmospheric flows, this result is applicable for the tropic regions as well as ...
ULTRAmass Datasheet - CN100
... 1) Avoid pipeline stresses on the ULTRAmass MKII. 2) The ULTRAmass MKII should be supported at the process pipelines near to the connections with the meter. 3) Avoid supporting the ULTRAmass MKII body directly. 4) Pipeline should be arranged such that the ULTRA mass MKII is constantly filled ...
... 1) Avoid pipeline stresses on the ULTRAmass MKII. 2) The ULTRAmass MKII should be supported at the process pipelines near to the connections with the meter. 3) Avoid supporting the ULTRAmass MKII body directly. 4) Pipeline should be arranged such that the ULTRA mass MKII is constantly filled ...