Design specifications
... A key feature of the device is that it can work with a wide range of engines. It is expected that the device should be able to handle the mass flow rates of not only small displacement engines, but engines with displacements of up to 5.7L. This brings in two aspects: the Maximum Output flow rate and ...
... A key feature of the device is that it can work with a wide range of engines. It is expected that the device should be able to handle the mass flow rates of not only small displacement engines, but engines with displacements of up to 5.7L. This brings in two aspects: the Maximum Output flow rate and ...
Diapositive 1 - Aptar
... A systematic control of extractables should be performed for the critical components (or the raw material provided that a correlation can be established between the two). The extraction and analytical methods should be based on the controlled extraction studies: •The extraction should be done using ...
... A systematic control of extractables should be performed for the critical components (or the raw material provided that a correlation can be established between the two). The extraction and analytical methods should be based on the controlled extraction studies: •The extraction should be done using ...
The Terra Nova Intrusive Complex (Victoria Land, Antarctica)
... processes induced by the displacement of a more viscous fluid by a less viscous fluid. In the viscous fingering phenomenon, the viscosity ratio VR=1/2, defined as the ratio of the viscosity of displaced fluid ( 1) to that of driving fluid (2), influences the overall shape of fluid interfaces tha ...
... processes induced by the displacement of a more viscous fluid by a less viscous fluid. In the viscous fingering phenomenon, the viscosity ratio VR=1/2, defined as the ratio of the viscosity of displaced fluid ( 1) to that of driving fluid (2), influences the overall shape of fluid interfaces tha ...
DILV - Children`s Heart Clinic
... Chest X-ray: Normal heart size and pulmonary vascularity when pulmonary blood flow is normal or decreased. The heart size is large and pulmonary vascularity is increased when pulmonary blood flow is increased. EKG: Abnormal Q waves are present in either the right precordial leads, both the right ...
... Chest X-ray: Normal heart size and pulmonary vascularity when pulmonary blood flow is normal or decreased. The heart size is large and pulmonary vascularity is increased when pulmonary blood flow is increased. EKG: Abnormal Q waves are present in either the right precordial leads, both the right ...
Double Inlet Left Ventricle (DILV)
... Chest X-ray: Normal heart size and pulmonary vascularity when pulmonary blood flow is normal or decreased. The heart size is large and pulmonary vascularity is increased when pulmonary blood flow is increased. EKG: Abnormal Q waves are present in either the right precordial leads, both the right ...
... Chest X-ray: Normal heart size and pulmonary vascularity when pulmonary blood flow is normal or decreased. The heart size is large and pulmonary vascularity is increased when pulmonary blood flow is increased. EKG: Abnormal Q waves are present in either the right precordial leads, both the right ...
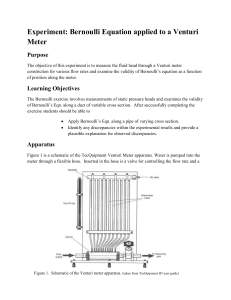
FLUID FLOW IDEAL FLUID BERNOULLI`S PRINCIPLE
... A pitot tube can be used to determine the speed of an aeroplane relative to the surrounding air. The device consists of a U shaped tube containing a fluid with a density ρ. One end of the tube A opens to the air at the side of the plane, the other end B is open to the air in the direction the plane ...
... A pitot tube can be used to determine the speed of an aeroplane relative to the surrounding air. The device consists of a U shaped tube containing a fluid with a density ρ. One end of the tube A opens to the air at the side of the plane, the other end B is open to the air in the direction the plane ...
956 aperture 5
... The numerical solution of the incompressible unsteady Navier-Stokes equations is performed using the finite-volume method on a staggered grid. The convective term is discretized using the Quadratic Upwind Interpolation for Convective Kinematics (QUICK) (Hayase et al. (1992)). The Semi-Implicit Metho ...
... The numerical solution of the incompressible unsteady Navier-Stokes equations is performed using the finite-volume method on a staggered grid. The convective term is discretized using the Quadratic Upwind Interpolation for Convective Kinematics (QUICK) (Hayase et al. (1992)). The Semi-Implicit Metho ...
Basic Biomechanics, (5th edition) by Susan J. Hall, Ph.D.
... Chapter 15 Human Movement in a Fluid Medium Basic Biomechanics, 6th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D. ...
... Chapter 15 Human Movement in a Fluid Medium Basic Biomechanics, 6th edition By Susan J. Hall, Ph.D. ...
Module 1
... 2 or more materials with different physical & chemical properties combined to produce a material with characteristics different from individual components Eg: fiber glass, concrete ...
... 2 or more materials with different physical & chemical properties combined to produce a material with characteristics different from individual components Eg: fiber glass, concrete ...
Current Electricity Homework (NAT5)
... minutes. What is the size of the electric current in amps? (2) 2. The following passage is taken from NASA research into lightning: “Lightning is the effect of static electricity build-up within a thunderstorm cloud system. It is a giant electrical spark that can have a peak current flow greater tha ...
... minutes. What is the size of the electric current in amps? (2) 2. The following passage is taken from NASA research into lightning: “Lightning is the effect of static electricity build-up within a thunderstorm cloud system. It is a giant electrical spark that can have a peak current flow greater tha ...
How we arrive at a steady state/linear velocity profile, i.e., = constant
... opposite direction (i.e., -x direction) of that exerted at the top of the fluid parcel. The problem is, initially the fluid is not in steady state! However, when the two are equal and opposite throughout the entire fluid, we have reached an equilibrium state whereby there is a force acting (upper pl ...
... opposite direction (i.e., -x direction) of that exerted at the top of the fluid parcel. The problem is, initially the fluid is not in steady state! However, when the two are equal and opposite throughout the entire fluid, we have reached an equilibrium state whereby there is a force acting (upper pl ...
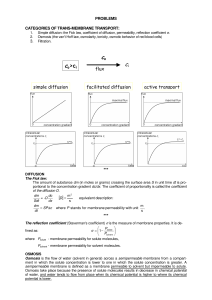
Basics of transmembrane transport of solutes
... Osmosis is the flow of water (solvent in general) across a semipermeable membrane from a compartment in which the solute concentration is lower to one in which the solute concentration is greater. A semipermeable membrane is defined as a membrane permeable to solvent but impermeable to solute. Osmos ...
... Osmosis is the flow of water (solvent in general) across a semipermeable membrane from a compartment in which the solute concentration is lower to one in which the solute concentration is greater. A semipermeable membrane is defined as a membrane permeable to solvent but impermeable to solute. Osmos ...
Physiological bases of hemodymanic
... In capillaries blood flow resistance is lower because of such mechanism. In capillaries blood cells move one after another, dividing only by plasma, which decreases friction between blood cells and capillary wall. On other side, capillaries are shorter, than arterioles, which caused lower blood flow ...
... In capillaries blood flow resistance is lower because of such mechanism. In capillaries blood cells move one after another, dividing only by plasma, which decreases friction between blood cells and capillary wall. On other side, capillaries are shorter, than arterioles, which caused lower blood flow ...
Slide 1
... Archimedes’ principle: Any object completely or partially submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. FB = Fg (displaced fluid) = mfg magnitude of buoyant force = weight of fluid displaced ...
... Archimedes’ principle: Any object completely or partially submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. FB = Fg (displaced fluid) = mfg magnitude of buoyant force = weight of fluid displaced ...
Hopkins Imaging Conference Poster Contest
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
Stresses due to Axial Force - Aerospace Engineering
... The action P acting on the cross-sectional area needs to be characterized. The following observations are important. ● The material is not “stressed” as much at locations where the cross-sectional area is large. ● Small cross-sections are more likely to fail than larger sections. ● It is assumed tha ...
... The action P acting on the cross-sectional area needs to be characterized. The following observations are important. ● The material is not “stressed” as much at locations where the cross-sectional area is large. ● Small cross-sections are more likely to fail than larger sections. ● It is assumed tha ...
Simulations of dynamic crack propagation using the material point method
... generalized interpolation material point (GIMP) method. Multiple velocity fields are used in GIMP to enable handling of discrete discontinuity on either side of the interface. Multilevel refinement is adopted in the region around the crack-tip to resolve higher strain gradients. Numerical simulation ...
... generalized interpolation material point (GIMP) method. Multiple velocity fields are used in GIMP to enable handling of discrete discontinuity on either side of the interface. Multilevel refinement is adopted in the region around the crack-tip to resolve higher strain gradients. Numerical simulation ...
chapter 2 properties of fluids
... separation between them is normally negligible by comparison with the distances involved in the practical situation being studied Although the properties of a fluid arise from its molecular structure,engineering problem are usually concerned with the bulk behavior of fluids Under these conditions, i ...
... separation between them is normally negligible by comparison with the distances involved in the practical situation being studied Although the properties of a fluid arise from its molecular structure,engineering problem are usually concerned with the bulk behavior of fluids Under these conditions, i ...